
目录
电气导管系统有多种材质和配置:金属材质(例如 EMT、IMC 和 RMC)、非金属材质(例如 PVC 和 HDPE)以及柔性材质(例如液密型或波纹型)。每种类型都有其独特的特性,并受特定规范和性能标准的约束。其中, 40号PVC导管 由于其强度高、重量轻、价格实惠和耐腐蚀性,它成为最受欢迎和用途最广泛的选择之一,被广泛使用。
选择合适的导管不仅对项目效率和规范合规性至关重要,而且对长期安全和性能也至关重要。不匹配或不合规的导管可能会导致代价高昂的故障、检验不合格,甚至造成电气危险。2025年,随着标准不断演变、绿色建筑倡议不断涌现以及对能源基础设施(例如电动汽车充电和太阳能)的需求不断增长,了解合适的导管比以往任何时候都更加重要。
在本指南中,我们将探讨您需要了解的有关 Schedule 40 PVC 导管的所有信息,以便您可以对任何电气安装项目做出明智的决定。
什么是 Schedule 40 PVC 导管?

Schedule 40 PVC 导管是一种刚性、 非金属电气导管 由聚氯乙烯 (PVC) 制成,专为保护和布线而设计。“Schedule 40”指的是其壁厚,更广泛地反映了其耐用性和机械强度。
Schedule 40 电线导管的生产符合特定的电气规范和标准,例如 UL 651 和 NEMA TC-2,这些规范和标准注重阻燃性、抗冲击强度和电线拉拔的便捷性等因素。它通常为灰色,表明其适用于电气应用。
40号PVC导管的主要特性
材料: 非金属硬质聚氯乙烯(PVC)
颜色:浅灰色
壁厚: 中等强度——足够用于地下和露天使用,但比 Schedule 80 轻
阻燃性: 符合 UL 可燃性标准
耐腐蚀性: 对大多数酸、碱、盐和湿气具有优异的抵抗力
绝缘性能: 不导电且耐电流
温度范围: 通常为 -10°C 至 60°C(14°F 至 140°F),但会因配方而异
3 种 40 号 PVC 导管
虽然所有 Schedule 40 PVC 导管都具有相同的基准壁厚和材料,但制造商提供各种不同的导管以满足不同的安装需求:
平端导管
直导管,端部未经过修改。
需要联轴器或溶剂胶进行连接。
通常用于狭窄空间或需要切割和定制长度连接的情况。
喇叭口导管
导管的一端在工厂形成有插座(钟形),可直接插入下一个导管部分。
无需单独的联轴器,从而加快了安装速度。
非常适合地下安装等长距离连续运行。
抗紫外线配方
一些 Schedule 40 PVC 导管在制造时添加了紫外线稳定剂,以防止因长时间暴露在阳光下而发生降解。
通常标记 “抗紫外线” 或者 “耐阳光” 并符合 UL 651 户外使用要求。
建议用于预计会受到阳光照射的地面以上外部应用。
尖端: Ledes 报价 太阳能用 Sch 40 导管,有兴趣的可以点击链接了解一下。
40号PVC导管的7种常见应用
40号PVC导管以其多功能性而闻名,使其成为各种电线安装的首选解决方案。它兼具机械强度、耐腐蚀性和经济实惠性,适用于各种住宅、商业、工业和基础设施领域。
以下是 Schedule 40 PVC 导管最常见和新兴的应用:
住宅电气安装
40号PVC导管常用于家庭照明、插座、暖通空调系统和车库电路的布线,尤其是在地下室或外墙等潮湿区域。它也常用于独立车库、棚屋或户外照明系统的地下线路。
商业和机构建筑
在商业环境中,例如办公室、学校或医疗保健机构,Schedule 40 PVC 通常用于保护楼板结构或地下管廊中的分支电路布线。它因其使用寿命长且易于安装而备受青睐。
- 包裹在混凝土中或埋在地下
- 用于配电和照明系统
- 非常适合低压和通信线路保护
工业和公用事业项目
工业应用包括发电厂、工厂、变电站以及其他负载不大的应用。40号PVC管尤其适用于金属导管容易老化的腐蚀性环境。
- 优异的耐化学性和耐湿性
- 用于控制线路、过程自动化和传感器网络
- 通常与膨胀配件结合使用以适应热运动
太阳能和可再生能源装置
随着全球向清洁能源的转变,40 号 PVC 导管在保护光伏板、汇流箱、逆变器和电池之间的接线方面发挥着至关重要的作用——尤其是在地面安装的太阳能发电场和屋顶系统中。
- 常用于地下直流/交流馈线电缆
- 抗紫外线型号非常适合暴露安装
- 重量轻,易于在太阳能场建设期间搬运
基础设施和交通
40号PVC导管广泛应用于公共基础设施,例如街道照明、高速公路标识、交通信号控制和机场跑道。其成本低廉、安装简便,使其成为大型项目的首选导管。
- 用于道路、桥梁沿线地下管道铺设
- 保护智能交通系统 (ITS) 的线路
数据中心和通信系统
随着数据中心在 2025 年继续扩张,Schedule 40 PVC 导管还用于组织和保护通信和光纤电缆基础设施,尤其是在架空地板下方或平板安装中。
- 为敏感电缆提供非金属隔离
- 有助于满足电源和数据分离的要求
户外和潮湿的地方
当与适当的配件和防风雨外壳搭配使用时,Schedule 40 PVC 可安全用于室外和潮湿环境,例如泳池设备布线和码头设施。
- 必须具有抗日光紫外线的能力
- 常与防水接线盒一起使用
- 确保潮湿环境下符合规范
附表 40 PVC 导管规范合规性

为确保 40 号 PVC 导管安全耐用且适用于电气安装,其必须符合多项关键行业规范和标准。这些由国家和国际组织制定的法规规定了材料质量、物理性能、制造一致性和安全安装的最低要求。了解这些标准有助于确保导管符合法律要求、通过检查并长期可靠运行。
下面简要介绍一下适用于 Schedule 40 PVC 导管的主要规范和标准:
UL 651 – 40 号和 80 号 PVC 导管和配件标准:
UL 651是美国主要的安全标准,由美国保险商实验室(Underwriters Laboratories)发布,该标准专注于硬质PVC导管的测试和认证。它规定了尺寸精度、机械强度、抗冲击性、抗压性、阻燃性和其他性能的要求。
专业提示: 想了解更多关于 UL651 标准的信息吗?您可以查看我们上一篇关于 PVC导管的UL651应用指南.
NEMA TC-2 – 电气聚氯乙烯 (PVC) 导管:
NEMA TC-2 由美国国家电气制造商协会开发,符合 UL651 标准,提供详细的制造指南、尺寸公差和材料规格,以确保 PVC 导管产品的质量和性能始终如一。
该标准由 ASTM International 发布,对导管生产中使用的 PVC 材料的物理和化学特性进行了分类。
指定用于导管制造的硬质 PVC 化合物的最低材料要求。
大多数电线导管使用的材料的细胞分类至少为 12454 或更高的强度和稳定性。
笔记: 阅读 ASTM 规范专家指南 可以帮助您详细了解ASTM对PVC管道原材料的要求。
CSA C22.2 No. 211.2 – 加拿大硬质 PVC 导管标准
该标准由加拿大标准协会发布,规定了加拿大使用的硬质PVC导管的安全性和性能。要求其在阻燃性、机械强度和耐化学性方面具有类似的性能。
专业提示: 不知道加拿大标准 PVC 导管?阅读这篇文章 CSA C22.2 标准硬质 PVC 导管要求 帮助您快速了解加拿大导管规范并选择正确的规范。
Sch 40 导管的性能要求和测试
为了确保 Schedule 40 PVC 导管的可靠性、安全性和长期耐用性,制造商必须满足 UL 651(硬质 PVC 导管的行业基准标准)规定的严格性能要求。该标准规定了一系列全面的测试,用于评估导管的性能和质量。通过所有测试标准的产品有资格获得 UL 认证,表明其符合国家认可的安全标准。
以下是 UL 651 对 Schedule 40 PVC 导管所要求的关键性能领域和测试:
尺寸要求
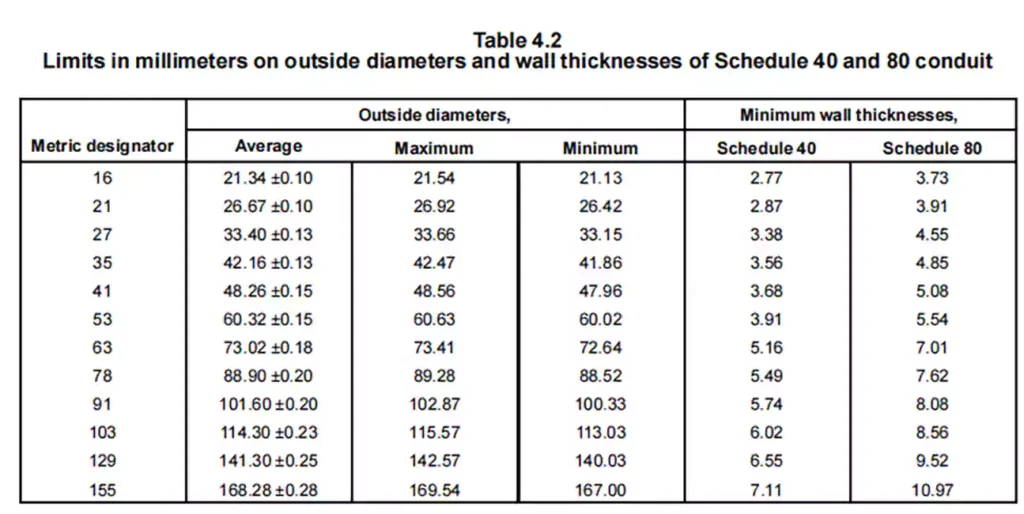

该标准对40号和80号PVC导管以及其他类型的硬质PVC导管(贸易尺寸从1/2英寸到6英寸)设定了具体的尺寸要求。测量范围包括外径、壁厚、最小内径、长度和整体插座尺寸,以确保它们符合规定的公差范围。
抗拉强度
该测试是为了确认导管材料是否能够承受拉力而不会失效,这在电缆拉动或受压时至关重要。
方法: 使用试验机以每分钟10.0±2.5毫米的固定速率从导管上切下标准试样(哑铃形),包括老化和未老化的试样,将其拉开。这测量了材料在断裂前可承受的最大应力。
要求: 对于 Schedule 40 硬质 PVC 导管,拉伸强度不得低于 5000 psi,并且在热老化后保持至少 95% 强度。
吸水率
目的: 确保吸水不会降低导管的电气或机械性能,特别是在潮湿环境中的应用。
方法: 将样品干燥、称重,然后浸入23°C的水中24小时。取出后,干燥表面,然后再次称重。
要求: 因水而增加的重量必须≤0.50%。
抗冲击测试
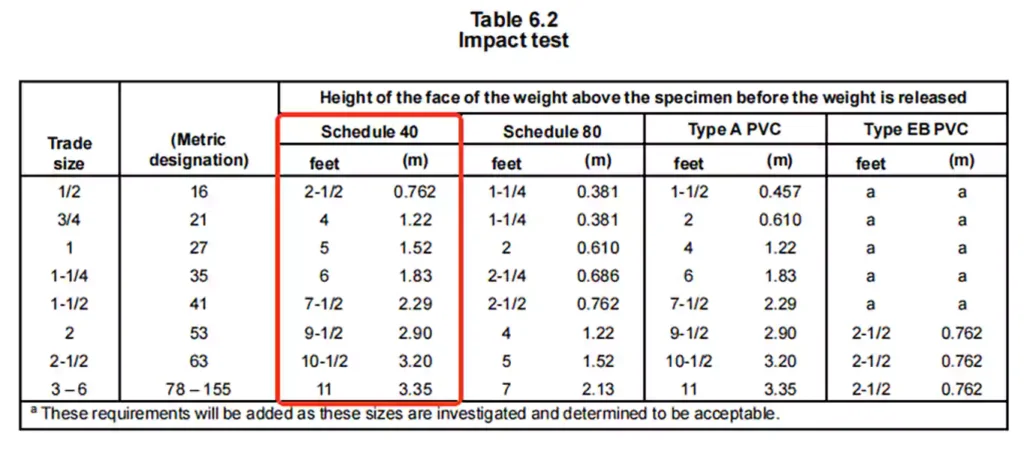
评估导管承受机械冲击而不破裂或撕裂的能力,确保搬运和安装过程中的耐用性。
测试方法: 将十个样本在 23.0 ±2.0°C (73.4 ±3.6°F) 的温度下放置至少 4 小时。
每个 Schedule 40 导管样品都要在特定高度承受 20 磅(9.1 公斤)的冲击力。
要求: 十个样本中有七个的外表面不得出现长度超过 1/32 英寸(0.8 毫米)的裂纹或撕裂。
负载下挠度试验
该测试检查 Schedule 40 PVC 导管在暴露于热和机械应力时抵抗弯曲的能力。
测试方法: 将成品导管加工成试样,两端支撑,中心加载,浸入加热液体中。温度逐渐升高,直至试样弯曲(挠曲)0.010英寸(0.25毫米)。
要求: 为了通过测试,发生偏转时的平均温度必须至少为 轻负载(66 psi)下 70°C(158°F) 和 较大负载 (264 psi) 下为 62°C (143.6°F).
这些结果有助于确认导管在高温条件下能保持其形状和强度,使其适合暴露在高温下的安装。
压碎(压缩)试验
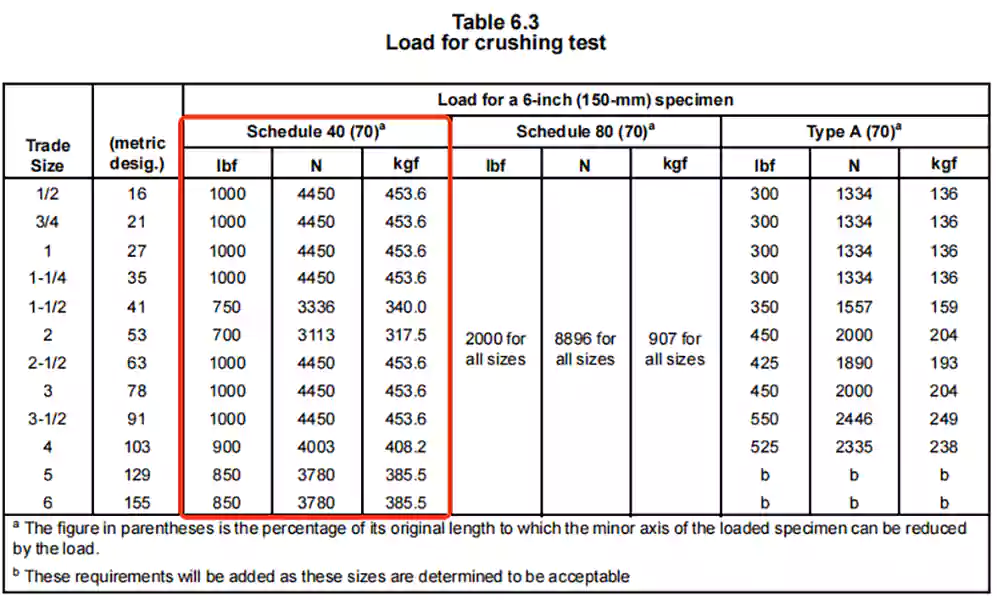
该测试评估了 Schedule 40 PVC 导管在重外部负载下抵抗变形的能力。
方法: 将一段6英寸长的导管放置在两块扁平钢板之间,并以稳定的速率进行压缩。目的是模拟导管埋入地下或安装在地板下时可能承受的压力。
要求: 要通过测试,导管不得弯曲或脱离板材。压缩后,扁平导管的内径(短轴)仍须至少为原始内径的 70%。这确保导管即使在负载下也能保持其形状并留出导线空间。
阻燃测试
该测试检查 Schedule 40 PVC 导管抵抗着火和火焰蔓延的能力。
测试方法: 将一根18英寸长的垂直导管置于火焰中三次,每次持续60秒,中间间隔30秒。导管下方放置棉花,以检测是否有燃烧颗粒或滴落物。
要求: 要通过测试,导管必须在每次接触火焰后5秒内停止燃烧。它还必须不会点燃其下方或周围的棉花,并且棉花不能完全燃烧。这确保了导管在实际应用中不会助长火势蔓延。
对特定试剂的耐药性
该测试评估 40 号和 80 号硬质 PVC 导管在特定腐蚀性试剂中的耐化学性。测试包含两个关键部分:试剂吸收测试和抗压强度测试,模拟导管在长期化学环境中可能浸泡或经常接触腐蚀性物质(例如油、溶剂或化学品)的情况。
- 将测试样本(通常为贸易尺寸 1(27)或更小)浸入具有规定温度和浓度的试剂中 60 至 120 天。
- 试剂吸收测试测量重量变化的百分比,以确保其保持在可接受的范围内(≤2.50%),并控制随时间的吸收率,以防止过度降解。
- 抗压强度测试比较了老化和未老化样品在暴露后的机械完整性。该测试确保导管至少保留其原始抗压强度的85%,并且不会出现开裂或塌陷等结构故障。
该测试对于确认管道在化学腐蚀性装置中的性能至关重要,并验证其在工业和腐蚀环境中的长期耐用性。
耐日光性测试(UV测试)
目的: PVC 导管系统通常安装在室外或暴露环境中,会持续受到紫外线 (UV) 辐射。该测试评估 40 号硬质 PVC 导管在模拟阳光和湿气环境下的长期抗紫外线性能。
方法: 样品在氙弧老化箱中分别进行 720、1080 和最多 1440 小时的老化,然后按照 ASTM D256 进行缺口伊佐德冲击试验。
要求: 导管必须在长时间紫外线照射后仍保持足够的抗冲击性才能通过测试。性能成功表明该产品适用于阳光照射的应用,并符合 “耐日光” 指定。
该测试对于验证太阳能系统、电信基础设施和裸露电线等户外设施中导管的可靠性至关重要。
适用于 90°C 电线

40 号(和 80 号)硬质 PVC 导管有时会安装在必须承载额定连续工作温度为 90°C (194°F) 的导体的环境中。为确保导管材料在长期热应力下保持完整性,UL 651 要求进行专门测试,以验证导管在长期暴露于高温下时其关键性能不会显著下降。
测试方法: 该测试将导管样品放入 80°C (176°F) 的循环空气烘箱中进行加速老化,最长可达 360 天。每隔 60、120、180、240 和 360 天,取出样品,冷却后采用钢落锤试验评估其冲击强度。以未老化样品作为基准,绘制冲击强度随时间下降的曲线。
要求: 要通过测试,冲击强度必须稳定在未老化样品测量值的50%以上。这确保了导管即使长时间暴露于导体高温下,也能保持足够的机械完整性和抗冲击性。
符合此要求的导管标有“最高 90°C 电线”或“最高 90°C”,是高性能、高热密集型电气系统的可靠选择。
40号PVC导管的优点和缺点
Schedule 40 PVC 导线管是住宅、商业和轻工业领域最广泛使用的电线管类型之一。它之所以受欢迎,源于其在性能、成本效益和易用性方面的平衡。然而,与任何材料解决方案一样,它也有其优势和局限性。了解这些优缺点对于您确定它是否适合您的项目环境至关重要。
40号PVC导管的6大优点
重量轻且易于安装
40号PVC导管比80号PVC导管和金属导管系统(例如EMT或RMC)轻得多。这减少了人工和安装时间,尤其是在大规模安装或架空应用中。其轻便的特性也最大限度地降低了运输和搬运成本。
耐腐蚀
PVC 的主要优势之一是其耐锈蚀、腐烂和化学腐蚀的特性。40 号 PVC 导管非常适合潮湿或腐蚀性环境,包括地下设施、农业环境和污水处理设施。
经济高效
与金属导管系统相比,Schedule 40 PVC 的前期材料成本更低,安装所需的专用工具也更少。因此,无论对于小型还是大型电力项目,它都是经济实惠的选择。
非导电且电绝缘
PVC 本身不导电,因此在许多应用中无需额外接地。这一特性在需要最大限度降低触电风险的环境中增强了安全性。
耐候、耐紫外线(含添加剂)
使用适当的紫外线稳定剂或安装适当的覆盖物时,Schedule 40 PVC 可以承受阳光照射和户外条件。
良好的耐化学性
40号PVC对多种化学物质(包括酸、盐和碱)具有很强的耐受性。这一特性使其适用于恶劣的工业或化学加工环境。
40号PVC导管的5个缺点
机械强度较低
虽然 Schedule 40 PVC 适用于多种应用,但与 Schedule 80 PVC 或金属导管相比,其抗冲击和抗压性能较差。它可能不适用于交通繁忙、机械磨损或深埋环境,且无需额外保护。
有限的温度范围
PVC 导管通常在 -18°C (0°F) 至 60°C (140°F) 的温度下性能良好,但在极冷条件下会变脆,在高温条件下会软化。这限制了其在某些工业或高温设施中的使用。
在寒冷气候下易碎
在极寒环境下,PVC会变得更脆,容易开裂。安装人员在零度以下环境下搬运和安装时必须小心谨慎,或考虑使用其他材料。
燃烧时会产生烟雾和有毒气体
虽然PVC具有自熄性,但燃烧时会产生烟雾和潜在的有害气体。与 低烟无卤 (LSZH) 导管 或金属导管,在火灾危险环境中提供更好的性能。
易受热膨胀和收缩的影响
PVC 在温度变化时比金属膨胀和收缩得更快。如果没有使用伸缩接头或设计调整进行适当的补偿,这种变形会随着时间的推移导致管道位移或接头应力。
哪些地方允许使用 40 号 PVC 导管?

40 号 PVC 导管在市场上广泛使用,国家电气规范 (NEC) 对允许安装的位置提供了全面的指导。 NEC 352.10 指定可以安全使用 Schedule 40 PVC 导管的地方。
隐蔽安装(墙壁、地板、天花板)
40号PVC导管可隐藏在住宅和商业建筑的墙后、地板下和天花板上方。其低调且无腐蚀的特性使其适用于不易受到物理损坏的室内布线系统。
混凝土包裹
它可以直接嵌入混凝土板、梁或墙内。这在地基工程和地下管道群中很常见,因为管道受到混凝土外壳的保护,免受环境影响。
腐蚀环境
PVC 导管在高腐蚀性场所(例如化工厂、沿海地区和污水处理厂)尤其具有优势,因为在这些场所,金属导管会迅速劣化。只要 PVC 材料符合特定化学物质的防护等级,美国国家电气规范 (NEC) 允许在这些环境中使用 PVC。
煤渣填充区域
PVC导管可安装在充满工业煤渣或矿渣的区域。这些环境腐蚀性极强,而PVC导管则是一种非反应性金属导管系统的替代方案。
潮湿场所(例如,奶牛场、洗衣店、洗车场)
在潮湿或经常冲洗的区域,允许使用 PVC 导管。在这种情况下,安装人员必须确保系统防水,包括使用兼容的 PVC 盒、配件以及耐腐蚀硬件,例如不锈钢螺钉或镀锌带。
干燥和潮湿的地方
它适用于干燥和潮湿的室内环境,例如地下室、储藏室和公用设施区域。除非 NEC 352.12 中列出的具体规则另有禁止,否则 NEC 允许在这些场所使用 PVC。
暴露装置
40号PVC导管可采用明装方式安装,例如未装修空间内沿墙或天花板安装。然而,如果存在物理冲击或机械应力的潜在影响,则需要使用80号PVC导管进行额外保护。
地下设施
PVC导管广泛应用于地下,可直接埋入土壤或包裹在混凝土中以提供额外的机械保护。它是服务入口、停车场和道路照明的常见解决方案。
绝缘温度兼容性
您可以在 PVC 导管内使用额定温度更高的导线,但其工作温度不得超过导管的额定温度(通常为 50°C 或 60°C,具体取决于产品)。这可以防止导管因高温而变形或损坏。
Schedule 40 PVC 导管用途广泛,关键在于导管类型和安装方法要与具体环境条件相匹配。NEC 352.12 还规定了不允许使用导管的应用场景,更多详情请参阅 NEC 标准。
40 号 PVC 导管是如何制造的?
Schedule 40 PVC 导管的制造过程是一个严格控制的工业操作,旨在确保产品质量稳定、符合标准并在电气安装中长期保持性能。以下是生产这种广泛使用的非金属导管的七个关键阶段的细分:
原材料准备
Schedule 40 PVC 导管使用的主要原材料是聚氯乙烯 (PVC) 树脂,它与各种添加剂相结合以增强特定性能:
- 稳定剂: 防止加工过程中的降解并延长热稳定性。
- 润滑剂: 提高加工性能并减少挤压过程中的摩擦。
- 抗冲改性剂: 增强最终产品的韧性和抗冲击性。
- 颜料: 提供典型的灰色并在需要时防止紫外线降解。
- 填充物 (例如碳酸钙):用于调整机械性能和成本。
这些成分被干混成一种均匀的粉末,称为化合物或 PVC 配方,以满足特定的性能标准,包括阻燃性和机械强度。
挤压
将准备好的化合物送入 PVC 挤出机,材料在此熔化并形成导管的形状:
- 材料在带有旋转螺杆的机筒中被加热至熔融状态。
- 然后,它被强制通过一个专门设计的模头,形成一个适合 Schedule 40 的特定壁厚的圆柱形管道。
- 模具下游的真空定径和冷却槽有助于在管道凝固时保持严格的尺寸公差。
- 挤压速度和冷却速度经过精心调节,以避免变形并确保壁厚均匀。
切割和扩口
一旦导管完全成型并冷却:
- 它被切割成标准长度,通常为 10 或 20 英尺。
- 一端呈喇叭口状(扩张),以便在安装过程中进行溶剂焊接。喇叭口工艺使用加热模具将管端扩口,以便牢固地安装下一段管材。
- 另一端保持平直(插口)。
标记和打印
每根导管长度均需标注强制性信息,通常采用喷墨或热印方式。这些信息包括:
制造商名称或商标
公称尺寸
附表指定(附表 40)
相关标准(例如UL 651)
批号和生产日期
使用等级(例如,耐日光,如果适用)
质量控制和测试
Schedule 40 PVC 导管经过严格的质量控制检查,包括:
尺寸检查: 确保内径和外径符合标准公差。
机械强度测试: 确认导管能够承受机械应力而不破裂。
阻燃测试: 验证其是否符合 UL 94 V-0 或同等标准的防火安全要求。
标记耐久性: 确保在处理和存储过程中保持清晰易读。
一些制造商还进行红外 (IR)、热重分析 (TGA) 或差示扫描量热法 (DSC) 测试,以检查化合物的一致性并确保各批次的配方正确。
包装和运输
检查合格后,导管将进行捆扎和包装,使用方法如下:
- 带子或塑料带
- 端盖可防止灰尘或湿气进入
- 用于跟踪和库存的标签
然后将它们装运,通常放在托盘或板条箱中,以便进行国内或国际分销。
如何安装 40 号 PVC 导管?(9 个步骤)
安装 40 号 PVC 导管需要周密的规划、合适的工具,并严格遵守电气规范,以确保电气系统安全、耐用且合规。以下是常规安装流程的专业概述。
规划管道路线
开始之前,请检查您的布局以确定:
- 管道路径(地上、地下、嵌入混凝土或隐藏在墙壁内)。
- 箱子、面板和终端的入口和出口点。
- 所需弯头和配件的数量和类型。
请参阅 NEC 填充表以确保导管尺寸适合所有预期导体。
切割并准备导管
使用细齿锯、导管切割器或电动斜切锯将导管切割至所需长度。
使用去毛刺工具或锉刀去除毛刺并打磨光滑切割边缘,以防止电线绝缘层损坏。
涂抹溶剂胶并组装
首先将所有组件干装以检查对齐情况。
清洁导管末端和接头插座。
将认可的 PVC 溶剂胶均匀涂抹在管道和配件上。
快速将导管插入接头并轻轻扭转,以均匀分布水泥。
保持在一起直至凝固。
Support the Conduit Properly
Secure conduit at intervals as required by code.
Use corrosion-resistant straps or clamps that are compatible with PVC material.
Accommodate Thermal Expansion
PVC expands and contracts with temperature changes. For long runs or outdoor installations:
Install expansion joints as recommended by the manufacturer.
Leave room for slight movement within fittings.
Make Bends with Heat (If Needed)
Use factory-made elbows when possible.
If custom bends are needed, apply uniform heat with a heat blanket or conduit heater.
Bend slowly and evenly, avoiding kinks or flattening.
Install Conduit into Boxes and Enclosures
Use terminal adapters, female adapters, or conduit bodies as needed.
Ensure tight, secure connections and proper gasket seals in wet or outdoor locations.
Pull Conductors
Once the conduit system is complete and fully cured:
Use a fish tape or pulling line to route the conductors.
Apply wire-pulling lubricant if needed to reduce friction.
Test and Inspect
Check for continuity, grounding (if applicable), and physical integrity.
Comply with local electrical inspection requirements before energizing the system.
Proper installation not only ensures code compliance but also extends the life of the conduit and protects wiring from damage.
7 Commons Fitting for Schedule 40 PVC Conduit
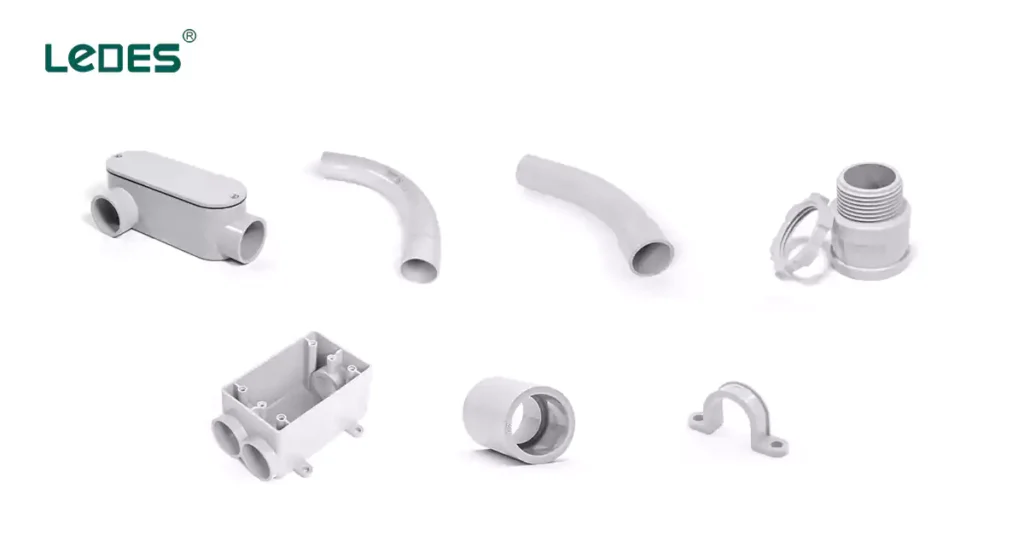

Fittings are essential components in any electrical conduit system. They allow Schedule 40 PVC conduit to connect, change direction, adapt to other systems, and safely terminate or support electrical wiring. Choosing the right fittings ensures a secure, code-compliant, and long-lasting installation. This section explores the most common types of fittings used with Schedule 40 PVC conduit, their applications, and installation considerations.
Conduit Couplings
Join two straight pieces of conduit end-to-end.
类型:
Standard Solvent Weld Couplings: Most common, joined with PVC cement.
膨胀联轴器: Designed to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction.
Conduit Elbows
Change the direction of conduit runs.
Bend Angles: 90°, 45°, 30°, 22.5°, and 11.25° are commonly available.
类型:
标准弯头: For general direction changes.
Sweep Elbows: Longer radius to ease wire pulling, often required for large or complex conduit runs.
Conduit Adapters
Transition from PVC conduit to boxes or other raceway systems.
类型:
母接头: It transitions the conduit to a threaded connection, typically to attach to a threaded male fitting, electrical box, or enclosure.
Terminal Adapters: Connect to electrical boxes; often come with a threaded end and a locknut.
电气箱
Serve as junction points, pull points, or for housing electrical devices.
类型:
接线盒: Available in square, round, or rectangular shapes.
Pull Boxes: Used to facilitate wire pulling in long conduit runs.
Device Boxes: Such as gang boxes, accommodate outlets, switches, and other fixtures.
Bushings and Caps
Bushings: Protect conductor insulation from abrasion at conduit ends.
End Caps: Seal unused conduit ends to prevent ingress of debris or moisture.
Straps and Clamps
Secure conduit runs to walls, ceilings, or other surfaces.
材料: Corrosion-resistant plastic or metal; must support conduit without causing deformation.
Conduit Bodies (Type LB, LL, LR, T, etc.)
Provide access to wiring for pulling, splicing, or inspection.
Conduit bodies must be clearly marked and listed for use with PVC systems.
Material and Compatibility
All fittings used with Schedule 40 PVC conduit must:
- Be UL Listed or CSA Certified, depending on local code.
- Be made from compatible PVC material to ensure uniform thermal and mechanical behavior.
- Support the conduit size and Schedule 40 wall thickness (although many are also compatible with Schedule 80).
Joining Methods
Schedule 40 PVC conduit and fittings are typically joined using:
Solvent Welding: A chemical bond formed by applying primer and cement to both the conduit and fitting surfaces. This creates a strong, watertight, and permanent connection.
Threaded or Mechanical Connections: Used with adapters or transition fittings to interface with metal conduit, boxes, or equipment.
Installation Considerations
Expansion Control: Use expansion fittings where temperature variations could lead to conduit movement.
Support: Install support straps within NEC specified distances (usually within 3 ft of boxes and every 3 or up to 8 ft for horizontal runs).
Weather Exposure: For outdoor applications, use fittings labeled as UV-resistant or sunlight-resistant.
密封: In wet or underground locations, ensure fittings and boxes are properly sealed against moisture ingress.
Schedule 40 PVC Conduit vs. Schedule 40 PVC Pipe

Although Schedule 40 PVC conduit and Schedule 40 PVC pipe look similar and even share the same outer diameter dimensions, they are not interchangeable and serve very different purposes. Understanding the key differences is essential for ensuring both code compliance and installation performance.
1. Application Purpose
40 号 PVC 导管 is specifically designed for electrical wiring systems. It protects electrical cables from moisture, chemical exposure, and mechanical damage.
40 号 PVC 管, on the other hand, is designed for plumbing systems, such as water supply, drainage, and irrigation.
2. Standards and Certifications
导管 is manufactured according to UL 651 or NEMA TC-2 standards, meeting NEC (National Electrical Code) requirements.
Pipe typically complies with ASTM D1785, ASTM D2665 and NSF standards for potable water or drain/waste/vent (DWV) applications.
3. Wall Thickness and Strength
- While both have the same nominal Schedule 40 wall thickness, conduits are optimized for pull strength and easier wire pulling rather than water pressure.
- Pipes are pressure-rated for hydraulic performance and durability under sustained fluid flow.
4. Sunlight Resistance
Electrical conduit is often made with UV-resistant additives, making it suitable for outdoor exposed applications.
Plumbing pipe is not always UV-rated and can degrade over time if installed in direct sunlight without protection.
5. Fittings and Connections
Conduit fittings are designed to accommodate wiring systems and are generally solvent-welded or threaded. They may also have special features to prevent water ingress.
Pipe fittings are designed for fluid-tight seals and may include pressure-rated couplings, tees, and elbows specific to plumbing.
6. Fire Performance and Color
- Schedule 40 PVC conduit is often gray in color and must meet flame and smoke performance requirements for electrical applications.
- Schedule 40 PVC pipe is usually white, and fire resistance is not a standard requirement for plumbing systems.
Using PVC pipe in place of conduit for electrical installations is not permitted by the NEC. Doing so can result in code violations, safety hazards, and potential system failure.
Summary Table
特征 | 40 号 PVC 导管 | 40 号 PVC 管 |
目的 | 电气线路保护 | Water/fluid transport |
标准 | UL 651, NEMA TC-2 | ASTM D1785, ASTM D2665, NSF |
抗紫外线 | Often UV-rated | Usually not UV-rated |
Pressure Rating | Not pressure-rated | Pressure-rated |
防火性能 | Must meet NEC, UL fire standards | 无需 |
配件 | Designed for wire pulling systems | Designed for hydraulic sealing |
颜色 | Gray | 白色的 |
While Schedule 40 PVC conduit and pipe may look alike, they serve entirely different roles. For safe, compliant, and long-lasting electrical installations, always use Schedule 40 PVC conduit in accordance with NEC requirements—never substitute it with standard plumbing pipe.
Schedule 40 vs. Schedule 80 PVC Conduit (5 Different)
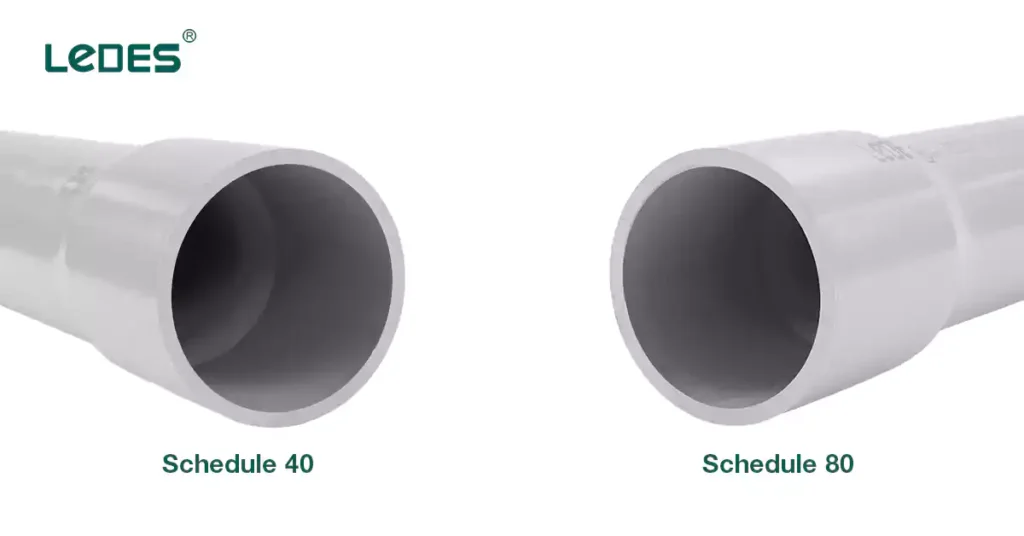

When choosing PVC conduit for an electrical installation, understanding the difference between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 is crucial. Both types are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial applications, but each has unique features, strengths, and code-specific uses. Below is a comprehensive comparison to help you select the right conduit for your project.
1. 壁厚和强度
- Schedule 40 PVC Conduit has thinner walls, making it lighter and easier to handle and cut. It is ideal for above-ground or underground installations in areas where physical damage is unlikely.
- Schedule 80 PVC Conduit has thicker walls, offering greater mechanical strength and resistance to impact. This makes it better suited for environments with potential for physical damage or high traffic, such as exposed installations in industrial areas.
Inner Diameter (ID)
The outer diameter of both Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 conduit is the same, ensuring compatibility with fittings.
However, due to its thicker wall, Schedule 80 has a smaller inner diameter, which reduces wire-pulling space and can affect conduit fill calculations.
2. Fire and UV Resistance
Both Schedule 40 and 80 conduits are available with UV-resistant formulations and must meet NEC flame performance requirements.
Neither is inherently flameproof like metallic conduit, but they are self-extinguishing and designed to resist spreading flames.
3. Chemical and Corrosive Resistance
Both types are nonmetallic and corrosion-resistant, making them suitable for chemical environments.
Schedule 80 is often preferred in more aggressive or corrosive locations due to its added thickness and toughness.
4. Use in Physical Damage Areas
According to NEC 352.10(K), Schedule 80 must be used “where subject to physical damage,” such as:
Exposed outdoor installations
Warehouses or factory floors
Locations with frequent equipment movement
5. Weight and Installation
Schedule 40 is easier to work with due to its lightweight and flexibility, reducing labor costs for large installations.
Schedule 80, while stronger, is heavier and more rigid, which can require more effort to cut, bend, and secure.
Comparison Table
特征 | 40 号 PVC 导管 | 80 号 PVC 导管 |
标准 | UL 651, NEMA TC-2 | UL 651, NEMA TC-2 |
壁厚 | 更薄 | 更厚 |
重量 | 打火机 | 更重 |
Inner Diameter | Larger (more wire space) | Smaller (less wire space) |
机械强度 | 缓和 | 高的 |
成本 | 降低 | 更高 |
安装 | Easier to cut and bend | Harder to work with |
Choosing between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC conduit comes down to the environment and application demands. For most standard electrical work, Schedule 40 is sufficient. However, when installation sites demand higher impact resistance or face harsher conditions, Schedule 80 is the safer and code-compliant choice.
Ledes Schedule 40 PVC Conduit Solutions

As a professional electrical conduit products manufacturer, Ledes offers a premium line of Schedule 40 PVC conduit solutions designed to meet the demands of residential, commercial, industrial, and infrastructure projects. Built for durability, easy installation, and environmental resistance, Ledes Schedule 40 PVC conduits are trusted by electricians and contractors worldwide.
Product Features
- Standard Trade Sizes: 1/2″ through 6″ available.
- Bell-end design for easy solvent-welding installation.
- High impact resistance 和 crush strength for tough environments.
- Smooth inner wall for easy cable pulling and reduced friction.
Engineered to Perform
Ledes Schedule 40 PVC conduit is manufactured from high-quality, rigid polyvinyl chloride (PVC) materials that are:
- 耐腐蚀, ideal for use in wet, damp, and underground environments.
- 非导电, ensuring safe isolation of electrical conductors.
- UV-resistant, with added stabilizers for superior outdoor performance.
- Fire-retardant, formulated to meet UL 651 standards for flame resistance.
Code-Compliant and Certified
Ledes conduits are rigorously tested to comply with international and regional standards:
- UL 651 认证 for rigid PVC conduit and fittings.
- NEMA TC-2 compliant, meeting dimensional and performance specifications.
- Compliant with NEC 第 352 条 for rigid PVC conduit use.
Comprehensive Conduit Systems
Ledes doesn’t just stop at conduit. To provide a full installation solution, they offer:
- Compatible Schedule 40 fittings, including couplings, elbows, adapters, boxes, and more.
- Custom lengths and packaging options for large-scale projects or distribution.
为何选择 Ledes?
Choosing Ledes means choosing:
Certified quality
Proven performance
Global availability
Expert technical support
Whether you’re wiring a new home, upgrading a commercial facility, or building infrastructure for the future, Ledes Schedule 40 PVC conduit solutions offer the reliability and compliance your project demands.
PVC Conduit Buying Guide and Expert Advice
Choosing the right Schedule 40 PVC conduit isn’t just about picking a size—it involves evaluating compliance, compatibility, project needs, and supplier reliability. This guide breaks down what to consider before making a purchase, ensuring you get the right product for your electrical infrastructure.
8 Key Considerations Before Buying
1. Conduit Size (Diameter)
Choose the correct nominal trade size (e.g., ½”, ¾”, 1″, 2″) based on the number and type of conductors.
Follow NEC conduit fill tables and ensure adequate space for pulling and heat dissipation.
2. Wall Thickness
Ensure it’s Schedule 40 wall thickness as required—provides the appropriate strength for most residential and light commercial applications.
For areas subject to physical damage, consider upgrading to Schedule 80.
3. Compliance with Standards
Verify that the conduit is UL Listed (UL 651) or CSA certified, and meets NEC Article 352.
Check compliance with regional standards if outside North America
4. Material Quality
Use high-quality, virgin or certified reprocessed PVC materials.
Look for chemical resistance, UV resistance (if exposed outdoors), and heat tolerance.
5. Project Quantity Estimation
Calculate the total linear footage needed, including extra length for bends and waste.
Don’t forget accessories like couplings, adapters, and boxes.
6. Fittings Compatibility
Ensure fittings (elbows, adapters, boxes) are listed for use with Schedule 40 PVC conduit.
7. Transportation and Handling
Plan for safe transportation—PVC can be damaged by improper loading or impact.
Store in a dry, shaded area to prevent UV degradation and warping.
8. Reputable Brands and Manufacturers
Choose products from well-established manufacturers with quality control, technical documentation, and support.
Consider availability of compatible accessories and fittings.
Expert Advice
Tip 1: Don’t Mix Pipe and Conduit
Even if Schedule 40 PVC pipe and conduit look similar, PVC water pipe is not electrically rated. Use only UL-listed conduit for wire runs.
Tip 2: Plan for Expansion
PVC expands and contracts with temperature changes. Use expansion couplings in long runs, especially outdoors.
Tip 3: Use Primer and Solvent Cement for Watertight Seals
In wet or underground environments, follow best practices for gluing joints. Allow cure time before burial or pulling wires.
Tip 4: Match Temperature Ratings
Conductors must not exceed the maximum temperature rating of the PVC conduit—typically 90°C (194°F).
结论
Schedule 40 PVC conduit stands out as one of the most widely used electrical conduit solutions in both residential and commercial applications. Its blend of durability, corrosion resistance, ease of installation, and cost-effectiveness makes it a trusted choice for protecting electrical wiring across a variety of environments—from underground systems to interior walls and exposed outdoor runs.
Throughout this guide, we’ve explored its core features, relevant NEC code permissions, manufacturing processes, fittings, and comparisons with other types like Schedule 80 and standard PVC pipe. We’ve also covered essential buying tips and practical installation guidelines to help ensure your project is both safe and compliant.
As with any electrical infrastructure product, choosing the right conduit involves more than just picking a size—it’s about understanding performance needs, environmental conditions, and code requirements. Whether you’re a contractor, builder, or engineer, Schedule 40 PVC conduit offers a flexible, reliable solution that continues to evolve with modern building demands.
常见问题解答
Schedule 40 PVC 导管用于什么?
40号PVC导管主要用于住宅、商业和工业应用中的电线保护和布线。它适用于地上和地下安装,包括墙体、天花板、地板、直埋和混凝土包覆。与兼容配件配合使用时,它还适用于潮湿和腐蚀性环境。
40 号 PVC 管道的用途是什么?
40号PVC管通常用于管道应用,例如饮用水分配、灌溉和排水系统。虽然它看起来与导管相似,但它设计用于流体输送,不适用于电气用途。
40 号 PVC 可以埋入地下吗?
是的,Schedule 40 PVC 导管经批准可用于直埋或嵌入混凝土,前提是其安装符合 NEC 第 352 条和当地规范。但是,在易受物理损坏的区域,可能需要使用 Schedule 80。
PVC 导管在混凝土下应埋多深?
一般来说,非金属导管需要埋深24英寸(约60厘米),如果在商业或工业环境中的混凝土板下,通常必须埋深至少18英寸(约45厘米)。埋深要求可能因电压、位置和交通负荷而异,因此请务必咨询当地法规官员。
可以混合 Schedule 40 和 Schedule 80 PVC 吗?
是的,Schedule 40 和 80 PVC 导管可以使用标准配件连接,因为两种导管的外径相同。然而,它们的壁厚和强度等级不同,因此混合使用时应谨慎,通常仅在不同防护要求的区域之间过渡时才使用。
可以使用 Schedule 40 PVC 进行电线布线吗?
电气安装仅可使用 40 号 PVC 导管(标有电气用途标识)。普通的 40 号 PVC 管道不能替代管道,因为它不符合电气规范的阻燃和防烟要求。
如何弯曲 Schedule 40 PVC 导管?
Schedule 40 PVC 导管可以使用热源(例如热风枪或专用 PVC 加热毯)进行弯曲。软化后,可以使用弯曲模具或导轨进行定型。必须将其冷却到位才能保持形状。但应避免过热。
Schedule 40 PVC 导管的使用寿命是多久?
如果正确安装并防止极端紫外线照射或机械损伤,Schedule 40 PVC 导管的使用寿命可达 50 年或更长时间。其耐腐蚀、防潮和耐化学腐蚀性能使其在大多数环境中都具有极高的耐用性。
白色PVC和灰色PVC有什么区别?
White PVC is typically used for plumbing and water systems and is not rated for electrical use.
Grey PVC is specifically manufactured for electrical applications, is UV-resistant, and complies with UL and NEC requirements for flame retardance and insulation.




