
Table of Contents
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different 10 types of electrical conduit, the pros and cons, and top 10 tips of electrical PVC conduit before you buying. Let’s get start.
Electrical conduit is a system of pipes, tubes, or channels used to protect and route electrical wires in buildings, homes, and industrial settings. It serves several critical purposes:
- Protection: Conduit provides physical protection for electrical wiring, cables, and conductors, shielding them from damage due to impact, moisture, chemicals, and other environmental factors. It helps prevent accidental contact with live wires, reducing the risk of electrical shocks and fire hazards.
- Routing and Organization: Conduit helps in organizing and routing electrical wires and cables in a structured manner. It allows for neat and orderly installation, making it easier to identify and trace specific circuits or cables when troubleshooting or making changes.
- Grounding: Conduit systems can serve as an effective grounding path for electrical equipment and circuits. By connecting metallic conduit to grounding systems, it helps to dissipate electrical faults and provides an additional safety measure against electrical faults and surges.
- Future Flexibility: Conduit installations offer future flexibility by allowing for easy modification, expansion, or replacement of electrical wiring and cables. It simplifies the process of adding or upgrading electrical systems, reducing the need for extensive rework and minimizing disruptions to the existing infrastructure.
There are many types of electrical conduits available, each with its own characteristics and applications. Here are 10 common types of electrical conduits:
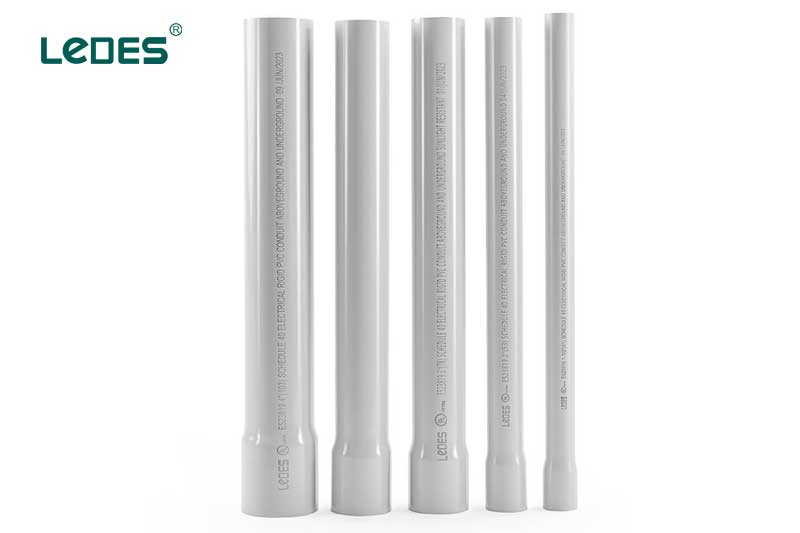

Rigid PVC conduit, also known as PVC pipe, is a popular choice for electrical wiring installations. It is made from a durable thermoplastic material, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which offers excellent resistance to moisture, chemicals, and corrosion. Rigid PVC conduit is available in various sizes and is known for its rigid structure, providing robust protection for electrical wires.
Rigid structure for enhanced protection.
Excellent resistance to moisture, chemicals, and corrosion.
Lightweight and easy to handle.
Non-conductive, making it safe for electrical applications.
Smooth interior for easy wire pulling.
Cost-effective compared to metal conduit options.
Suitable for both aboveground and underground installations.
Resistant to sunlight and UV rays.
Can withstand a wide range of temperatures.
Ideal for residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
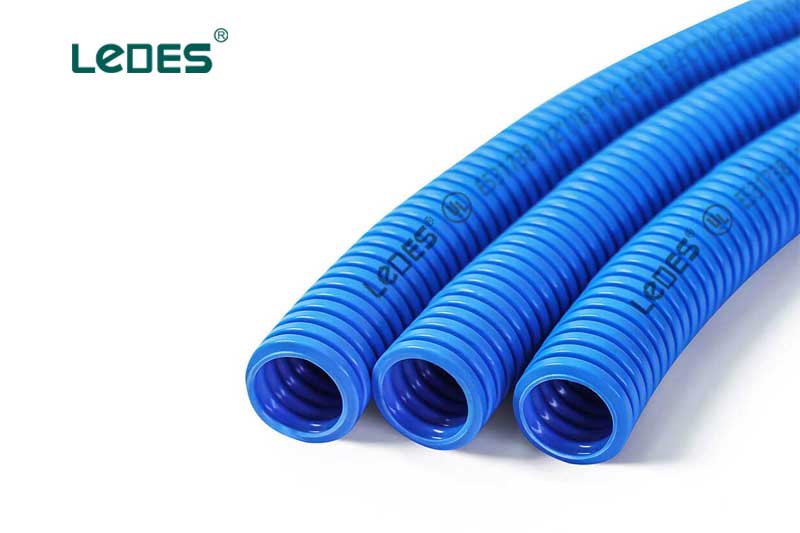

ENT conduit is a flexible, corrugated plastic conduit that is easy to handle and install. It is commonly used in both indoor and outdoor applications where flexibility is required as it can bend by hand on field without requiring any special tools, and provides good protection against moisture. ENT conduit is often utilized in residential wiring, including installations behind walls and in concrete slabs.
Flexible and easy to bend.
Corrugated exterior for added strength.
Smooth interior for effortless wire pulling.
Flame-retardant properties for enhanced safety.
Lightweight and easy to handle.
Resistant to moisture and corrosion.
Suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Ideal for concealed and exposed installations.
Compatible with a wide range of electrical boxes and fittings.
Lower impact resistance compared to rigid conduits.
May require additional support in horizontal installations.
Limited temperature range compared to some other conduit types.
LFNC is a type of conduit that is designed to be waterproof and dustproof. It features a liquidtight outer jacket that provides resistance to moisture, oils, and other non-hazardous liquids. LFNC is frequently employed in outdoor and wet locations where protection against moisture exposure or liquid ingress is necessary.
Flexible and easy to bend.
Resistant to moisture, oil, and chemicals.
Suitable for wet locations.
Provides strain relief for wires.
Ideal for outdoor and underground applications.
Resistant to corrosion and rust.
Easy to install and modify.
Can be used in areas with exposure to chemicals.
Suitable for use with liquid-tight fittings.
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) conduit is a durable and versatile option for electrical wiring installations. HDPE conduit is made from high-density polyethylene, a thermoplastic known for its excellent strength, impact resistance, and chemical resistance.
High strength and impact resistance.
Lightweight and flexible.
Resistant to chemicals, moisture, and UV radiation.
Excellent long-term performance.
Suitable for both aboveground and underground installations.
Can be used in various environmental conditions.
Resistant to corrosion and abrasion.
Can withstand a wide range of temperatures.
Ideal for outdoor and industrial applications.
Requires specialized tools for cutting and joining.
Higher cost compared to some other conduit types.
Less rigid than PVC or metal conduits.
Metallic conduit is stronger, more durable, and more fire-resistant than non-metallic conduit. It is often used in industrial, commercial, and hazardous environments.
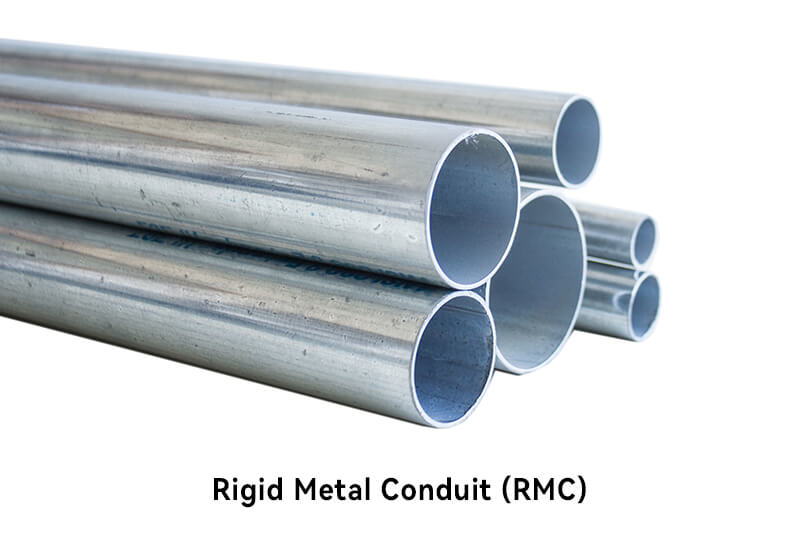

RMC is a heavy-duty conduit made of galvanized steel or stainless steel and is threaded for assembly. It provides excellent mechanical protection and is suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications. RMC is commonly used in industrial and commercial settings where there is a risk of physical damage and high levels of protection are required.
Sturdy and rigid construction.
Excellent mechanical protection for wires.
High resistance to impact and physical damage.
Provides grounding path for electrical systems.
Suitable for hazardous locations.
Offers maximum protection against mechanical stress.
Resistant to fire, heat, and corrosion.
Ideal for industrial and commercial installations.
Provides electromagnetic shielding.
Can be used in exposed or concealed applications.
Heavier and more challenging to handle compared to other conduit types.
Requires specialized tools for cutting and bending.
Higher cost compared to non-metallic conduits.
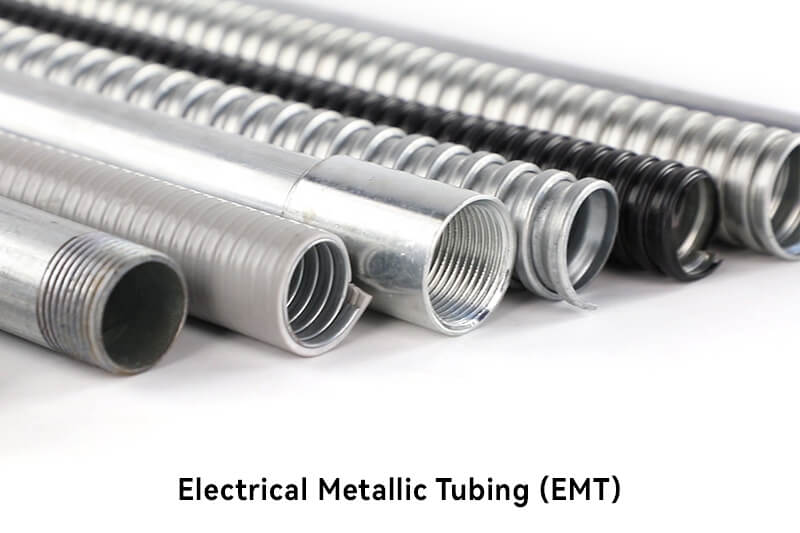

EMT is a lightweight, thin-walled conduit made of galvanized steel or aluminum. It is easier to bend and install than RMC and is often used in residential and light commercial applications. It is commonly used for exposed indoor wiring in dry and damp locations.
Lightweight and easy to handle.
Thin walls for efficient use of space.
Smooth interior for easy wire pulling.
Provides a grounding path for electrical systems.
Easy to cut, bend, and install.
Cost-effective compared to other metallic conduits.
Suitable for exposed and concealed applications.
Ideal for residential and light commercial installations.
Compatible with a wide range of fittings and accessories.
Offers good protection against physical damage.
Less impact-resistant compared to rigid metal conduit.
Limited suitability for environments with high humidity or corrosion.
Not recommended for hazardous locations.
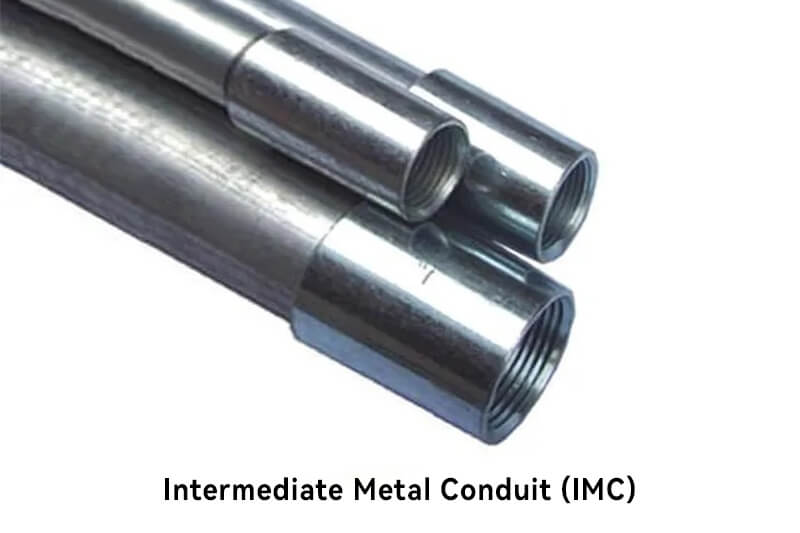

Intermediate Metal Conduit, known as IMC, is a versatile metallic conduit option that offers a balance between the strength of rigid metal conduit and the flexibility of electrical metallic tubing. It is made from galvanized steel and is suitable for various electrical wiring applications.
Strong and rigid construction.
Thicker walls compared to EMT for increased protection.
Corrosion-resistant due to galvanized coating.
Easy to cut, thread, and bend.
Provides grounding path for electrical systems.
Offers enhanced mechanical protection for electrical wires.
Resistant to fire, heat, and corrosion.
Suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Compatible with standard fittings and connectors.
Provides electromagnetic shielding.
Heavier and more challenging to handle compared to EMT.
Requires specialized tools for cutting and bending.
Higher cost compared to EMT.
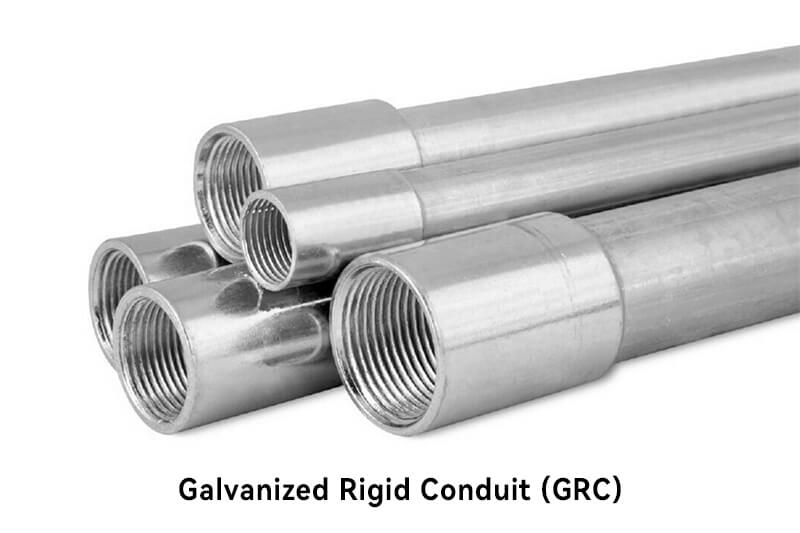

GRC is the heaviest and most durable type of metallic conduit that made of galvanized steel. It offers superior mechanical protection, making it ideal for harsh environments. GRC is commonly used in industrial applications, outdoor installations, and in hazardous environments where there is a risk of fire or explosion.
Sturdy and rigid construction.
Zinc-coated for corrosion resistance.
Excellent mechanical protection for wires and cables.
Provides grounding path for electrical systems.
Suitable for hazardous locations.
Offers maximum protection against mechanical stress and corrosion.
Resistant to fire, heat, and moisture.
Ideal for outdoor and underground applications.
Provides electromagnetic shielding.
Compatible with standard fittings and connectors.
Heavier and more challenging to handle compared to other conduit types.
Requires specialized tools for cutting and bending.
Higher cost compared to non-metallic conduits.
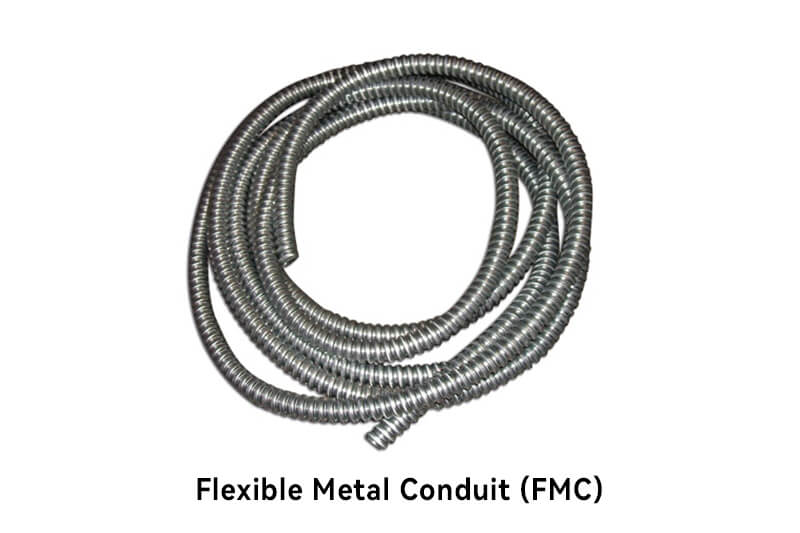

FMC, also known as “Greenfield,” is a flexible conduit made of spiral-wound metal strips, usually galvanized steel or aluminum. It provides good flexibility for routing wires in tight or curved spaces. FMC is commonly used in exposed indoor applications where flexibility is required.
Flexible and easy to bend.
Corrugated exterior for added strength.
Smooth interior for easy wire pulling.
Provides grounding path for electrical systems.
Resistant to impact and physical damage.
Offers flexibility in routing wires through complex spaces.
Suitable for both exposed and concealed installations.
Compatible with standard fittings and connectors.
Easy to cut, bend, and install.
Provides good protection against mechanical stress.
Less rigid compared to rigid metal conduit.
Limited suitability for areas with high humidity or corrosive environments.
Not recommended for hazardous locations.
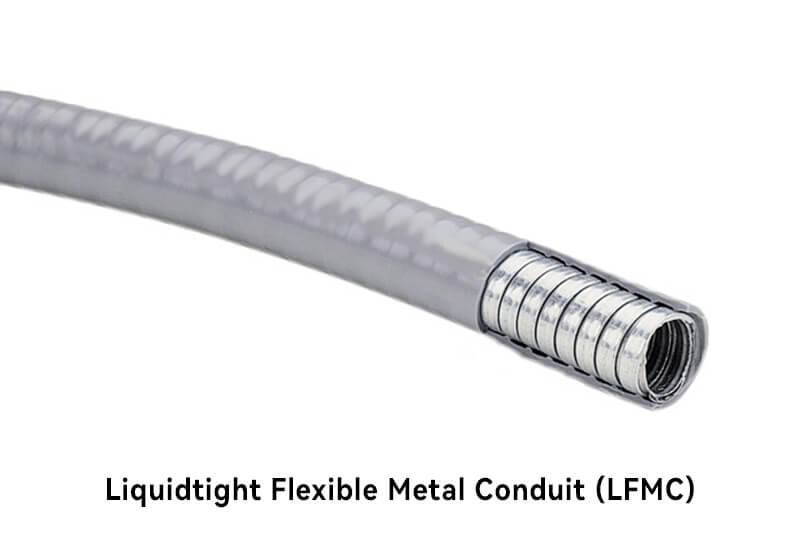
LFMC features a liquidtight outer jacket, providing protection against water, oils, and other liquids, is a type of FMC that is designed to be waterproof and dustproof. It is commonly used in outdoor and wet locations, such as outdoor lighting or areas with exposure to moisture.
Flexible and easy to bend.
Corrugated exterior for added strength.
Liquid-tight jacket for protection against liquids.
Provides grounding path for electrical systems.
Resistant to impact and physical damage.
Ideal for outdoor and wet locations.
Resistant to moisture, oils, and chemicals.
Provides strain relief for wires.
Suitable for use with liquid-tight fittings.
Compatible with standard fittings and connectors.
Limited temperature range compared to some other conduit types.
May require additional support in horizontal installations.
Not suitable for high-impact or heavy-duty applications.

- Cost: Plastic conduit, such as PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) or HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene), is generally more cost-effective than metal conduit options.
- Lightweight: Plastic conduits are lightweight, making them easier to handle and install, especially in overhead or complex routing situations.
- Corrosion Resistance: Unlike metal conduits, plastic conduits are not susceptible to corrosion, making them suitable for areas with high humidity, chemicals, or corrosive substances.
- Non-Conductive: Plastic conduits are non-conductive, eliminating the need for grounding in most applications.
- Wide Range of Sizes: Plastic conduits are available in various sizes, allowing for flexibility in accommodating different wire or cable diameters.
Mechanical Strength: Plastic conduits have lower mechanical strength compared to their metal counterparts. They may not provide as much physical protection to wiring, especially in areas prone to impact or mechanical stress.
Temperature Limitations: Plastic conduits have temperature limitations and may not be suitable for high-temperature environments or applications where fire-resistance is required.
UV Resistance: Some types of plastic conduits may degrade over time when exposed to UV radiation, so they may require additional UV protection if used outdoors.
Expansion and Contraction: Plastic conduits can expand and contract with temperature changes, which may require appropriate allowances during installation.
- Durability and Mechanical Strength: Metal conduits, such as RMC, IMC, or EMT, offer superior mechanical protection and durability, making them ideal for applications that require robust physical shielding for wiring.
- Fire Resistance: Metal conduits typically have better fire resistance properties compared to plastic conduits, making them suitable for installations where fire safety is a concern.
- Grounding: Metal conduits provide a grounding path for electrical systems, ensuring proper electrical safety and compliance with grounding requirements.
- EMI/RFI Shielding: Metal conduits provide electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) shielding, which is beneficial in environments with sensitive electronic equipment and for reducing electrical noise.
- Compliance with Codes: In some areas, local electrical codes may require the use of specific types of metal conduits for certain applications.
Cost: Metal conduits, especially rigid options, tend to be more expensive than plastic conduits.
Installation Complexity: Metal conduits may require specialized tools, such as conduit benders and threaders, for cutting, bending, and installation. They may also require more labor-intensive installation compared to plastic conduits.
Corrosion: While metal conduits are generally coated or galvanized to resist corrosion, they can still be susceptible to rust and degradation over time, especially in corrosive environments. Proper corrosion protection measures should be considered.
Weight: Metal conduits are heavier than plastic conduits, which can make handling and installation more challenging, particularly in overhead or long-run applications.
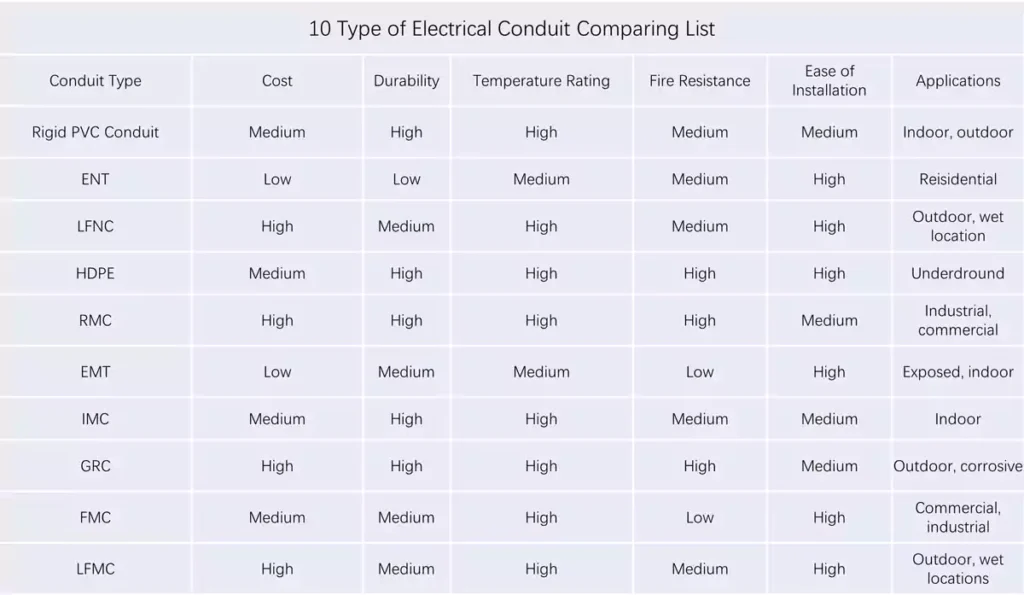
10 Type of Electrical Conduit Comparing List

When it comes to outdoor electrical installations, selecting the right conduit is crucial to ensure the protection and longevity of the wiring system. Outdoor environments pose unique challenges such as exposure to weather elements, UV radiation, temperature variations, and potential mechanical stress. Here are some conduit options suitable for outdoor applications, along with weather-resistant materials and appropriate fittings:
Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC): It provides excellent mechanical protection and durability, making it suitable for outdoor installations.
Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC): IMC is another option for outdoor use, offering a balance between rigidity and flexibility. IMC is suitable for outdoor applications where moderate mechanical protection is required, such as outdoor lighting installations or underground conduit runs.
PVC Conduit: PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) conduit is a common choice for outdoor applications due to its affordability, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation.
PVC conduit is available in different schedules, with Schedule 40 being the most common for outdoor use.
HDPE Conduit: Known for its exceptional durability and resistance to impact, chemicals, and UV radiation. It is commonly used for underground or direct burial installations in outdoor environments.
When installing conduit outdoors, it is crucial to use appropriate weather-resistant fittings and connectors that provide a secure and watertight seal. These fittings may include weatherproof couplings, rain-tight connectors, gaskets, or compression fittings designed for outdoor use. Additionally, proper sealing techniques, such as using suitable sealants or tapes, should be employed to prevent water intrusion.
Conduit is an essential component in electrical installations, providing protection, organization, and safety for electrical wiring. It consists of pipes, tubes, or channels that enclose and shield electrical conductors, ensuring they are safeguarded from physical damage, moisture, chemicals, and other external factors. Here’s why and when conduit is necessary:
Protection: Conduit serves as a protective barrier for electrical wiring, shielding it from accidental damage, impact, and exposure to harsh environments. It helps prevent risks such as short circuits, electrical fires, and electrocution.
Organization: Conduit allows for neat and organized routing of electrical cables, facilitating easier identification, maintenance, and future modifications or upgrades.
Safety: By enclosing electrical conductors, conduit reduces the risk of accidental contact, especially in areas where wiring is exposed or accessible to people or equipment.
Compliance: Conduit installation is often required by local electrical codes and regulations to meet safety standards and ensure proper installation practices.
Flexibility: Conduit provides flexibility in terms of future expansion or changes to the electrical system. It allows for the addition or removal of wires without the need for extensive rework or disruption.
Commercial and Industrial Buildings: Local codes typically mandate conduit usage in commercial and industrial buildings to meet safety requirements and facilitate easy maintenance and modifications.
Outdoor Installations: When electrical wiring is exposed to outdoor elements, conduit is often required to protect it from moisture, UV radiation, temperature variations, and physical damage. This includes applications like outdoor lighting, irrigation systems, or underground conduit runs.
Hazardous Locations: Conduit is necessary in hazardous locations where flammable gases, vapors, or combustible dusts are present. It helps contain any potential sparks or electrical faults, reducing the risk of ignition and explosions.
Areas Prone to Mechanical Stress: Conduit is necessary in areas where there is a high likelihood of mechanical stress, such as construction sites, industrial facilities, or areas with heavy machinery. It provides added protection against accidental impacts, vibrations, or crushing.
Public Spaces: In public spaces like schools, hospitals, or government buildings, conduit is often required to enhance electrical safety, prevent tampering, and facilitate efficient maintenance.

Selecting the appropriate conduit for your electrical installation is essential for ensuring safety, compliance, and functionality. Here’s a guide on how to choose the right conduit, taking into account various factors:
- Material:
Evaluate the material options available for conduits, such as PVC, metal (e.g., steel or aluminum), or flexible conduit (e.g., liquid-tight or corrugated). Consider the specific properties of each material, such as durability, corrosion resistance, and suitability for the intended application.
- Environmental Factors:
Evaluate the environmental conditions where the conduit will be installed, such as exposure to moisture, chemicals, extreme temperatures, or mechanical stress.
Choose a conduit material that can withstand these conditions. For example, PVC conduits are resistant to moisture and corrosion, while metallic conduits offer better protection against mechanical stress.
- Mechanical Strength:
Determine the required mechanical strength based on the application. Consider factors such as impact resistance, load-bearing capacity, resistance to pressure and ability to withstand vibrations or external forces.
- Installation Location:
Consider the specific location of the conduit installation, whether it is indoors, outdoors, underground, or exposed.
Different locations may require different types of conduit. For outdoor or underground installations, you may need conduits with higher durability and weather resistance.
- Resistance to Chemicals:
Assess whether the conduit will be exposed to chemicals or corrosive substances. Choose a conduit material that offers suitable resistance to these substances to ensure long-term performance and safety.
- Certifications:
Look for conduits that meet industry standards and certifications relevant to your application. Examples include UL (Underwriters Laboratories) certifications for electrical safety in the US or CSA certifications for conduits in Canada, and AS/NZS certifications in Australia. Understanding your local codes and regulations for electrical conduit, and choose those suppliers who obtained the product certicates already.
- Flexibility and Future Modifications:
Consider the need for flexibility in your electrical system. Will you need to make future modifications, additions, or upgrades?
Flexible conduit options, such as liquid-tight flexible metal conduits or flexible non-metallic conduits, provide easier access and allow for changes without extensive rework.
- Sizes and Dimensions:
Determine the appropriate size and dimensions of the conduit based on the number and size of cables or wires that will be housed within it. Ensure that the selected conduit can accommodate the required capacity.
- Brands:
Research reputable brands that offer high-quality conduits and have a track record of reliability.
Consider factors such as the brand’s reputation, customer reviews, and the availability of their products in your area.
- Cost and Availability:
Evaluate the cost-effectiveness and availability of conduit options.
Compare the costs of different conduit materials, considering both the upfront cost and long-term maintenance requirements.
Ensure that the chosen conduit is readily available in your area to avoid delays in the installation process.
Remember to consult with electrical professionals, such as electricians or engineers, for specific recommendations based on your project requirements. They can provide valuable insights and ensure compliance with local regulations.
Here are some projects that Ledes has participated in and the conduit types we provided for these projects.
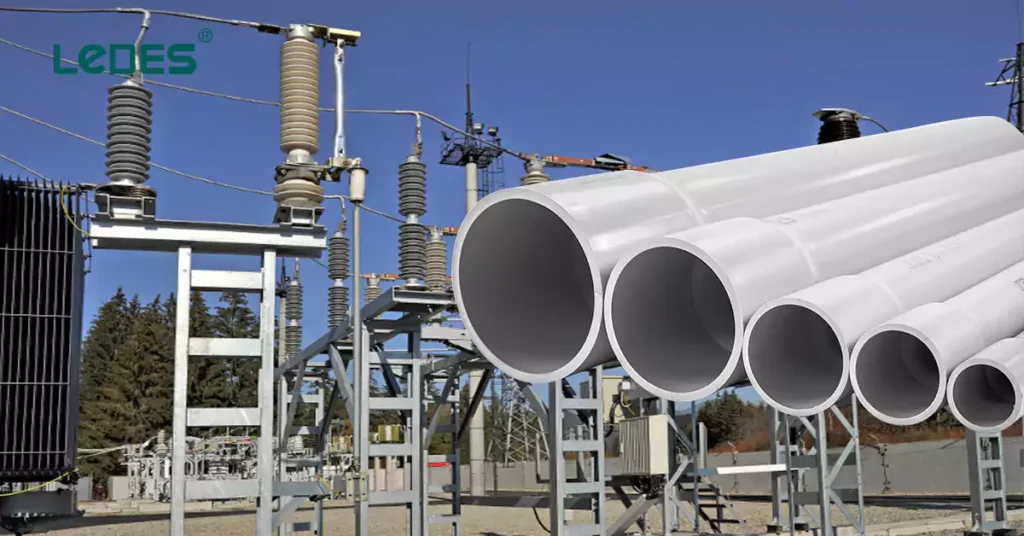

The Champlain Hudson Power Express® (CHPE) is an innovative renewable power transmission project that aims to deliver clean and reliable energy to New York. This high-voltage direct current (HVDC) underwater and underground power cable project will connect the Quebec area to the neighborhood of Astoria in Queens, New York City.
The CHPE project plays a significant role in the state’s energy transformation by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and contributing to a cleaner environment. It is designed to lower reliance on fossil fuels and promote the adoption of renewable energy sources. By delivering low-cost renewable energy to New York, the project not only helps meet the state’s energy demands but also contributes to economic growth and job creation.
The CHPE project has selected Ledes’ UL Listed Schedule 40 PVC conduit as the conduit of choice for its electrical installation. Ledes’ Schedule 40 rigid PVC conduit is a durable and reliable option that provides excellent protection for electrical wiring. PVC conduits are resistant to moisture, corrosion, and various environmental factors, making them suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications. The selection of Ledes’ Schedule 40 rigid PVC conduit ensures the safety and longevity of the electrical infrastructure associated with the CHPE project.
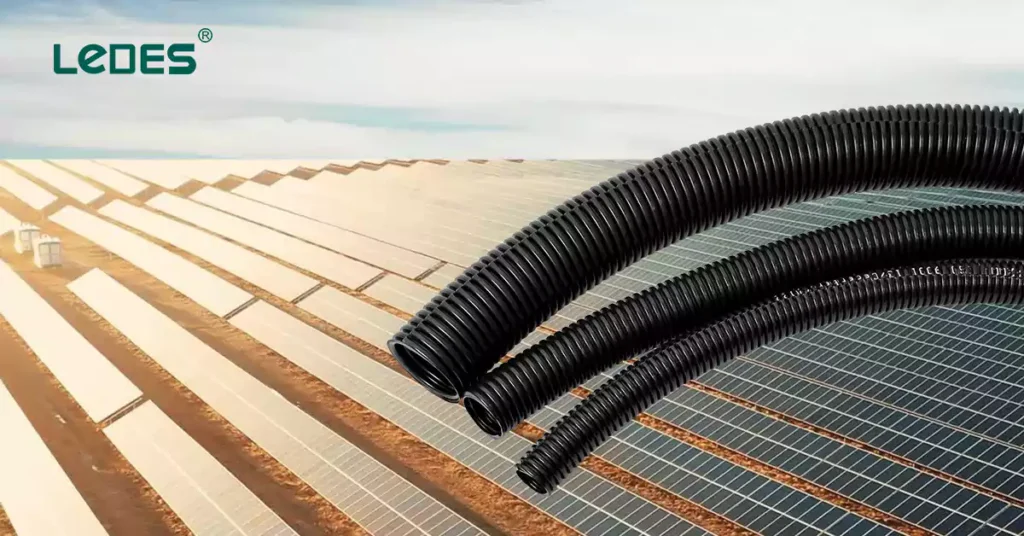

Al Dhafrah PV2 Solar Power Project and 2.6 GW PV project in Saudi Arabia are the two biggest solar projects in the world. They are significant contributor to the country’s renewable energy goals and committed to transitioning towards sustainable energy sources. These two projects involve the development and and implementation of a large-scale power generation capacity of 2GW and 2.6 gigawatts (GW) using renewable energy sources.
In line with the project’s requirements, Ledes’ solar series corrugated conduits have been chosen as the conduit solution. Ledes’ solar series conduits offer reliable protection for the electrical infrastructure associated with solar and wind power projects. They are designed to withstand the demanding environmental conditions found in renewable energy installations, ensuring the safety and longevity of the electrical wiring and cabling.
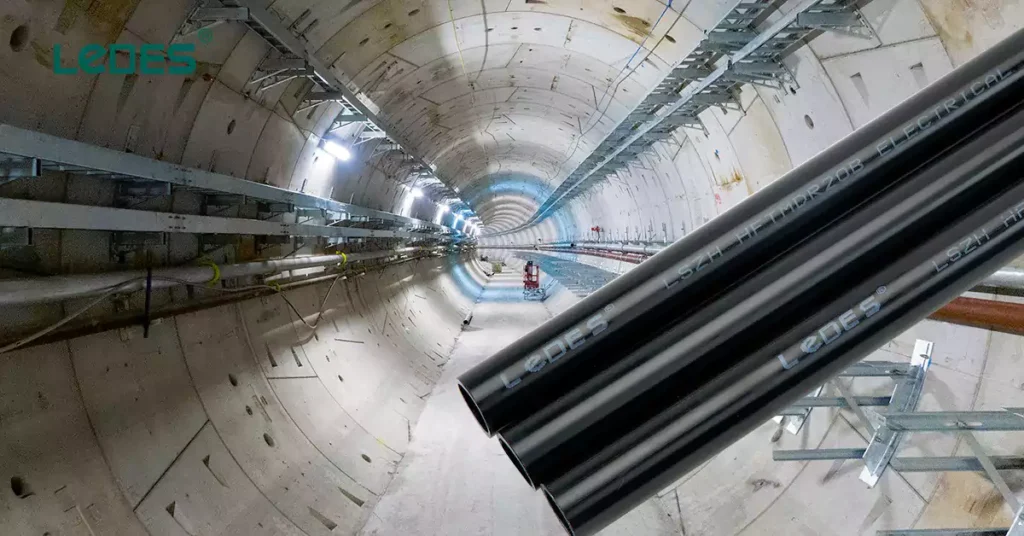

The Melbourne Metro Rail project is one of the largest and most complex infrastructure projects in Australia. The Metro Tunnel includes the construction of twin 9- kilometre rail tunnels with five new underground stations. This underground project includes the installation of high capacity signalling and operation electricity, which has strict requirements for electrical and fire safety.
To meet the electrical safaty requirements, it choosed Ledes’ Low Smoke Halogen Free conduit and fittings for its electrical wiring system. Ledes’ low smoke halogen free conduits are insulated and provide better prevention against electrical shock accidents. They have excellent fire resistant performance, certified with V0 rating fire resistance. And it does not produce dense smoke and toxic fume during the fire event. Provide additional protection for the electrical system and personnel.
In conclusion, selecting the right electrical conduit is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of wiring system. You need to understand the different types of electrical conduit available and specific project requirements. And consider from these factors we’ve talked in the article and together with your own specific needs to decide which conduit type to choose. Remember to prioritize safety, durability, and compliance with local regulations.
If you’re not sure which type of electrical conduit to choose for your application, LEDES’ professional team can help provide the best electrical solution for you.



