
Table of Contents
In modern electrical infrastructure, durability and safety are non-negotiable. That’s where Schedule 80 PVC conduit comes in. Known for its thick walls and high impact resistance, Schedule 80 conduit is a go-to choice for demanding environments where mechanical protection is critical. Whether referred to as schedule 80 electrical conduit, sch 80 conduit, or schedule 80 PVC electrical conduit, this material stands out for its robust performance across industrial, commercial, and utility applications.
In this article, we’ll explore the purpose of Schedule 80 PVC conduit, its available sizes, how it meets key code compliance requirements and installations. If you’re designing or installing electrical systems that demand extra protection, understanding the advantages of sch 80 PVC conduit can help ensure long-term system reliability and safety.
What is Schedule 80 PVC Conduit?

Definition
Schedule 80 PVC conduit, commonly labeled as sch 80 PVC conduit, schedule 80 electrical conduit, SCH 80 or Sch 80 PVC conduit. It is a type of nonmetallic raceway made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) that specifically designed for high-stress environments. The “Schedule 80” term refers to the wall thickness of the conduit, not the physical size of the conduit or its pressure capacity, which are sometimes confused.
Compared to Schedule 40, Schedule 80 conduit features a significantly thicker wall, providing greater impact resistance, crush resistance, and mechanical strength. This structural upgrade makes it a preferred choice for environments where the conduit is subject to physical abuse or where enhanced protection is required for critical electrical systems.
The Role of SCH 80 PVC Conduit
The primary function of Schedule 80 PVC electrical conduit is twofold:
Mechanical Protection
- It shields electrical wires and cables from physical hazards such as impact, crushing, and environmental stresses (UV exposure, corrosion, vibration, etc.). It’s particularly valuable in:
- Industrial facilities
- Outdoor installations
- Underground wiring systems
- High-traffic or heavy-equipment zones
Efficient Wire Routing
As a rigid raceway, it offers a reliable and code-compliant pathway for running and pulling conductors, simplifying wire replacement and inspection during future maintenance or upgrades.
When conduit is exposed to mechanical risk and high stress, the durability of Schedule 80 conduit becomes a necessity, not an option. Its thicker wall helps comply with National Electrical Code rules regarding protection against physical damage.
Pro Tips: Want to learn more about electrical raceways and how to choose the right one? You can read this comprehensive guide to the electrical raceway to learn more.
SCH 80 PVC Conduit Sizes and Dimensions
Schedule 80 PVC conduit is available in a wide range of sizes to accommodate various wiring demands, from light residential circuits to complex industrial systems. Understanding the available sizes and specifications is essential for selecting the right conduit size for your project.
Trade Size (Inch) | Metric Designator (mm) |
1/2 | 16 |
3/4 | 21 |
1 | 27 |
1-1/4 | 35 |
1-1/2 | 41 |
2 | 53 |
2-1/2 | 63 |
3 | 78 |
3-1/2 | 91 |
4 | 103 |
5 | 129 |
6 | 155 |
These are nominal trade sizes, and the actual outer diameter (OD) is the same as that of Schedule This wide selection allows contractors and engineers to select the most suitable size for specific conductor quantities, environmental conditions, and installation locations.
Outer Diameter Consistency of Sch 80 Conduit
The outer diameter (OD) of Schedule 80 PVC conduit is the same as that of Schedule 40 conduit of the same nominal size. This ensures compatibility with standard fittings and accessories across conduit types. However, due to the thicker wall of Schedule 80, the inner diameter (ID) is smaller, which affects internal capacity.
Dimensions and Wall Thickness of Sch 80 Conduit
According to UL651, the dimensions of SCH 80 PVC conduit are as follows:
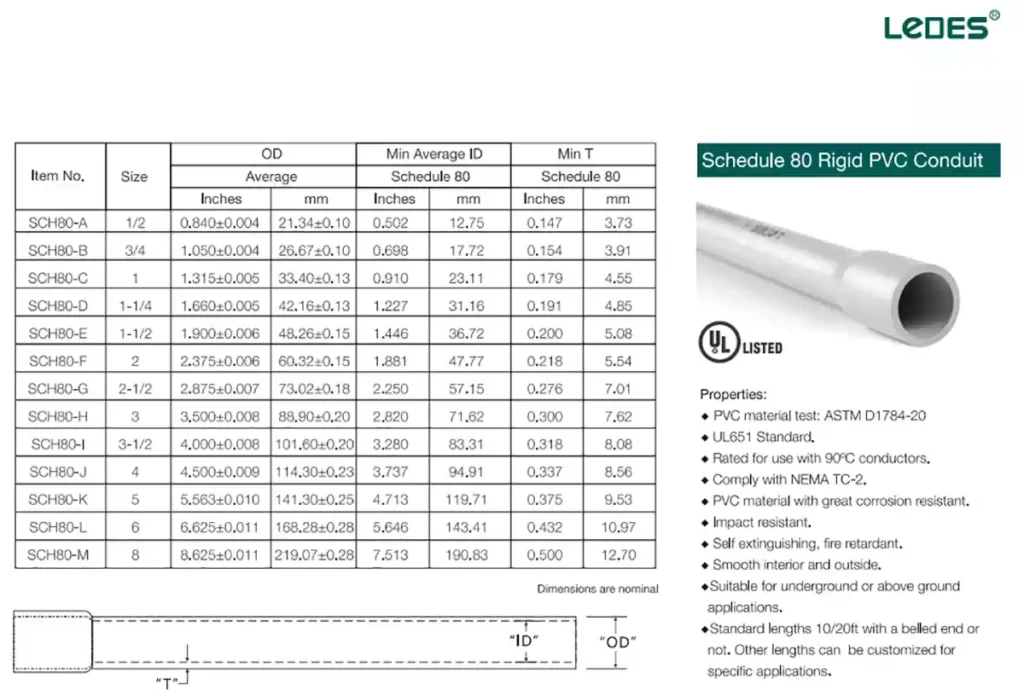
Smaller sizes (½” to 1″) are frequently used in residential and light commercial installations, while larger sizes (2″ and above) are often seen in industrial, utility, or infrastructure projects, where larger conductor bundles or higher levels of physical protection are required.
Length and Configuration of Sch 80 Conduit
Most Schedule 80 PVC electrical conduit is supplied in:
- 10 feet or 20 feet lengths as standard
- With one end plain and the other bell-end for solvent welding joining, or both ends in plain.
Conduits can be bent with heat (could be hard due to thick walls) or joined with PVC elbows, couplings, and fittings, which are also rated for Schedule 80 wall thickness.
Pros and Cons of Schedule 80 PVC Conduit

Schedule 80 PVC electrical conduit is known for its enhanced durability and protection capabilities, especially in environments where mechanical impact or exposure to harsh elements is a concern. However, as with any conduit type, it comes with both benefits and trade-offs. Understanding these advantages and disadvantages helps engineers, contractors, and electricians make informed choices for each application.
Schedule 80 PVC Conduit Advantages
Thicker Wall for Greater Strength
The most prominent feature of SCH 80 PVC conduit is its thicker wall compared to Schedule 40, which results in:
- Improved resistance to physical impact
- Higher compression strength
- Better protection against crushing or deformation in buried or exposed applications
This makes it ideal for demanding installations like industrial plants, utility substations, or direct burial in high-traffic zones.
Enhanced Protection in Harsh Environments
Due to its robust wall structure, SCH 80 offers better protection for electrical wires and cables against:
- Mechanical abrasion
- Accidental puncture
- Rodents or debris in underground installations
It is frequently used in outdoor and corrosive environments, especially when conduit integrity is critical.
Long-Term Durability and Corrosion Resistance
As with all PVC conduits, SCH 80 is non-metallic and corrosion-resistant, making it suitable for:
- Moist or corrosive environments
- Chemical plants or wastewater facilities
- Marine or coastal installations
Its added thickness further extends its life cycle in aggressive settings.
UV Resistance (with Additives)
Most manufacturers offer Schedule 80 conduits with UV-resistant formulations, making them suitable for extended outdoor use when exposed to sunlight.
Schedule 80 PVC Conduit Disadvantages
Reduced Internal Space (Smaller ID)
The thicker wall of SCH 80 reduces its internal diameter, resulting in:
- Less space for conductors
- Potentially higher conduit size requirements for the same wire count compared to Schedule 40
- More frequent fill calculations to ensure code compliance
This can be a limitation in space-constrained designs or projects aiming to minimize material volume.
Increased Weight and Harder for Installation
Schedule 80 conduit is heavier and less flexible, which can lead to:
- More difficult handling during installation
- Greater labor or equipment needs, especially for large-diameter conduits
- Higher shipping and transport costs
Higher Material Costs
Due to its increased wall thickness and resin content, SCH 80:
- Costs more per foot than Schedule 40 or DB-rated conduit
- Might impact project budgets for large-scale installations if not absolutely necessary
Understanding these pros and cons allows professionals to determine when Schedule 80 PVC conduit is the best choice, not just based on strength, but also on project efficiency and cost.
Sch 80 PVC Conduit Code Compliance
Schedule 80 PVC conduit is widely used in electrical systems where enhanced mechanical protection is required. To ensure safety, performance, and regulatory compliance, this type of conduit must meet several industry standards. The most relevant are UL 651, ASTM D1784, and the National Electrical Code (NEC). This section breaks down each of these in detail, with a focus on how they apply specifically to Schedule 80 conduit.
ASTM D 1784: PVC Compound Material Classification
ASTM D1784 is the standard specification that governs the physical and mechanical properties of the polyvinyl chloride (PVC) compound used in manufacturing Schedule 80 rigid PVC conduit. This specification ensures that the material can perform reliably under mechanical, thermal, and electrical stress over time.
Required Cell Classification of SCH 80
According to UL651, the compound of Schedule 80 PVC conduit must have cell class equal to or greater than 12123, ensuing minimum thresholds in five property categories:
Property Category | What It Describes |
Base Resin | Type of PVC resin used (e.g., homopolymer or copolymer) |
Impact Strength | Resistance to sudden force or impact (lzod impact value) |
Tensile Strength | Maximum stress the material can withstand when stretched, indicates structural strength under pulling forces. |
Modulus of Elasticity | Flexibility or stiffness of the material, reflects rigidity |
Deflection Temperature Under Load (DTUL) | Temperature at which material deforms under a load, important for high-temperature installations |
These characteristics are critical for ensuring long-term performance of rigid conduits in both indoor and outdoor electrical systems, especially where higher mechanical strength is necessary.
Why ASTM D1784 Matters
Compliance with ASTM D1784 helps manufacturers and specifiers ensure that:
- The PVC compound is rigid, durable, and weather-resistant
- The material performs reliably across a wide temperature range
- The conduit maintains structural integrity under mechanical load
- The product can meet UL 651 testing without failure
In essence, ASTM D1784 forms the material foundation upon which performance standards like UL 651 and installation standards like the NEC are built.
UL651: Safety Standard for Rigid PVC Conduit and Fittings
UL 651 is the principal standard for both Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC conduit. Since Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 share most of the same test criteria, we’ll briefly summarize the key points here. For a detailed review of UL 651 testing, see our article of introducing Schedule 40 PVC Conduit.
UL 651 Test Requirements
Both Schedule 40 and 80 rigid PVC conduits must meet the following performance criteria, detailed testing method and requirements, check on the previous article of Schedule 40 conduit introduction:
Requirements | Description |
Tensile Strength | Must meet a minimum of 5,000 psi, ensuring adequate resistance to pulling forces. |
Extrusion Quality | PVC must be uniformly extruded, free from cracks, blisters, or voids to maintain structural integrity. |
Low-Temperature Handling | Conduit is tested for flexibility and durability at low temperatures to avoid brittleness and cracking. |
Water Absorption Resistance | Material must resist absorbing water, ensuring long-term mechanical and dielectric performance. |
Deflection Under Load | Assesses how much the conduit deforms under mechanical load, simulating real-world stresses. |
Flame Resistance | Tested to ensure the conduit self-extinguishes and limits flame spread per UL safety standards. |
Resistance to Specified Reagents | Conduit must resist degradation when exposed to chemicals like acids and oils, suitable for industrial use. |
Sunlight Resistance | To be suitable for outdoor and exposed environments, the Schedule 80 should made of UV-resistant formulations to pass the UV-resistant test. |
Rated for 90°C Conductors | Certified for use with conductors rated up to 90°C, suitable for modern electrical wiring loads. |
Schedule 80 Vs Schedule 40 Codnuit Specific Differences
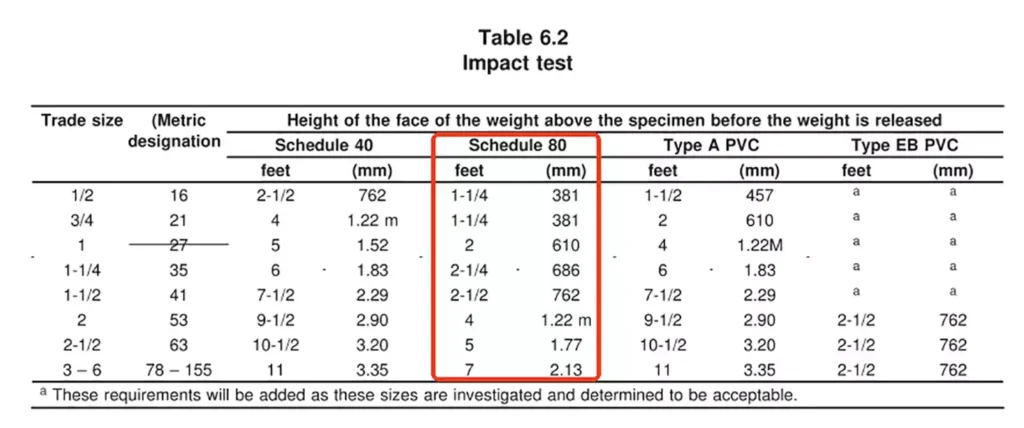
While many test methods are identical to those for Schedule 40, UL 651 specifies stricter mechanical requirements for Schedule 80 conduit in two main areas:
- Impact Resistance:
Schedule 40 PVC Conduit: 20 lb (9.7 kg) weight, 2 in (51 mm) diameter cylinder
Schedule 80 PVC Conduit: 75 lb (34 kg) weight, 6 in (150 mm) diameter cylinder
Drop height varies by size, as defined in Table 6.2 of UL 651.
- Crush Resistance:
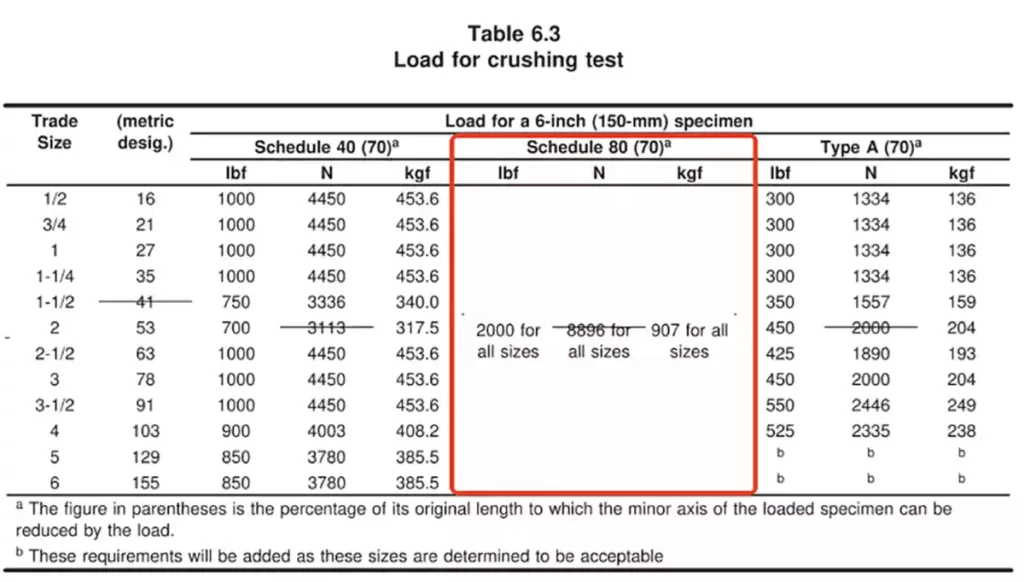
Same testing method as Schedule 40, but higher load requirements, as listed in Table 6.3 of UL 651.
These enhancements ensure that Schedule 80 conduit is more robust and suitable for applications with increased mechanical stress.
National Electrical Code (NEC) - Article 352
The National Electrical Code (NEC) is the governing document for electrical installations in the United States. Article 352 specifically addresses Rigid Polyvinyl Chloride Conduit (PVC).
352.10(K) - Use Where Exposed to Physical Damage
NEC mandates that Schedule 80 must be used in locations where the conduit is “subject to physical damage.” Such as areas in commercial or industrial settings with heavy equipment traffic.
352.12 - Uses Not Permitted
PVC conduit (both SCH 40 and 80) cannot be used in hazardous locations or areas subject to ambient temperatures that excess of 50°C unless listed or properly protected.
353.22 - Number of Conductors
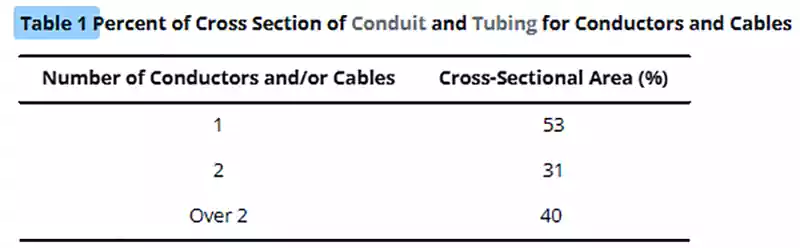
The allowable number of conductors in a conduit is determined by Table 1 in Chapter 9 and the conduit’s internal space, which is smaller in Sch 80 than in Sch 40. This results in reduced cable fill capacity for the same nominal size.
Annex C - Conduit Fill
Conduit fill refers to the amount of space inside a conduit that is occupied by electrical conductors. Proper conduit fill is essential to ensure safe heat dissipation, ease of conductor installation, and long-term system reliability.
Annex C Table C.10(A) provides conductor fill charts for Schedule 80 PVC conduit.
Type | Trade Size (Metric Designator) | |||||||||||||
3/8 | 1/2 | 3/4 | 1 | 11/4 | 11/2 | 2 | 21/2 | 3 | 31/2 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
CONDUCTORS | ||||||||||||||
RHH, RHW, RHW-2 | 14 | — | 3 | 5 | 9 | 17 | 23 | 39 | 56 | 88 | 118 | 153 | 243 | 349 |
12 | — | 2 | 4 | 7 | 14 | 19 | 32 | 46 | 73 | 98 | 127 | 202 | 290 | |
10 | — | 1 | 3 | 6 | 11 | 15 | 26 | 37 | 59 | 79 | 103 | 163 | 234 | |
8 | — | 1 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 8 | 13 | 19 | 31 | 41 | 54 | 85 | 122 | |
6 | — | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 11 | 16 | 24 | 33 | 43 | 68 | 98 | |
4 | — | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 12 | 19 | 26 | 33 | 53 | 77 | |
3 | — | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 11 | 17 | 23 | 29 | 47 | 67 | |
2 | — | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 9 | 14 | 20 | 25 | 41 | 58 | |
1 | — | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 9 | 13 | 17 | 27 | 38 | |
1/0 | — | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 11 | 15 | 23 | 33 | |
2/0 | — | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 10 | 13 | 20 | 29 | |
3/0 | — | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 11 | 17 | 25 | |
4/0 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 15 | 21 | |
250 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 11 | 16 | |
300 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 10 | 14 | |
350 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 9 | 13 | |
400 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 8 | 12 | |
500 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 10 | |
600 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 8 | |
700 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | |
750 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | |
800 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 7 | |
900 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 6 | |
1000 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 | |
1250 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | |
1500 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | |
1750 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
2000 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | |
352.44(A)- Thermal Expansion and Contraction
When installed in environments with wide temperature swings, expansion fittings may be required to comply with NEC guidelines Table 352.44(A) and prevent conduit stress or deformation.
By ensuring compliance with UL, ASTM, and NEC standards, Schedule 80 PVC conduit offers a highly reliable and code-approved solution for demanding electrical environments.
NEMA TC 2: Requirements for Electrical PVC Conduit
NEMA TC-2, established by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), outlines the specifications for rigid polyvinyl chloride (PVC) conduit used in electrical systems. Schedule 80 PVC conduit, known for its thicker walls and higher mechanical strength, must meet the criteria defined in this standard to ensure consistent quality, performance, and safety across a wide range of applications.
NEMA TC-2 covers key aspects such as:
Material Composition
Ensures the use of virgin or quality reprocessed PVC compound with reliable insulating and mechanical properties.
Dimensional Consistency
Defines the outer diameter, wall thickness, and length tolerances to ensure compatibility with standard fittings and uniform performance.
Color
Schedule 80 rigid PVC conduit should be gray in color, other colors mat acceptable if agreed to third parties involved.
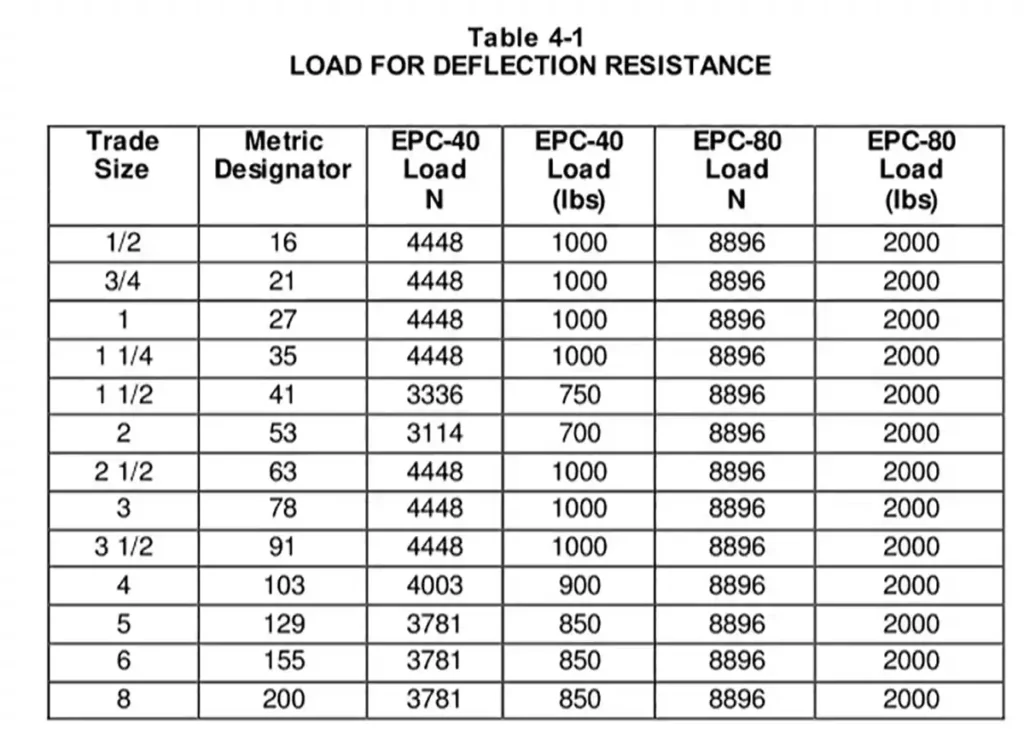
Deflection Test
To verify the conduit’s ability to withstand compression and return to near-original shape.
he conduit is compressed at a uniform rate using rigid steel plates.
The inside diameter must retain at least 70% of its original size under the specified load (as per Table 4-1 of the standard).
Leakage at Solvent-Cemented Joints
To confirm the water-tightness of bonded conduit joints under pressure.
Solvent-cemented joints are subjected to water pressure testing.
Joints must withstand 25 psi (172.4 kPa) for one hour without leaking.
Flattening
To assess the conduit’s resistance to crushing or cracking under compressive load.
The conduit is compressed between flat plates to 40% of its original outer diameter.
No splitting or tearing is permitted through the wall during or after compression.
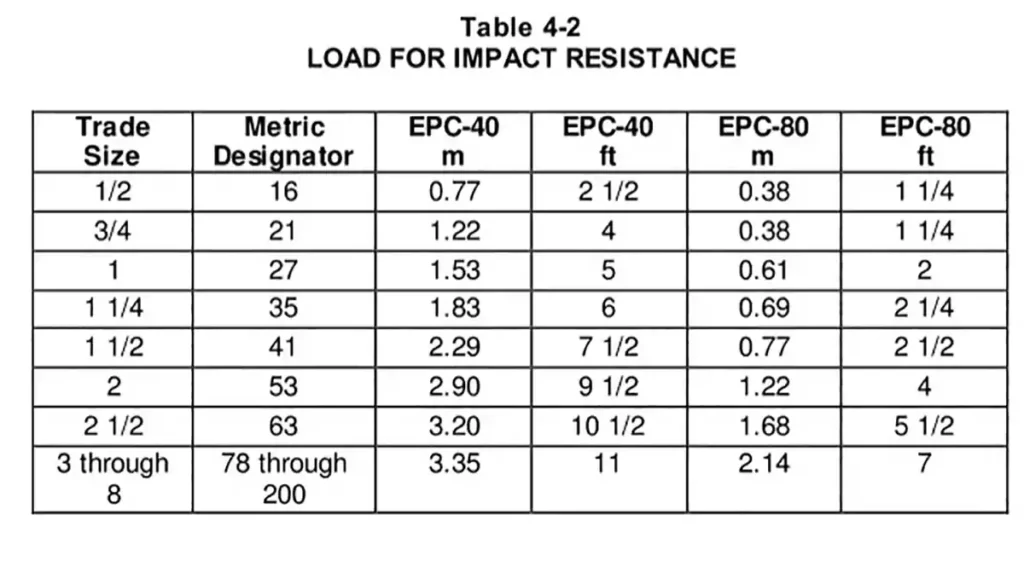
Impact Resistance
To evaluate the conduit’s toughness and ability to resist fracture from external impacts.
A 75 lb ± 12 oz weight (same as UL651) is dropped onto the conduit supported over a steel base.
A minimum of 7 out of 10 tested samples must show no cracks or tears upon inspection.
The weight drop heights are as specified in Table 4-2:
Marking Requirements for Sch 80 PVC Conduit
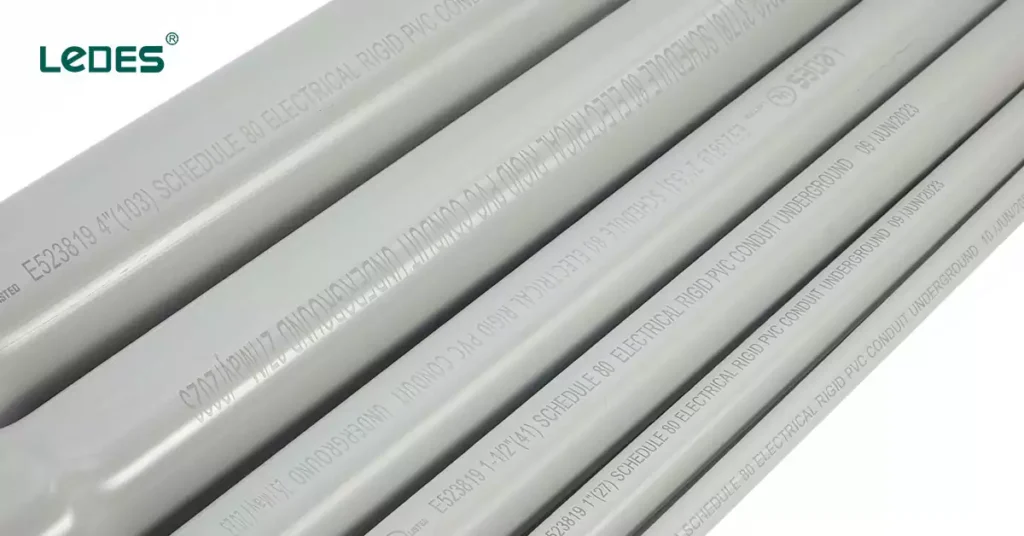

Proper marking on Schedule 80 PVC conduit is essential for product identification, code compliance, and safe installation. These markings are governed primarily by UL 651 and ensure that users can easily verify key specifications such as product type, manufacturer, and suitability for certain applications.
Key Marking Elements Required:
- Manufacturer’s Name or Trademark
- Trade size of the conduit
- Product Type “Schedule 80 Electrical Rigid PVC Conduit”
- Standard Compliance: such as UL651 Listed
- Date of manufacture
- SUNLIGHT RESISTANT or MAX 90°C WIRE if rated
Importance of Proper Marking
Proper markings on Schedule 80 PVC conduit serve multiple purposes:
- Field Verification by electricians and inspectors.
- Compliance Checks during project approval or inspection stages.
- Warranty Validation and manufacturing traceability.
Failure to include or follow these marking requirements may result in installation rejection by code enforcement or inspectors and may impact system reliability or safety.
7 Applications of Schedule 80 PVC Conduit
Schedule 80 PVC conduit is engineered for demanding environments that require both electrical protection and mechanical durability. Due to its thicker wall construction compared to Schedule 40, it is often the conduit of choice for industrial, commercial, and high-impact installations.
Below are the common application scenarios where Schedule 80 PVC electrical conduit (Sch 80 PVC conduit) is preferred or required:
1. Exposed Above-Ground Installations
In environments where conduit is exposed to potential impact, such as in warehouses, mechanical rooms, or outdoor industrial areas, Schedule 80’s thicker walls offer superior protection against:
Physical damage
Accidental impact from vehicles or tools
Vandalism
2. Underground Installations
While both Schedule 40 and DB-rated ducts are commonly used for underground wiring, Schedule 80 is often specified in areas where:
Soil pressure is high (e.g., under roads or driveways)
There’s potential for heavy loading above ground
The installation depth is shallow and lacks external reinforcement
Its high crush strength and impact resistance make it reliable in critical underground raceway systems.
3. Corrosive Environments
Thanks to the inherent chemical resistance of PVC material, Schedule 80 conduit is suitable for environments exposed to:
Salt air (coastal facilities)
Chemicals and acids (chemical processing plants)
Wastewater treatment plants
Agricultural or fertilizer-handling areas
Unlike metallic conduit, PVC does not corrode or rust, making it ideal for long-term durability.
4. Hazardous Locations (when allowed)
In classified hazardous locations, non-metallic conduit systems like Schedule 80 can be used if:
Properly sealed
Approved by the Authority Having Jurisdiction (AHJ)
Installed in compliance with the NEC and any applicable UL-listed fittings
Always confirm with local electrical codes.
5. Industrial and Manufacturing Facilities
Factories and heavy-duty environments often contain machinery and operational hazards. Schedule 80 conduit is used to:
Route power to motors and control panels
Protect communication wiring or fiber optics
Maintain clean wire paths in production lines
Its high tensile strength and impact resistance reduce downtime caused by conduit damage.
6. Institutional and Commercial Buildings
In public or commercial spaces such as:
Hospitals
Schools
Stadiums
Utility rooms
Schedule 80 is installed where additional conduit protection is required due to high foot traffic or maintenance equipment access.
7. Renewable Energy and Utility Projects
In solar and wind energy systems, particularly in utility-scale installations:
Conduits are exposed to UV, wind, and physical wear
Schedule 80 is often specified for exposed vertical runs and risers
Sunlight-resistant variants ensure long-term performance
Installation Guide for Sch 80 PVC Conduit (9 Steps)
Proper installation is essential to maximize the performance, safety, and code compliance of Schedule 80 PVC conduit (Sch 80 conduit). While its thicker wall provides superior durability, it also requires careful handling and preparation, especially in more demanding environments.
Notes: Read more about conduit installation tips, compliance requirements, and considerations in our Electrical Conduit Installation Expert Advice.
Here outlines the best practices and essential considerations for installing Schedule 80 electrical conduit in accordance with industry standards and the NEC.
1. Choosing the Right Conduit Size
Selecting the correct Schedule 80 PVC conduit size is crucial to ensuring a safe, efficient, and code-compliant electrical system. The size you choose depends on the following factors:
Project requirement
Number and type of conductors
Conductor fill capacity
2. Cutting and Deburring
Schedule 80’s thick walls require a bit more effort to cut than Schedule 40. So you better use a fine-toothed saw for cutting, conduit cutter can also be used for small size but could be hard.
3. Solvent Welding
PVC conduit sections are typically joined using solvent cement welding:
Clean both surfaces: inside the fitting and outside the conduit.
Apply primer to soften the plastic and improve adhesion (required for most code-compliant installs).
Apply solvent cement while the primer is still wet.
Insert the conduit into the fitting with a 1/4 twist to distribute the cement evenly.
Hold for 30 seconds, then allow proper curing (check cement manufacturer’s instructions).
4. Expansion and Contraction Management
PVC expands and contracts significantly with temperature changes.
For outdoor or long runs:
Use expansion fittings to accommodate movement (required when temperature variation exceeds 25°F/13.9°C).
Refer to NEC Table 352.44(A) for guidance on expansion fitting spacing.
5. Bending Conduit
Unlike ENT or flexible conduit, Schedule 80 PVC must be heat bent if custom angles are required:
But due to it’s thick wall, it’s not that easy for heat bending, factory-made elbows and sweeps are often recommended for consistency and code compliance.
6. Support and Securing
Schedule 80 conduit must be properly supported according to NEC 352.30:
Horizontal runs: Secure within 3 feet (0.91 m) of each box or fitting and at intervals not exceeding 10 feet (3.05 m).
Vertical runs: Use straps or clamps rated for PVC, considering expansion/contraction movement.
7. Underground Installation
Schedule 80 is ideal for direct burial without additional encasement. Installation must comply with:
NEC 300.5 for minimum burial depths
Soil compaction and backfill without sharp rocks or debris
Use of bushings to protect conductors at entry/exit points
8. Conduit Fill and Wire Pulling
Follow NEC Chapter 9, Table 1 and Annex C for conduit fill calculations.
Use fish tape to help the wire pulling and avoid pulling at high tension to prevent insulation damage.
9. Inspection
Check and ensure all installed conduit is properly supported, sealed, and compliant with applicable codes.
Installations are reviewed by the Authority Having Jurisdiction (AHJ) when required.
Each manufacturer may provide specific guidance based on their Schedule 80 product formulation and listings (e.g., temperature ratings, pressure resistance, fire performance). Always consult their documentation in addition to national codes.
Burial Depth for Sch 80 PVC Conduit
Schedule 80 PVC conduit is often used underground, when used underground, the burial depth mush comply with NEC Table 300.5, which outlines minimum cover requirements based on voltage, installation location, and protection level.
Location & Application | Minimum Burial Depth |
All locations not specified | 18 in. (450mm) |
In trench below 50mm thick concrete | 12 in. (300mm) |
Under a building | 0 |
Under streets, highways, roads | 24 in. (600mm) |
Under min. 102mm thick concrete slab with no vehicle traffic | 4 in. (100mm) |
In or under airport runways | 18 in. (450mm) |
Always verify with local code enforcement or utility provider as local amendments may require deeper installation or additional protection methods.
Schedule 80 vs. Schedule 40 PVC Conduit
Schedule 80 PVC conduit and Schedule 40 PVC conduit are two commonly used types of rigid nonmetallic conduit, each with different wall thicknesses, mechanical properties, and application focuses. Understanding their differences is essential for choosing the right one based on environmental conditions, load-bearing needs, and regulatory compliance.
Feature | Schedule 80 | Schedule 40 |
Wall Thickness | Thicker | Thinner |
Outside Diameter | Same as SCH 40 | Same as SCH 80 |
Inside Diameter | Smaller | Larger |
Conductor Fill Capacity | Lower | Higher |
Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
Cost | Higher | Lower |
Mechanical Strength | High | Lower |
Ease of Installation | Harder to cut and install | Easier to cut and install |
Typical Applications | Industrial, direct burial, exposed to physical damage | Residential, above-ground, light duty environments |
SCH 80 PVC Conduit vs. DB Conduit
When planning an underground installation, both Schedule 80 PVC conduit and DB conduits can be used, then which one to choose and what are their differences?
What Is DB Conduit?
“DB” stands for Direct Burial, and DB conduits are specifically designed for underground use. These conduits are not intended to be exposed above ground and are often used by power utilities and telecom companies. DB conduit is categorized by wall thickness ratings, such as:
- DB60 – Light-duty wall, used where minimal protection is acceptable.
- DB100 – Medium-duty wall, suitable for many utility applications.
- DB120 – Heavy-duty wall, but still thinner than Schedule 40 and 80.
They are manufactured to NEMA TC 6 & 8 standard.
Feature | Schedule 80 PVC Conduit | DB PVC Conduit |
Primary Use | Exposed or underground wiring subject to physical damage | Underground only – direct burial in trenches |
Wall Thickness | Thicker then SCH 40 and DB conduits | Thinner then SCH 40 and 80, even at DB120 rating |
Standard | UL 651 | NEMA TC 6 & 8 |
Mechanical Strength | High impact and crush resistance | Lower mechanical strength |
UN Resistance | Yes if rated, suitable for above-ground exposure | No, for underground use |
Bendability | Less flexible, more rigid | More flexible, easier to handle |
Cost | Higher (due to thicker wall and UL listing) | Lower (more economical for buried-only installations) |
When to Use
Use SCH 80 PVC Conduit for:
Above-ground runs
Underground runs exposed to physical damage
Harsh environments requiring added protection
Use DB Conduit (DB60/100/120) for:
Underground-only electrical and communication ducting
Long-distance trenching
Projects where cost efficiency and physical damage risk is low
Pro Tips: Still confused about the direct burial conduit type and code compliance? You can click the link above to read our newest guide.
Why Choose Schedule 80 PVC Conduit?
Among the various options available, Schedule 80 PVC conduit stands out as a top-tier choice when high mechanical strength and code compliance are essential. And why choose it over other alternatives?
Superior Wall Thickness and Strength
The most defining characteristic of Schedule 80 PVC conduit is its thicker wall, which provides:
- Greater impact resistance – ideal for locations prone to mechanical abuse, such as warehouses, garages, or commercial risers.
- Higher crush resistance – suitable for installations under roadways or in areas with potential soil pressure or heavy equipment traffic.
- Compliance with more demanding installation environments.
Code Compliance in High-Risk Areas
Schedule 80 PVC conduit is often required by the NEC and local authorities when wiring systems are:
Exposed to potential damage
Installed on posts, risers, or exterior walls
Transiting from underground to above-ground systems
Its UL 651 listing and robust test performance give inspectors and engineers confidence in its use for demanding applications.
Versatility Across Applications
Unlike DB conduit which is limited to underground use, Schedule 80 PVC conduit is suitable for:
Above-ground and underground installations
Indoor and outdoor environments
Wet, dry, and corrosive areas
Transition points in residential, commercial, industrial, and utility projects
Sunlight and Corrosion Resistance
Schedule 80 PVC conduit is designed for UV exposure and corrosive atmospheres:
Gray coloring includes UV inhibitors, allowing long-term outdoor installation without degradation.
Excellent chemical resistance makes it ideal for water treatment plants, agricultural facilities, or coastal regions.
Smooth Interior for Easier Pulling
Despite its thicker walls, Schedule 80 still offers:
A smooth bore that reduces friction
Easier wire pulling compared to metal conduit
Non-conductive material that eliminates the need for grounding in many cases
Broad Size Availability
Schedule 80 conduit is available in a wide range of diameters, from ½ inch to 6 inches, accommodating everything from branch circuits to large-scale service entrances. With matching fittings, couplings, boxes, and adapters, it supports end-to-end solutions in even the most complex wiring designs.
Cost-Effective Alternative to Metal
While more expensive than Schedule 40 or DB conduit, Schedule 80 is still significantly more affordable and easier to install than rigid metal conduit (RMC). It provides a high-performance and corrosion-proof alternative without the need for cutting oils, special tools, or grounding.
Specialized Schedule 80 PVC Conduit
While standard Schedule 80 PVC conduit is already a durable and versatile solution, but modern electrical systems, especially in solar energy and sensitive environments often demand more specialized materials.
Schedule 80 Solar Conduit
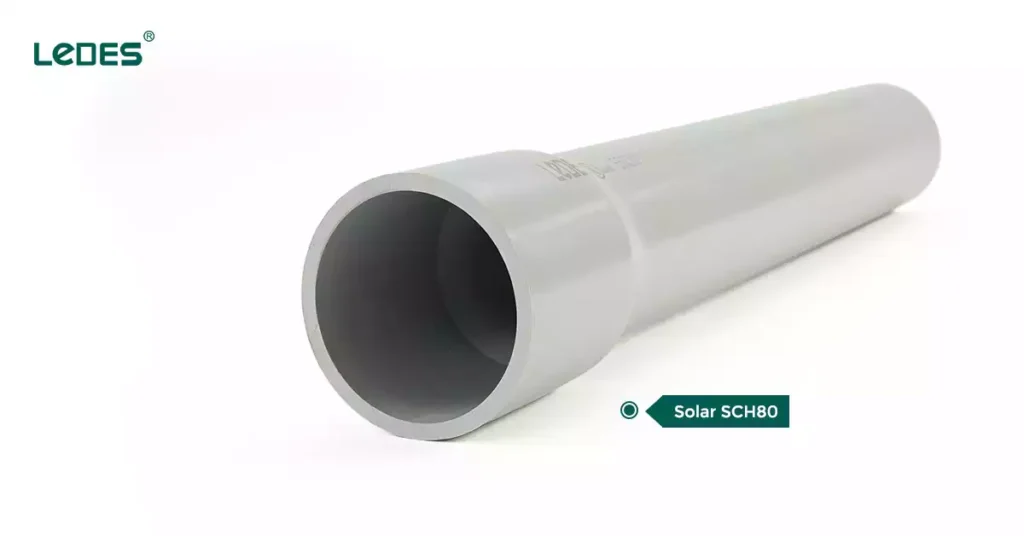

Solar installations, particularly those exposed to harsh environmental conditions, require conduits that can withstand:
- Intense UV exposure
- Wide temperature fluctuations
- Mechanical stresses from wind and other environmental factors
Schedule 80 solar conduits specifically designed for solar applications feature:
- Enhanced UV resistance: Tested for prolonged exposure to sunlight without degradation.
- High mechanical strength: Withstands outdoor harsh environments, ensuring durability under mechanical stress.
- Fire rating: Ensures self-extinguishing properties for added safety.
Such conduits are ideal for rooftop solar arrays, ground-mounted systems, and other installations where long-term durability and safety are paramount.
LSZH Schedule 80 Conduit
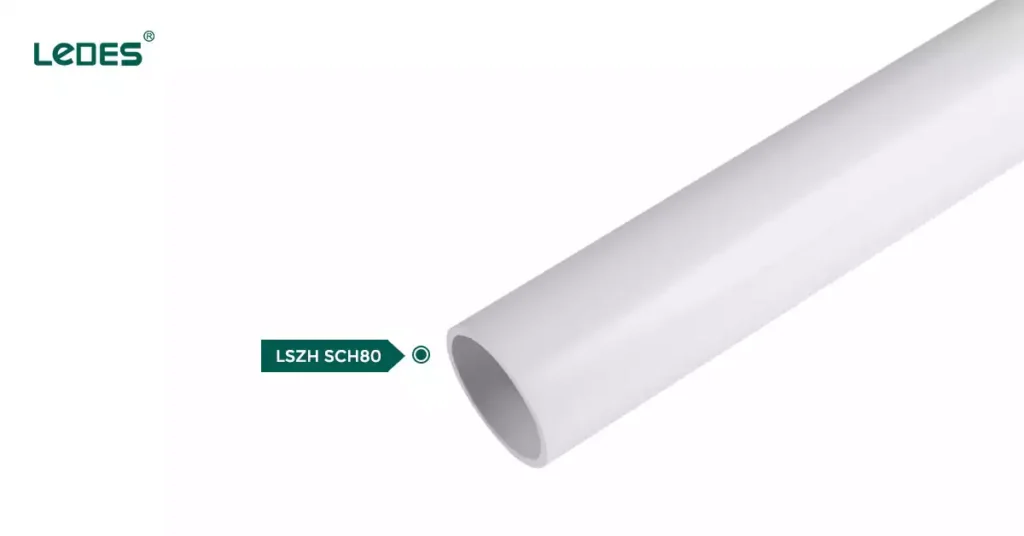

In settings like hospitals, data centers, tunnels, and transportation hubs, minimizing smoke and toxic emissions during a fire is crucial. Low Smoke Zero Halogen Sch 80 conduits address this need by:
- Reducing smoke emissions: Facilitates safer evacuation and reduces damage to equipment.
- Eliminating halogens: Prevents the release of toxic gases when exposed to fire.
- Maintaining mechanical strength: Offers tensile strength comparable to standard Schedule 80 conduits.
This type of SCH 80 is ideal for application where not only exposed to physical damage but also have strict fire safety requirement.
Trends in Schedule 80 PVC Conduit Use
As construction practices evolve and industries demand more resilient, sustainable, and safer infrastructure solutions, the use of Schedule 80 PVC conduit continues to adapt. Here are several key trends shaping its development and adoption:
1. Rising Demand in Renewable Energy Projects
With the global shift toward solar, wind, and battery storage systems, there’s an increased need for conduit systems that can withstand UV exposure, harsh climates, and mechanical stress. Schedule 80 PVC conduit, due to its rigidity and durability, is often used in exposed environments, especially when paired with proper UV-rated formulations.
2. Growing Focus on Fire Safety and Emissions
More industries, especially data centers, transportation hubs, and healthcare facilities are prioritizing low-smoke, halogen-free alternatives to traditional PVC. Although standard Schedule 80 conduit is not inherently LSZH, demand is growing for similar products that meet fire safety and toxicity standards without compromising mechanical strength.
3. Increasing Use in Industrial and Urban Infrastructure
Urbanization and heavy industrial development are pushing the need for more robust conduit systems that can endure vibration, mechanical wear, and frequent maintenance activity. Schedule 80 PVC’s thicker wall structure makes it a favorable choice in such settings, particularly in manufacturing plants and utility systems.
4. Advancements in Material Engineering
Material improvements are leading to enhanced UV resistance, improved impact tolerance, and longer service life, even in extreme climates. Manufacturers are innovating PVC compounds to better meet specific application requirements-resulting in more application-specific Schedule 80 products.
5. Integration with Smart Infrastructure
While traditionally rigid conduits aren’t associated with smart technologies, they’re now being integrated into broader “smart city” infrastructure plans. For instance, Schedule 80 conduit is increasingly used to house and protect fiber optics, sensor cables, and control systems in utility corridors that demand higher mechanical protection.
6. Regulatory Pressure and Environmental Standards
Governments and regulatory agencies are raising standards for conduit materials, requiring compliance with environmental and safety directives. Schedule 80 PVC continues to evolve to meet stricter building codes, UL listings, and ASTM classifications, ensuring long-term market relevance.
Ledes Schedule 80 PVC Conduit Solution

When reliability, strength, and compliance are top priorities, Ledes Schedule 80 PVC Conduit offers a premium solution for demanding electrical installations. Designed to meet the needs of both commercial and industrial projects, Ledes UL listed SCH 80 conduit combines high mechanical durability with consistent code compliance, making it a trusted choice for professional worldwide.
Product Overview
Ledes Schedule 80 PVC conduit is a rigid nonmetallic conduit that exceeds industry requirements in strength and longevity.
- Sizes Range: 1/2” to 8” trade size
- Lengths: 10 feet or 20 feet with belled ends or without belled end
- Custom lengths and chamfer design are available upon request
Features and Benefits
- Thick-Walled Protection: Superior wall thickness offers enhanced resistance to physical damage and external pressure, perfect for exposed and underground use.
- High Impact Resistance: Compliant with UL 651 standards, Ledes SCH 80 withstands higher impact loads compared to Schedule 40 (75 lb impact weight with 6-inch drop cylinder).
- Smooth Interior: Ensures easy wire pulling and reduced cable abrasion.
- Corrosion-Free & Non-Conductive: Unlike metallic conduits, it resists corrosion and is safe to use around sensitive electrical and communication systems.
Codes Compliance and Certifications
Ledes Schedule 80 PVC conduit is:
- UL 651 Listed
- Marked for 90°C rated conductors
- Flame tested and classified as UL94 – V0 rating
Ledes Schedule 80 PVC conduit is more than a product, it’s a complete solution built for performance, compliance, and durability in today’s most challenging environments.
Conclusion
Schedule 80 PVC conduit is a high-strength electrical conduit designed to meet the demands of rigorous environments. Its thicker walls, compared to Schedule 40 and DB-rated conduits, provide increased resistance to impact, crushing, and mechanical damage, making it ideal for exposed installations, industrial settings, and areas with high traffic or physical stress.
In this article, we’ve covered the full scope of what professionals and installers need to know about Schedule 80 PVC conduit—including its definition and purpose, available sizes, advantages and disadvantages, and installation guidelines. We’ve also explored the relevant code and standard requirements like UL 651, ASTM D1784, and NEC provisions, and explained how to choose the right size based on conductor fill and project requirements.
Ultimately, Schedule 80 PVC conduit is a durable, code-compliant, and versatile solution that serves both general-purpose and specialized needs, especially when mechanical strength and long-term safety are priorities.
FAQs
What is Schedule 80 PVC Conduit?
Schedule 80 PVC conduit is a rigid nonmetallic conduit with a thicker wall than Schedule 40, designed for use in electrical systems requiring extra mechanical protection. It complies with UL 651 and is suitable for both aboveground and underground installations.
What is Schedule 80 PVC Pipe?
Schedule 80 PVC pipe is similar in appearance and wall thickness to Schedule 80 conduit, but it is typically used for plumbing and pressure water systems, not electrical wiring. While both are made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), they are not interchangeable due to differences in application, standards, and interior finish.
What Color Is Schedule 80 PVC Conduit?
Schedule 80 PVC pipe and conduit are typically gray.
Where Is Schedule 80 PVC Conduit Required?
Schedule 80 PVC conduit is required in locations where extra strength and impact resistance are needed, such as:
Exposed outdoor environments (subject to damage or UV exposure)
Underground in high-traffic areas (under driveways or roads)
Industrial settings with mechanical hazards
Utility installations where deeper burial or load-bearing is required
When to Use Schedule 80 PVC Conduit vs. Schedule 40?
Use Schedule 80 when:
You need higher mechanical protection
Installing in harsh environments
Codes mandate extra durability
Use Schedule 40 in typical indoor or low-risk underground runs where heavy-duty protection isn’t essential.
Can Schedule 80 PVC Conduit Be Buried?
Yes. Schedule 80 PVC conduit is suitable for direct burial, and often preferred over Schedule 40 in areas with heavy loads or frequent traffic, such as driveways or commercial sites. Always check NEC and local codes for burial depth requirements.
Is Schedule 80 PVC Conduit Fire-Rated?
Standard Schedule 80 PVC conduit is not fire-rated for high-temperature fire applications. However, it must pass the flame test in UL 651, ensuring basic flame resistance.
What is the difference between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC conduit?
The primary difference lies in wall thickness and strength.
Schedule 80 PVC has thicker walls than Schedule 40, offering greater mechanical protection and crush resistance.
However, this comes with a smaller internal diameter, affecting conduit fill capacity.
Both schedules are made from the same PVC material and offer the same chemical resistance and temperature ratings.
Is Schedule 80 PVC conduit required by code?
Yes, in certain applications.
The National Electrical Code (NEC) may require Schedule 80 when the conduit is subject to:
Physical damage (e.g., exposed areas in garages, warehouses, or outdoors)
Heavy-duty environments where extra protection is needed
Refer to NEC 352.10(F), which mandates Schedule 80 for above-ground installations where physical damage is likely.
How deep must I bury Schedule 80 PVC conduit?
Burying depth depends on location, voltage, and usage.
For residential electrical circuits:18 inches minimum burial depth is typically required.
If unprotected or under driveways, deeper burial is required—up to 24 inches.
Always check local amendments to the NEC for regional depth requirements.
Are there environmentally friendly PVC conduit options?
Yes. Some manufacturers offer:
Low-smoke, halogen-free (LSZH) PVC conduits
Conduits made with recycled PVC or eco-friendly stabilizers
These options reduce toxic emissions during fire and support sustainable construction goals, especially in green-certified buildings (e.g., LEED projects).
Can Schedule 80 PVC be used outdoors?
Absolutely if the conduit is made with additives.
UV-resistant (when marked “sunlight resistant” per UL 651)
Suitable for wet, damp, or corrosive outdoor environments
It performs well in above-ground or buried outdoor installations when properly rated.
What’s the max temperature rating of Schedule 80 PVC conduit?
Schedule 80 PVC typically used at a 50°C (122°F) and lower ambient temperatures, use with 75°C (167°F) wiring, but it can use with 90°C (194°F) if rated.
Is Schedule 80 required for underground use?
Not always.
Schedule 80 is not strictly required for all underground installations.
Schedule 40 PVC is permitted if buried or encased in concrete.
Schedule 80 is required where the conduit emerges from the ground and may be exposed to physical damage (NEC 352.10(F)).
But DB conduit is required for underground use.
Reference




