
Table of Contents
About NEC

The National Electrical Code (NEC), formally known as NFPA 70, is the benchmark standard for the safe installation of electrical wiring and equipment in the United States. Published by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), the NEC is widely adopted and enforced at the federal, state, and local levels. It serves as a foundational code for electrical design, construction, inspection, and maintenance across residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
Purpose of the NEC
The primary objective of the NEC is to protect people and property from electrical hazards. This is achieved by providing minimum standards for safe electrical installations, including guidance on materials, wiring methods, grounding, overcurrent protection, and more. Although the NEC is not a federal law, it is typically enforced through adoption by state and local jurisdictions and often integrated into building codes.
Notes: Want to learn more about the NEC Code? Here is the Ultimate Guide to the National Electrical Code, which describes the critical parts of the NEC.
Understanding PVC Conduit and Its Benefits
PVC conduit, or Polyvinyl Chloride conduit, is one of the most widely used types of nonmetallic electrical raceways in modern construction. Recognized for its versatility and reliability, PVC conduit is approved by the NEC for various residential, commercial, and light industrial applications. The two most common types governed by the NEC are:
- Rigid PVC Conduit (PVC Schedule 40 and Schedule 80) – Covered under NEC Article 352
- Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing (ENT) – Covered under NEC Article 362
Rigid PVC Conduit (Schedule 40 and 80)

Rigid PVC conduit is a solid-wall pipe that is moisture-resistant, corrosion-resistant, and flame-retardant. It is typically used in underground installations, concealed installations and exposed outdoor environments. Widely used for most residential, commercial and industrial applications. The difference between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 lies in the wall thickness—Schedule 80 has a thicker wall, providing higher mechanical protection in high-traffic or exposed areas.
Key features:
Non-conductive and corrosion-resistant
Suitable for direct burial and concrete encasement
Lightweight and easy to cut and join using solvent cement
Offers high mechanical strength
Available in long lengths with smooth interior walls to simplify wire pulling
Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing (ENT)

ENT is a flexible, corrugated plastic conduit often used for quick installations within walls, floors, or ceilings—especially in residential and light commercial buildings. It is not suitable for high-impact or exposed environments unless encased or otherwise protected.
Key features:
Flexible and bendable without special tools
Lightweight and snap-lock fittings make for faster installations
Non-corrosive and non-metallic, ideal for damp locations when encased in concrete
Commonly used for low-voltage and branch circuit wiring inside walls
Benefits of Using PVC Conduit
PVC conduit offers several advantages that make it a preferred wiring method in many applications:
Corrosion Resistance: Excellent resistance to chemicals, moisture, and corrosion—ideal for underground or damp environments.
Safety: Non-metallic and non-conductive, reducing shock hazard and improving insulation.
Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive than metal conduit systems and requires no threading tools.
Ease of Installation: Lightweight materials, solvent-welded joints (for rigid PVC), and snap-on fittings (for ENT) help reduce labor time.
Durability: Long-lasting material that withstands harsh conditions when properly installed.
Why the NEC Matters for PVC Conduit Installations
While PVC conduit offers clear advantages, its use is regulated by the National Electrical Code (NEC) to ensure safety, reliability, and consistency across installations. The NEC specifies:
- Where and how PVC conduit types may be used
- Proper securing and supporting methods
- Requirements for fittings, terminations, and transitions
- Minimum burial depths and protection in physical damage zones
- Special considerations in hazardous or high-temperature locations
By following NEC guidance, contractors and engineers can ensure that PVC conduit installations meet minimum safety standards, pass inspections, and function reliably over the long term.
General NEC Requirements for PVC Conduit
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) conduit is a widely used material in electrical installations due to its versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. PVC conduit is non-metallic, lightweight, and resistant to corrosion, moisture, and chemicals. These properties make it suitable for various applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial projects. Additionally, PVC conduit offers excellent electrical insulation properties and provides a high level of protection to embedded electrical cables.
General Requirements
The NEC sets forth general requirements that PVC conduit must meet to ensure safe electrical installations. These requirements include:
- Compliance with UL Standards: PVC conduit used in electrical installations must comply with the UL (Underwriters Laboratories) standards specifically designed for PVC conduit. This ensures that the conduit meets the necessary safety and performance criteria.
- Environmental Suitability: PVC conduit must be suitable for the environment in which it will be installed. Different types of PVC conduit are available for indoor, outdoor, wet, or corrosive environments. Choosing the appropriate type ensures the longevity and reliability of the conduit system.
- Marking and Identification: PVC conduit must bear proper markings for identification, including the manufacturer’s name or trademark, conduit size, and applicable electrical standard. These markings help in identifying the conduit and verifying its compliance with the required standards.
Sizing and Fill Requirements
Proper sizing and fill requirements of PVC conduit are essential to prevent overheating and ensure sufficient wire capacity. The NEC provides specific guidelines in this regard:
- The PVC conduit size shall be bigger than 1/2 inch and small than 6 inch, the sizes not within this ranges shall not be used.
- Fill Limit Calculation: Fill limit are calculated using the cross-sectional area of conductors and the size of the conduit. Adhering to these limits prevents overcrowding, overheating, and potential damage to the conductors. And the conductor number shall not exceed the allowable percentage fill.
- Special Considerations: Certain applications require special considerations, such as conduit bodies, conductor insulation types, and derating factors. These factors may affect the fill limits and must be taken into account during conduit sizing.
Installation and Supports
Proper installation techniques and adequate support for PVC conduit are critical to ensure its integrity and prevent damage. The NEC provides the following requirements:
- Secure Fastening and Support: PVC conduit must be securely fastened and adequately supported at intervals specified by the code, typically every 3 feet. This prevents excessive movement, sagging, or stress on the conduit.
- Vertical and Horizontal Runs: Both vertical and horizontal runs of PVC conduit require proper support to maintain their position and prevent sagging. Supports should be installed at appropriate intervals to ensure stability.
- Compatibility of Supports: Conduit supports must be compatible with PVC conduit and provide sufficient strength and stability. The supports should not cause damage to the conduit material or compromise its structural integrity.
Bends and Junctions
Properly executed bends and junctions in PVC conduit are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the electrical system. The NEC provides the following guidelines:
- Minimum Bend Radius: PVC conduit should be bent using the minimum bend radius specified by the manufacturer. This prevents damage to the conduit and ensures the conductors inside are not subjected to excessive stress.
- Bending Tools and Techniques: Appropriate bending tools and techniques should be employed to ensure smooth and accurate bends. Improper bending can lead to kinks, flattening, or other deformations that may affect the conduit’s performance.
- Junction Boxes and Conduit Bodies: Junction boxes and conduit bodies should be appropriately sized, easily accessible, and provide adequate space for connections and wire splices. These components play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the conduit system.
Grounding and Bonding
Proper grounding and bonding of PVC conduit systems are essential for electrical safety. The NEC outlines the following requirements:
- Adequate Grounding: PVC conduit systems must be properly grounded to facilitate fault current return and ensure electrical safety. Grounding conductors should be sized and installed according to NEC guidelines.
- Bonding with Metallic Enclosures or Conductors: When PVC conduit is used in conjunction with metallic enclosures or conductors, bonding jumpers or devices must be installed to maintain continuity and prevent potential differences.
For all specific details and requirements, please check the official NEC standard file.
A Deeper Understanding of NEC Requirement for PVC Conduit

NEC Article 352 – Rigid Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Conduit
Rigid Polyvinyl Chloride Conduit (PVC) is a widely used nonmetallic raceway system in electrical installations due to its durability, corrosion resistance, and ease of handling. However, to ensure it is used safely and appropriately, the National Electrical Code (NEC) provides detailed regulations under Article 352. These requirements cover where PVC conduit is permitted or prohibited, as well as how it must be installed, supported, marked, and protected. Below is a breakdown of the essential provisions outlined in NEC 352.
Where Rigid PVC Conduit is Allowed
According to the NEC, Rigid PVC conduit is allowed in a wide range of installations. Specifically, it is permitted for:
Exposed and concealed work.
Underground installations, including direct burial in the earth.
Support of conductors per other NEC articles.
Embedded use in concrete, floors, or walls.
Use in locations subject to corrosive influences, due to its chemical resistance
Environments with moisture or wet conditions.
Aboveground locations (if marked “sunlight resistant”).
Notably, the code also allows PVC conduit in structures where the walls are frequently washed down, as long as watertight fittings are used.
Where Rigid PVC Conduit is NOT Allowed
While versatile, rigid PVC conduit is not suitable for all applications. NEC 352.12 explicitly prohibits its use in the following conditions:
In areas subject to severe physical damage (unless protected or encased).
Where it is exposed to temperatures above the conduit’s rated limit.
For supporting luminaires or other equipment unless specifically permitted.
In hazardous (classified) locations, unless specifically permitted by other NEC articles.
In areas where the ambient temperature exceeds its listed rating or where damage due to heat or fire exposure is likely.
Installers must evaluate the environment carefully to avoid misapplication of the material.
Wet Locations
One of PVC conduit’s biggest advantages is its suitability for wet or damp locations. It may be installed in facilities such as laundries, food-processing plants, or car washes, where water exposure is common.
In these environments, the entire conduit system, including fittings and junction boxes must be assembled to prevent water ingress. Additionally, any supporting hardware like straps, screws, or hangers must be corrosion-resistant or properly protected.
Physical Damage Protection
When physical protection is a concern, such as in warehouses, utility areas, or locations where the conduit may be bumped or struck. The NEC requires the conduits have to provide excellent mechanical strength to protect the wiring systems.
Conduit Support Requirements
Proper support is crucial for maintaining alignment and preventing stress on the system. The NEC Article 352.30 provides specific guidelines for supporting rigid PVC conduit based on its size.
- Smaller sizes (e.g., ½” to 1″) must be supported every 3 feet (900 mm), while larger sizes can be supported at longer intervals, up to 8 feet (2.5 m) for 6″ conduit
- PVC conduit must also be securely fastened within 900 mm (3 ft) of all termination points such as boxes, cabinets, or enclosures.
For more specific information, check Table 352.30(B):
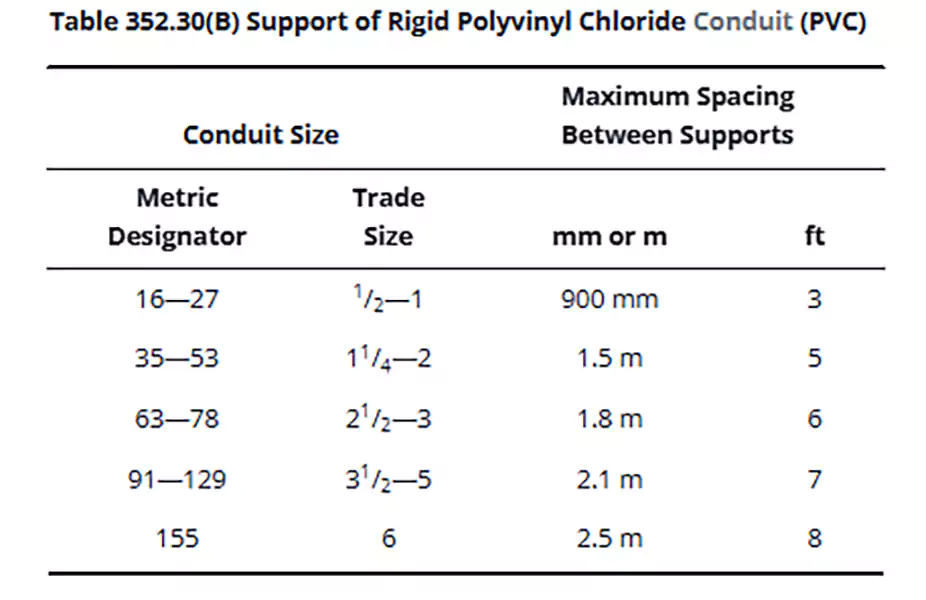
Horizontal conduit runs that pass through framing members can count as support, as long as the spacing meets NEC requirements. Following these rules not only ensures safety but also helps the system withstand expansion, contraction, and long-term stress.
Thermal Expansion
Because PVC is a thermoplastic material, it expands and contracts significantly with temperature changes. In long straight runs, this movement can lead to buckling or joint separation if not properly managed. To address this, the NEC requires the use of expansion fittings whenever temperature-driven length changes of ¼ inch (6 mm) or more are expected.
Installers must account for ambient temperature differences between installation and service conditions, and ensure fittings are installed between two fixed points like boxes or cabinets. A failure to do so can compromise system integrity and lead to costly repairs.
Grounding Requirements
While Rigid PVC conduit is a nonmetallic system and does not serve as a grounding path on its own, the National Electrical Code (NEC) outlines specific requirements for ensuring proper grounding when using this type of conduit. According to NEC 352.60, where equipment grounding is required, a separate grounding conductor must be installed inside the PVC conduit to provide a reliable fault-return path.
Marking Requirements
All rigid PVC conduits must be clearly marked to ensure proper identification and code compliance:
Markings must appear at least every 3 meters (10 feet).
They must indicate the material type (unless it’s visually obvious).
For above-ground installations, markings must be permanent.
For underground-use-only conduits, markings must remain legible until the time of installation.
Optional surface markings may include:
“Sunlight Resistant” for outdoor exposure
“Limited Smoke” for low smoke-producing applications
These markings help inspectors and installers verify proper use and performance capabilities.
NEC Article 362 – Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing (ENT) Requirements
ENT conduit is a flexible, lightweight, and nonmetallic raceway system commonly used in modern wiring installations, especially in commercial and residential construction. It is prized for its ease of installation, resistance to corrosion, and adaptability in tight or complex building layouts. The National Electrical Code (NEC) Article 362 outlines comprehensive regulations for the safe and effective use of ENT, including scope, permitted uses, construction specifications, and marking requirements.
Where ENT Can Be Used
Low-rise buildings (3 stories or less): ENT is allowed in both open (exposed) and hidden (concealed) spaces.
High-rise buildings (above 3 stories): ENT is allowed only in concealed spaces if protected by fire-rated materials, unless the building is fully sprinklered.
Above suspended ceilings: Allowed when the ceiling offers basic fire protection, or in sprinklered buildings.
Concrete applications: ENT can be encased in poured concrete or laid on sand within concrete slabs, if compatible fittings are used.
Dry and damp areas: ENT can be used in these locations if it’s listed for such use.
Wet areas: Permitted only if ENT and its fittings are approved for wet conditions.
Chemical/corrosive environments: Can be used if specially rated to withstand such exposure.
Where ENT Cannot Be Used
Outdoors in direct sunlight or where subject to physical damage (unless specially approved).
In unprotected high-rise areas without fire-rated coverings.
In hazardous (classified) locations unless clearly listed for that use.
Physical and Electrical Limitations
ENT is not permitted in trade sizes larger than 2½ inches (metric designator 63). It must also be installed using approved fittings and couplings to ensure joint integrity and system continuity.
The code permits ENT to be used with conductors or cables rated for higher temperatures only if those conductors are not operated above the temperature rating of the ENT. This provides some flexibility in cable selection while maintaining the safe thermal limits of the raceway system.
Additionally, ENT is not designed to support mechanical loads. It should not be used to hang or support luminaires, fans, or other equipment unless specifically approved for such applications.
ENT Support Requirements
Proper support is critical to maintaining the structural integrity and functionality of ENT systems. According to NEC requirements:
- Support Intervals: ENT must be securely supported within 3 feet (900 mm) of each box, fitting, or enclosure, and at intervals not exceeding 3 feet (900 mm) throughout its run.
- Horizontal and Vertical Runs: Both horizontal and vertical ENT installations must follow these support spacing guidelines unless otherwise permitted by the listing.
- Securing Devices: Use only approved straps, clamps, or other fittings specifically designed for ENT. These must not damage the tubing and should maintain mechanical protection.
- Embedded or Concealed Runs: When ENT is encased in concrete or concealed within walls, floors, or ceilings, additional support is not required at those points.
Grounding Considerations for ENT
Because ENT is nonmetallic and nonconductive, it does not provide an equipment grounding path. Therefore:
- A separate grounding conductor must be included inside the ENT when used to supply grounded (earthed) equipment.
- All metal boxes, enclosures, or devices connected to the ENT must be properly grounded using this separate conductor.
Marking Requirements
To ensure traceability and compliance:
ENT must be clearly and durably marked at least every 10 feet (3 meters).
Markings must include the material type and any limited smoke classification, if applicable.
When ENT is used in prewired assemblies, conductor type, size, and quantity must be shown on a printed tag or label attached to both ends of the tubing and on its packaging.
Special Occupancies and PVC Conduit Requirements

Beside general wiring methods for electrical systems, Chapter 5 of the NEC focuses on special environments that require more stringent safety considerations due to elevated risks. These include hazardous locations, health care facilities, recreational vehicles, agricultural buildings, and more. For PVC conduit installations, understanding the additional requirements outlined in Chapter 5 is critical to ensuring compliance and safety in these specialized settings, here are some of the special installation locations.
Hazardous Locations
In areas classified as hazardous due to the presence of flammable gases, vapors, or dusts, such as chemical plants or grain silos, conduit systems must provide robust protection against ignition sources.
PVC conduit may be restricted or permitted only under specific conditions in these environments:
- It is typically not permitted in Class I, Division 1 locations where explosive gases may be present under normal operation.
- In Division 2 areas, limited uses of PVC conduit may be allowed if it is buried or encased in concrete and properly sealed.
- Rigid nonmetallic conduit must be specifically listed and marked for use in hazardous environments if permitted.
Health Care Facilities
In hospitals, dental offices, and similar environments, wiring systems must meet strict standards to ensure continuous, reliable operation of life-support and diagnostic equipment. PVC conduit may be used in certain non-patient care areas but is often restricted in patient care spaces, where metallic raceways offering superior grounding and shielding may be required.
Key considerations:
Grounding continuity is crucial—since PVC is nonmetallic, a separate equipment grounding conductor must be installed.
Mechanical protection and fire resistance also matter, especially where conduits pass between floors or through fire-rated assemblies.
Recreational Vehicles Parks and Mobile Homes
PVC conduit is often used for underground distribution and service entrance conductors in RV parks and mobile home communities.
- It must be listed for direct burial, and proper transitions to above-ground enclosures or pedestals are required.
- Installation must comply with bending radius, conduit fill, and sealing requirements to prevent moisture ingress.
- Conductors must include an EGC, since PVC does not provide a grounding path.
Agricultural Buildings
Moisture, dust, ammonia, and corrosion are persistent hazards in agricultural facilities such as barns, poultry houses, and dairy operations. NEC Article 547 allows PVC conduit in these areas due to its resistance to chemicals and corrosion, provided it is watertight and securely installed.
All conduit systems must prevent moisture intrusion—a requirement especially important in wash-down areas.
Corrosion-resistant fittings and supports are mandatory.
PVC must be mechanically protected where physical damage is likely, often by using Schedule 80 conduit.
Other Special Conditions in NEC
As modern electrical systems evolve to include emergency power, energy storage, and communication infrastructure, the National Electrical Code (NEC) provides dedicated guidelines in Chapter 7 and Chapter 8. These chapters outline the special conditions and system-specific requirements that often affect how PVC conduit systems, including rigid PVC and ENT, must be designed and installed.
Emergency & Energy Storage Systems

Emergency Systems (Article 700)
Emergency systems provide power during outages to support critical operations such as emergency lighting, fire alarms, and communication systems.
- PVC conduit can be used in emergency system installations, but only if the system integrity is maintained under emergency conditions.
- Rigid PVC must be installed with attention to mechanical protection and separation from normal systems, and it must comply with any fire barrier requirements in the space.
Important Note: Emergency wiring must be segregated from other systems and clearly identified. PVC can help with color-coded raceways for identification but cannot serve as an equipment grounding path—a separate equipment grounding conductor (EGC) is always required.
Energy Storage Systems (ESS) (Article 706)
With the rise of battery energy storage systems (BESS), safe wiring becomes essential—especially for systems using lithium-ion or other advanced chemistries.
- PVC conduit is permitted for many ESS installations, especially in indoor or underground raceways.
- Conduits must be properly sized for heat dissipation and include EGCs.
- In many cases, local building/fire codes may impose additional rules—such as requiring metallic conduit or fire-rated enclosures for battery rooms—so PVC must be used judiciously and in compliance with all applicable standards.
Pro Tips: Want to know the different codes for ESS in the United States, Canada, and Australia? This article discusses the details of the Energy Storage System and the relevant code compliance in North America and Australia.
Communication Systems - Chapter 8
Chapter 8 covers systems such as telephone, internet, TV, and broadband—often referred to as low-voltage or extra-low-voltage systems.
PVC Conduit for Communications
Rigid PVC conduit is commonly used to protect communication cables—particularly in underground or outdoor installations—due to its corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness.
ENT can also be used in concealed indoor spaces if it meets the routing and bend radius requirements for communication cabling.
Key considerations:
Communication raceways must be segregated from power wiring to prevent electromagnetic interference.
PVC raceways for communication cables should be marked and routed clearly, especially when installed in plenum or riser spaces (note that LSZH or plenum-rated cable may be required instead of special conduit).
PVC used in communication pathways must still comply with bend radius, fill capacity, and support spacing requirements.
Pro Tips: Need to know more about communication conduit types and codes? You can read this expert guide to comms conduits.
Ledes PVC Conduit Solutions
Ledes PVC conduit systems are engineered to meet the demands across a wide range of installation environments, from general, special to communication system applications. Offering durability, compliance, and safety in even the most demanding applications.
Rigid PVC Conduit

Ledes rigid PVC conduits are designed and manufactured to comply with relevant NEC articles, including Article 352 for Rigid PVC Conduit. These products are:
- UL Listed, with third-party testing to meet UL 651 standards.
- Manufactured to meet flame resistance, crush resistance, and impact resistance thresholds required for indoor and outdoor installations.
- Offered in both Schedule 40 and Schedule 80, accommodating buried installations, exposed applications, and high mechanical stress environments.
- Available with markings every 3 meters (10 feet) as per NEC for traceability and identification.
These features make Ledes PVC conduits a reliable choice for general-purpose wiring in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings, supporting both concealed and exposed applications, including underground systems, underground and embedded concrete installations.
Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing (ENT)

Ledes also provides a full line of Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing (ENT) designed for compliance with NEC Article 362. Ledes ENT solutions are:
- UL 1653 certified for flame propagation, crushing, and bending performance.
- Lightweight and flexible, enabling quick installation in wall cavities, ceiling spaces, and floor assemblies.
- Designed for use above suspended ceilings or within fire-rated walls and slabs, where ENT is permitted by NEC under thermal protection or sprinkler system conditions.
- Suitable for installation in concrete slabs on grade.
Ledes ENT is especially useful in multi-family, healthcare, and light commercial settings where flexibility, speed, and fire-rated construction are necessary.
Conclusion
Understanding and applying the National Electrical Code (NEC) requirements for PVC conduit systems, such as Rigid PVC Conduit and Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing (ENT) are essential for safe, compliant, and long-lasting electrical installations. From general installation rules and permitted uses to specialized requirements for emergency systems, energy storage, and communication circuits, each aspect of the NEC is designed to ensure safety, functionality, and adaptability across diverse environments.
Ledes’ PVC conduit solutions are developed with these standards in mind. Whether it’s fire-resistance for buildings with stringent protection needs, corrosion resistance for chemical environments, or system compatibility for modern communication and energy infrastructures, Ledes provides reliable products that meet both code requirements and practical demands.
Looking ahead, as building systems evolve with growing emphasis on energy efficiency, smart infrastructure, and safety, it is more important than ever to align conduit system choices with NEC guidance. Thoughtful conduit selection not only ensures code compliance but also contributes to long-term reliability, simplified maintenance, and future-ready installations.
By combining a deep understanding of the NEC with proven product performance, electrical professionals can design systems that are both technically sound and ready for tomorrow’s challenges.
FAQs
Can PVC conduit be buried underground?
Yes, PVC conduit is suitable underground installations. However, it must be specifically rated and approved for burial. The depth of burial and any necessary protective measures, such as concrete encasement, should comply with local codes and regulations.
Can PVC conduit be used for both indoor and outdoor installations?
Yes, PVC conduit is available in types suitable for both indoor and outdoor installations. However, it is crucial to select the appropriate type based on the specific environmental conditions to ensure its longevity and performance.
Are there any restrictions on the number of bends allowed in PVC conduit?
Yes, the National Electrical Code (NEC) places a restriction on the number of bends in a run of PVC conduit (as well as other types of conduit).
According to NEC 352.26 for Rigid PVC Conduit, and similar rules for other raceway types:
The total number of bends between pull points (e.g., boxes, conduit bodies, or other access points) must not exceed 360 degrees.
This means:
You can have up to four 90-degree bends, or
Any combination of bends that does not exceed 360 degrees total.
Can PVC conduit be used in areas with high temperatures?
PVC conduit can be used in areas with elevated temperatures, but there are important limitations and considerations.
Standard rigid PVC conduit is typically rated for use up to 50°C (122°F) ambient temperature.
Some types may be rated for higher temperatures (e.g., 90°C [194°F] for the conductors inside), but the conduit itself may soften or lose strength at high temperatures.
Is PVC conduit suitable for corrosive environments?
PVC conduit is resistant to many common corrosive substances and is suitable for a wide range of environments. However, in highly corrosive environments, it is recommended to consult the manufacturer’s specifications and consider alternative conduit materials, such as PVC-coated rigid metal conduit or other corrosion-resistant options.
Are there specific color coding requirements for PVC conduit?
Yes, the NEC mandates color coding for various types of conduits. For instance, grey PVC conduit is often used for electrical systems, while orange PVC conduit is typically reserved for communication and data applications, and red is for fire alarm systems or high-voltage lines.
Can PVC conduit be used for high-voltage applications?
While PVC conduit is commonly used for low-voltage applications, it may also be suitable for some high-voltage applications, especially for systems up to 600V. For over 600V, ensure you’re using a conduit type listed and identified for that voltage class, and always install in accordance with the NEC, especially Articles 300 and 352.



