
Índice
Electrical conduit systems come in various materials and configurations: metallic (like EMT, IMC, and RMC), non-metallic (such as PVC and HDPE), and flexible types (liquid-tight or corrugated). Each type has distinct properties and is governed by specific codes and performance standards. Among them, Conduíte de PVC Schedule 40 stands out as one of the most popular and versatile options—widely used due to its strength, lightweight nature, affordability, and corrosion resistance.
Choosing the right conduit is essential not only for project efficiency and code compliance but also for long-term safety and performance. A mismatched or non-compliant conduit can lead to costly failures, inspection rejections, or even electrical hazards. In 2025, with evolving standards, green building initiatives, and the growing demand for energy infrastructure (such as EV charging and solar), understanding the right conduit is more important than ever.
In this guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about Schedule 40 PVC conduit, so you can make informed decisions for any electrical installation project.
What is Schedule 40 PVC Conduit?

Schedule 40 PVC conduit is a type of rigid, non-metallic electrical conduit made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and designed specifically to protect and route electrical wiring. The “Schedule 40” designation refers to its wall thickness, it more broadly reflects durability and mechanical strength.
Schedule 40 electrical conduit is manufactured to meet specific electrical codes and standards, such as UL 651 and NEMA TC-2, which focus on factors like flame resistance, impact strength, and ease of wire pull. It is typically gray in color, signaling its use for electrical applications.
Key Characteristics of Schedule 40 PVC Conduit
Material: Non-metallic, rigid polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
Color: Light gray
Espessura da parede: Moderate—strong enough for underground and exposed use, but lighter than Schedule 80
Resistência à chama: Meets UL flammability standards
Resistência à corrosão: Excellent resistance to most acids, alkalis, salts, and moisture
Propriedades isolantes: Non-conductive and resistant to electrical currents
Temperature Range: Typically -10°C to 60°C (14°F to 140°F), though varies with formulation
3 Types of Schedule 40 PVC Conduit
While all Schedule 40 PVC conduit shares the same baseline wall thickness and material, manufacturers offer variations to suit different installation needs:
Plain-End Conduit
Straight conduit with unmodified ends.
Requires couplings or solvent cement for joining.
Often used in tight spaces or when cutting and custom-length joins are needed.
Bell-End Conduit
One end of the conduit is factory-formed with a socket (bell) for direct insertion of the next conduit section.
Speeds up installation by eliminating the need for separate couplings.
Ideal for long, continuous runs such as underground installations.
UV-Resistant Formulations
Some Schedule 40 PVC conduit is manufactured with UV stabilizers to prevent degradation from prolonged sun exposure.
Typically marked “UV-resistant” ou “sunlight resistant” and compliant with UL 651 requirements for outdoor use.
Recommended for above-ground exterior applications where exposure to sunlight is expected.
Pontas: Ledes offer sch 40 conduit for solar power, you can click the link to learn if you are interested.
7 Common Applications of Schedule 40 PVC Conduit
Schedule 40 PVC conduit is known for its versatility, making it a go-to solution for a wide range of electrical wiring installations. Its unique combination of mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and affordability makes it suitable for use across various residential, commercial, industrial, and infrastructure sectors.
Below are the most common and emerging applications of Schedule 40 PVC conduit:
Residential Electrical Installations
Schedule 40 PVC conduit is frequently used in homes to route wiring for lighting, outlets, HVAC systems, and garage circuits—especially in areas exposed to moisture like basements or exterior walls. It’s also common in underground feeds to detached garages, sheds, or outdoor lighting systems.
Commercial and Institutional Buildings
In commercial settings, such as offices, schools, or healthcare facilities, Schedule 40 PVC is often used to protect branch circuit wiring in slab-on-grade construction, or in underground conduit banks. It is valued for its long lifespan and ease of installation.
- Encased in concrete or buried underground
- Used in power distribution and lighting systems
- Ideal for low-voltage and communication wiring protection
Industrial and Utility Projects
Industrial applications include the conduit’s use in power plants, factories, utility substations, and other applications that without very heavy loads. Schedule 40 PVC is especially suitable in corrosive environments where metal conduit would degrade.
- Excellent resistance to chemicals and moisture
- Used for control wiring, process automation, and sensor networks
- Often combined with expansion fittings to accommodate thermal movement
Solar and Renewable Energy Installations
With the global shift toward clean energy, Schedule 40 PVC conduit plays a vital role in protecting wiring between photovoltaic panels, combiner boxes, inverters, and batteries—especially in ground-mounted solar farms and rooftop systems.
- Frequently used for underground DC/AC feeder cables
- UV-resistant variants ideal for exposed installations
- Lightweight for easy handling during solar field construction
Infrastructure and Transportation
Schedule 40 PVC conduit is widely used in public infrastructure, such as street lighting, highway signage, traffic signal control, and airport runways. Its low cost and ease of installation make it the conduit of choice for large-scale projects.
- Used for underground conduit runs along roads and bridges
- Protects wiring for intelligent traffic systems (ITS)
Data Centers and Communication Systems
As data centers continue to expand in 2025, Schedule 40 PVC conduit is also used to organize and protect communication and fiber optic cabling infrastructure, especially beneath raised floors or in slab installations.
- Provides non-metallic isolation for sensitive cables
- Helps meet separation requirements for power and data
Outdoor and Wet Locations
When paired with proper fittings and weatherproof enclosures, Schedule 40 PVC can be safely used in outdoor and wet environments, such as pool equipment wiring, and marina installations.
- Must be sunlight-resistant for UV exposure
- Often used with watertight junction boxes
- Ensures code compliance in damp locations
Schedule 40 PVC Conduit Code Compliance

To ensure that Schedule 40 PVC conduit is safe, durable, and suitable for electrical installations, it must comply with several key industry codes and standards. These regulations, developed by national and international organizations, define the minimum requirements for material quality, physical performance, manufacturing consistency, and safe installation. Understanding these standards helps ensure the conduit meets legal requirements, passes inspections, and performs reliably over time.
Here’s a brief look at the major codes and standards that apply to Schedule 40 PVC conduit:
UL 651 – Standard for Schedule 40 and 80 PVC Conduit and Fittings:
UL 651 is the primary U.S. safety standard, published by Underwriters Laboratories, this standard focuses on the testing and certification of rigid PVC conduit. It sets requirements for dimensional accuracy, mechanical strength, impact resistance, crush resistance, flame retardancy and other properties.
Dicas profissionais: Need to know more about the UL651 standard? You can check out our last post about the UL651 application guide for PVC conduit.
NEMA TC-2 – Electrical Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Conduit:
Developed by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association, NEMA TC-2 is aligns with UL651, provides detailed manufacturing guidelines, dimensional tolerances, and material specifications to ensure consistent quality and performance across PVC conduit products.
Published by ASTM International, this standard classifies the physical and chemical properties of PVC materials used in conduit production.
Specifies the minimum material requirements for rigid PVC compounds used in conduit manufacturing.
Most electrical conduit uses compounds with a minimum cell classification of 12454 or higher for strength and stability.
Notas: Reading the ASTM Code Expert Guide can help you understand the ASTM requirements for PVC pipe raw materials in detail.
CSA C22.2 No. 211.2 – Canadian Standard for Rigid PVC Conduit
Issued by the Canadian Standards Association, this standard governs the safety and performance of rigid PVC conduit used in Canada. Requires similar performance in terms of flame resistance, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance.
Dicas profissionais: Don’t know about Canadian standard PVC conduit? Read this article about CSA C22.2 standard Rigid PVC Conduit requirements to help you quickly understand Canadian conduit codes and choose the right one.
Performance Requirements & Testing of Sch 40 Conduit
To ensure the reliability, safety, and long-term durability of Schedule 40 PVC conduit, manufacturers must meet strict performance requirements established under UL 651, the industry benchmark standard for rigid PVC conduit. This standard specifies a comprehensive series of tests that evaluate the conduit’s performance and quality. Products that pass all testing criteria are eligible for UL Listing, signifying that they meet nationally recognized safety standards.
Below are the key performance areas and tests required by UL 651 for Schedule 40 PVC conduit:
Requisitos dimensionais
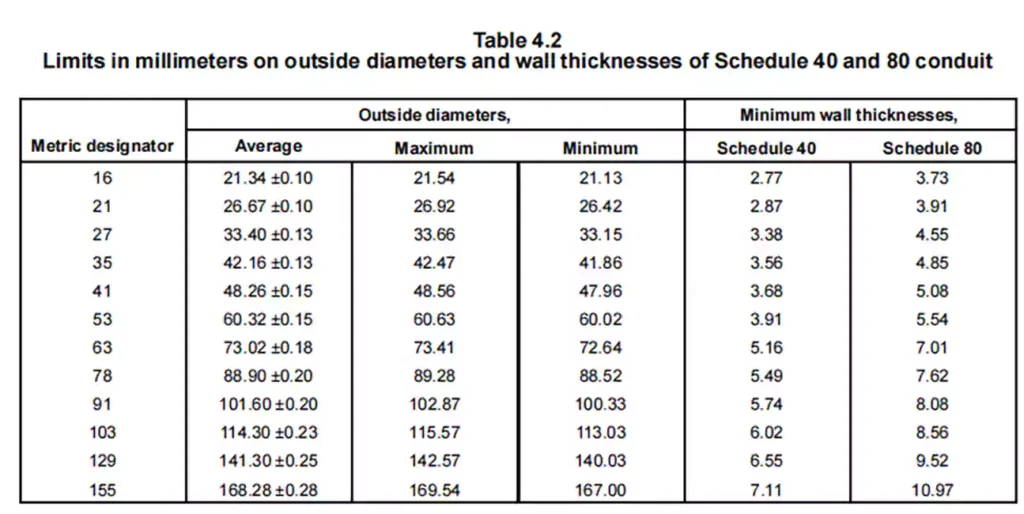

It sets specific dimensional requirement for PVC conduits of Schedule 40 and 80, and other types of rigid PVC conduit, from trade size 1/2” to 6”. Including outside diameter, wall thickness, minimum inside diameter, length and integral socket dimensions are measured to verify they fall within the specified tolerances.
Resistência à tracção
This test is to confirm the conduit material can withstand pulling forces without failure, critical during cable pulling or stress.
Method: Standard specimens (dumbbell-shaped) cut from the conduit, aged and unaged, are pulled apart using a testing machine at a fixed rate of 10.0 ±2.5 mm per minute. This measures the maximum stress the material can endure before breaking.
Exigência: For Schedule 40 rigid PVC conduit, the tensile strength must not less than 5000 psi and maintain at least 95% strength after heat aging.
Absorção de água
Propósito: Ensures water uptake doesn’t degrade the conduit’s electrical or mechanical performance, especially for applications in moist environments.
Method: A sample is dried, weighed, then immersed in water at 23 °C for 24 hours. It is removed, dried on the surface, and reweighed.
Exigência: The weight gain due to water must be ≤0.50%.
Impact Resistance Test
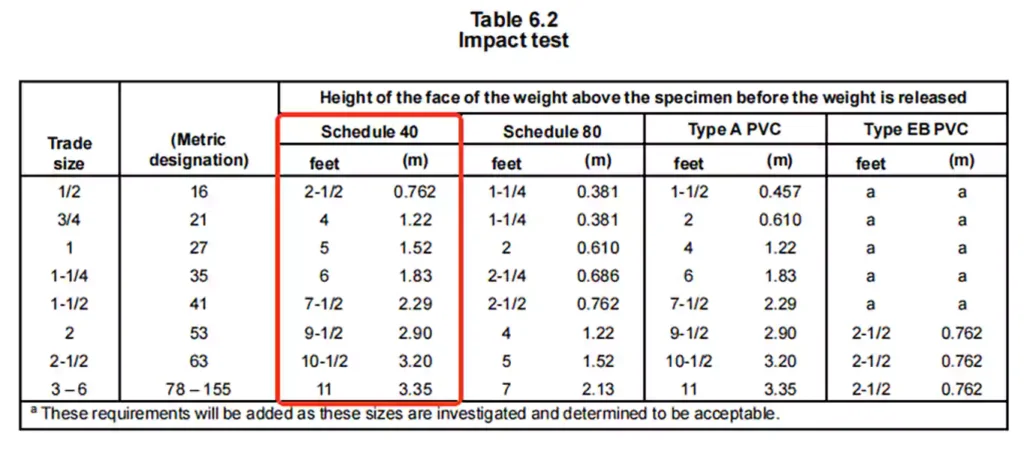
To evaluate the conduit’s ability to withstand mechanical shocks without cracking or tearing, ensuring durability during handling and installation.
Método de teste: Ten specimens are conditioned at 23.0 ±2.0°C (73.4 ±3.6°F) for at least 4 hours.
And each Schedule 40 conduit specimen is subjected to a 20 lbs (9.1kg) impact force at a specific height.
Requisitos: Seven out of ten specimen shall exhibit no cracks or tears longer than 1/32 inch (0.8 mm) along the outer surface.
Deflection Under Load Test
This test checks how well Schedule 40 PVC conduit resists bending when exposed to heat and mechanical stress.
Método de teste: Specimens machined from finished conduit are supported at both ends and loaded in the center while submerged in a heated liquid. The temperature is gradually increased until the specimen bends (deflects) by 0.010 inch (0.25 mm).
Exigência: To pass, the average temperature at which this deflection occurs must be at least 70°C (158°F) under a light load (66 psi) e 62°C (143.6°F) under a heavier load (264 psi).
These results help confirm that the conduit will maintain its shape and strength in hot conditions, making it suitable for installations exposed to high temperatures.
Crush (Compression) Test
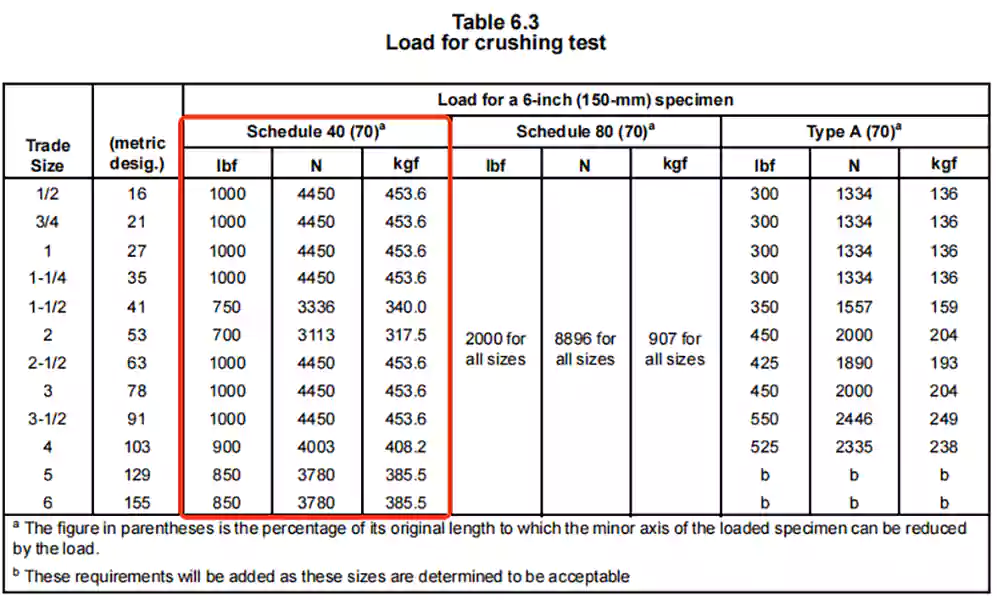
This test evaluates the ability of Schedule 40 PVC conduit to resist deformation under heavy external loads.
Method: A 6-inch section of conduit is placed between two flat steel plates and compressed at a steady rate. The goal is to simulate pressure the conduit might face when buried underground or installed under floors.
Exigência: To pass the test, the conduit must not buckle or pull away from the plates. After compression, the inner width (minor axis) of the flattened conduit must still be at least 70% of its original inner diameter. This ensures the conduit maintains its shape and allows space for wires even under load.
Flame Retardance Test
This test checks how well Schedule 40 PVC conduit resists catching fire and spreading flames.
Testing Method: An 18-inch vertical piece of conduit is exposed to a flame three times, each for 60 seconds, with a 30-second pause in between. Cotton is placed underneath to detect any burning particles or drips.
Exigência: To pass the test, the conduit must stop flaming within 5 seconds after each flame exposure. It must also not ignite the cotton below or around it, and it must not be completely consumed. This ensures the conduit won’t contribute to fire spread in real-world applications.
Resistência a Reagentes Específicos
This test evaluates the chemical resistance of Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 rigid PVC conduits when exposed to specific corrosive reagents. It includes two key components: the Reagent Absorption Test and the Crush Strength Test, which simulate long-term chemical exposure in environments where the conduit may be immersed or regularly contacted by aggressive substances such as oils, solvents, or chemicals.
- Test specimens (typically trade size 1 (27) or smaller) are immersed in a reagent at a defined temperature and concentration for 60 and 120 days.
- The Reagent Absorption Test measures the percentage of weight change to ensure it remains within acceptable limits (≤2.50%), and controls the rate of absorption over time to prevent excessive degradation.
- O Ensaio de Resistência ao Esmagamento compara a integridade mecânica de amostras envelhecidas e não envelhecidas após a exposição. Ele garante que o conduíte retenha pelo menos 85% de sua resistência ao esmagamento original e não apresente falhas estruturais, como rachaduras ou colapso.
Este teste é essencial para confirmar o desempenho do conduíte em instalações quimicamente agressivas e valida a durabilidade a longo prazo para ambientes industriais e corrosivos.
Teste de resistência à luz solar (teste UV)
Propósito: Os sistemas de conduítes de PVC são frequentemente instalados em ambientes externos ou expostos, onde estão sujeitos à radiação ultravioleta (UV) contínua. Este teste avalia a resistência UV a longo prazo de conduítes de PVC rígido Schedule 40 quando expostos à luz solar e à umidade simuladas.
Method: As amostras são condicionadas em uma câmara de intemperismo de arco de xenônio por 720, 1080 e até 1440 horas, seguidas de testes de impacto Izod entalhado de acordo com a norma ASTM D256.
Exigência: Os conduítes devem manter resistência suficiente ao impacto após exposição prolongada aos raios UV para passar no teste. O desempenho satisfatório indica que o produto é adequado para aplicações expostas à luz solar e se qualifica para o teste. “Resistente à luz solar” designação.
Este teste é essencial para verificar a confiabilidade de um conduíte em instalações externas, como sistemas de energia solar, infraestrutura de telecomunicações e linhas elétricas expostas.
Para uso com fio de 90°C

Os conduítes rígidos de PVC Schedule 40 (e Schedule 80) são, às vezes, instalados em ambientes onde devem transportar condutores classificados para operação contínua a 90 °C (194 °F). Para garantir que o material do conduíte mantenha a integridade sob estresse térmico de longo prazo, a norma UL 651 exige um teste especializado para verificar se o conduíte não sofre deterioração significativa de suas propriedades críticas quando exposto a temperaturas elevadas ao longo do tempo.
Testing Method: Este teste envolve submeter amostras de conduíte a envelhecimento acelerado em um forno de circulação de ar a 80 °C (176 °F) por períodos de até 360 dias. Em intervalos de 60, 120, 180, 240 e 360 dias, os espécimes são removidos, resfriados e avaliados quanto à resistência ao impacto por meio de um teste de queda de peso de aço. Os espécimes não envelhecidos servem como base, e a degradação da resistência ao impacto é plotada ao longo do tempo.
Exigência: Para passar no teste, a resistência ao impacto deve se estabilizar em pelo menos 50% do valor medido nas amostras não envelhecidas. Isso garante que o conduíte mantenha integridade mecânica e resistência ao impacto suficientes, mesmo após exposição prolongada a altas temperaturas do condutor.
Os conduítes que atendem a este requisito são marcados com“fio máximo 90°C” ou “máx. 90°C”, são uma escolha confiável para sistemas elétricos de alto desempenho e com alto consumo de calor.
Vantagens e desvantagens do conduíte de PVC Schedule 40
O conduíte de PVC Schedule 40 é um dos tipos de conduíte elétrico mais utilizados em aplicações residenciais, comerciais e industriais leves. Sua popularidade advém de um equilíbrio entre desempenho, custo-benefício e facilidade de uso. No entanto, como qualquer solução de material, ele tem seus pontos fortes e limitações. Entender essas vantagens e desvantagens é essencial para que você saiba se ele é adequado para o ambiente do seu projeto.
6 Benefícios do Eletroduto de PVC Schedule 40
Leve e fácil de instalar
O conduíte de PVC Schedule 40 é significativamente mais leve do que o conduíte de PVC Schedule 80 e sistemas de conduíte metálico, como EMT ou RMC. Isso reduz o esforço de mão de obra e o tempo de instalação, especialmente em instalações de grande porte ou aplicações aéreas. Sua leveza também minimiza os custos de transporte e manuseio.
Resistente à corrosão
Uma das principais vantagens do PVC é sua resistência à ferrugem, ao apodrecimento e à corrosão química. O conduíte de PVC Schedule 40 é ideal para ambientes úmidos ou corrosivos, incluindo instalações subterrâneas, ambientes agrícolas e estações de tratamento de águas residuais.
Custo-beneficio
Comparado aos sistemas de conduítes metálicos, o PVC Schedule 40 oferece um custo inicial de material menor e normalmente requer menos ferramentas especializadas para instalação. Isso o torna uma opção econômica para projetos elétricos de pequeno e grande porte.
Não condutivo e eletricamente isolante
O PVC é inerentemente não condutor, o que elimina a necessidade de aterramento adicional em muitas aplicações. Essa característica aumenta a segurança em ambientes onde os riscos de choque elétrico devem ser minimizados.
Resistente às intempéries e aos raios UV (com aditivos)
Com estabilizadores UV adequados ou quando instalado com revestimentos apropriados, o PVC Schedule 40 pode suportar a exposição à luz solar e às condições externas.
Boa resistência química
O PVC Schedule 40 apresenta forte resistência a uma ampla gama de produtos químicos, incluindo ácidos, sais e álcalis. Essa característica o torna adequado para ambientes industriais ou de processamento químico agressivos.
5 desvantagens do eletroduto de PVC Schedule 40
Menor Resistência Mecânica
Embora adequado para muitas aplicações, o PVC Schedule 40 apresenta menor resistência a impactos e esmagamentos em comparação ao PVC Schedule 80 ou a conduítes metálicos. Pode não ser adequado para ambientes com tráfego intenso, abuso mecânico ou enterramento profundo sem proteção adicional.
Faixa de temperatura limitada
Os conduítes de PVC geralmente apresentam bom desempenho entre -18 °C (0 °F) e 60 °C (140 °F), mas podem se tornar quebradiços em frio extremo ou amolecer em condições de alta temperatura. Isso limita seu uso em certas instalações industriais ou de alta temperatura.
Frágil em climas frios
Em temperaturas extremamente baixas, o PVC torna-se mais quebradiço e propenso a rachaduras. Os instaladores devem ter cuidado durante o manuseio e a instalação em ambientes abaixo de zero ou considerar materiais alternativos para tais condições.
Emite fumaça e gases tóxicos ao queimar
Embora o PVC seja autoextinguível, ele emite fumaça e gases potencialmente nocivos ao queimar. Isso é uma desvantagem em comparação com Conduítes de baixa emissão de fumaça e zero halogênio (LSZH) ou conduíte metálico, que oferecem melhor desempenho em ambientes críticos de incêndio.
Suscetível à expansão e contração térmicas
O PVC expande e contrai mais significativamente do que o metal quando exposto a mudanças de temperatura. Se não for devidamente compensado com juntas de dilatação ou ajustes de projeto, esse movimento pode levar ao deslocamento do conduíte ou à tensão na junta ao longo do tempo.
Onde é permitido o uso de conduítes de PVC do Anexo 40?

O conduíte de PVC Schedule 40 é amplamente utilizado no mercado, e o Código Elétrico Nacional (NEC) fornece orientação abrangente sobre onde ele pode ser instalado. NEC 352.10 especifica os locais onde o conduíte de PVC do Anexo 40 pode ser usado com segurança.
Instalações ocultas (paredes, pisos, tetos)
O conduíte de PVC Schedule 40 pode ser escondido atrás de paredes, sob pisos e acima de tetos em edifícios residenciais e comerciais. Suas propriedades discretas e não corrosivas o tornam adequado para sistemas de fiação interna que não estão expostos a danos físicos.
Envolto em concreto
Pode ser embutido diretamente em lajes, vigas ou paredes de concreto. Isso é comum em fundações e bancos de dutos subterrâneos, onde o conduíte é protegido do ambiente pelo revestimento de concreto.
Ambientes Corrosivos
Conduítes de PVC são particularmente vantajosos em locais altamente corrosivos — como indústrias químicas, áreas costeiras e estações de tratamento de águas residuais — onde conduítes metálicos se degradariam rapidamente. A NEC permite o uso de PVC nesses ambientes, desde que o material seja classificado para os produtos químicos específicos presentes.
Áreas de preenchimento de escória
Conduítes de PVC podem ser instalados em áreas com cinzas industriais ou materiais de escória. Essas condições podem ser altamente corrosivas, e o PVC oferece uma alternativa não reativa aos sistemas de conduítes metálicos.
Locais úmidos (por exemplo, laticínios, lavanderias, lavagens de carros)
Conduítes de PVC são permitidos em áreas onde a umidade ou as condições de lavagem são comuns. Nesses casos, os instaladores devem garantir que o sistema seja estanque — isso inclui o uso de caixas de PVC compatíveis, conexões e ferragens resistentes à corrosão, como parafusos de aço inoxidável ou cintas galvanizadas.
Locais secos e úmidos
É adequado para uso geral em ambientes internos secos e úmidos, como porões, depósitos e áreas de serviço. O NEC permite o uso de PVC nesses locais, a menos que seja proibido por regras específicas descritas no NEC 352.12.
Instalações Expostas
Conduítes de PVC Schedule 40 podem ser instalados em configurações expostas, como ao longo de paredes ou tetos em espaços inacabados. No entanto, onde houver potencial de impacto físico ou estresse mecânico, o uso de PVC Schedule 80 é necessário para proteção adicional.
Instalações subterrâneas
O conduíte de PVC é amplamente utilizado no subsolo, seja diretamente enterrado no solo ou revestido em concreto para proteção mecânica adicional. É uma solução comum para entradas de serviço, estacionamentos e iluminação pública.
Compatibilidade de temperatura de isolamento
Você pode usar condutores classificados para temperaturas mais altas dentro do conduíte de PVC, mas eles não devem operar acima da temperatura nominal do conduíte (normalmente 50 °C ou 60 °C, dependendo do produto). Isso protege o conduíte contra deformações ou falhas relacionadas ao calor.
O conduíte de PVC Schedule 40 pode ser usado em diversos locais. O principal é adequar o tipo de conduíte e o método de instalação às condições específicas do ambiente. A norma NEC 352.12 também especifica as aplicações em que não é permitido. Para mais detalhes, consulte a NEC para referência.
Como é fabricado o conduíte de PVC Schedule 40?
O processo de fabricação do conduíte de PVC Schedule 40 é uma operação industrial cuidadosamente controlada que garante qualidade consistente do produto, conformidade com as normas e desempenho a longo prazo em instalações elétricas. Aqui está uma análise das 7 principais etapas envolvidas na produção deste conduíte não metálico amplamente utilizado:
Preparação de matéria-prima
A principal matéria-prima usada no conduíte de PVC Schedule 40 é a resina de cloreto de polivinila (PVC), que é combinada com vários aditivos para melhorar propriedades específicas:
- Estabilizadores: Evite a degradação durante o processamento e aumente a estabilidade térmica.
- Lubrificantes: Melhore a processabilidade e reduza o atrito durante a extrusão.
- Modificadores de impacto: Aumente a tenacidade e a resistência ao impacto do produto final.
- Pigmentos: Proporciona a cor cinza típica e protege contra degradação UV quando necessário.
- Enchimentos (por exemplo, carbonato de cálcio): Usado para ajustar propriedades mecânicas e custo.
Esses ingredientes são misturados a seco em um pó homogêneo chamado composto ou formulação de PVC, que atende a critérios específicos de desempenho, incluindo resistência à chama e resistência mecânica.
Extrusão
O composto preparado é alimentado em uma máquina de extrusão de PVC, onde o material é derretido e moldado no formato de um conduíte:
- O material é aquecido em um cilindro com parafusos giratórios até um estado fundido.
- Em seguida, ele é forçado através de uma matriz especialmente projetada, que o molda em um tubo cilíndrico com uma espessura de parede específica adequada ao Anexo 40.
- Os tanques de dimensionamento a vácuo e resfriamento a jusante da matriz ajudam a manter tolerâncias dimensionais rigorosas à medida que o tubo solidifica.
- A velocidade de extrusão e a taxa de resfriamento são cuidadosamente reguladas para evitar deformações e garantir espessura de parede uniforme.
Corte e Belling
Uma vez que o conduíte esteja totalmente formado e resfriado:
- Ele é cortado em comprimentos padrão, normalmente de 10 ou 20 pés.
- Uma extremidade é abocardada (expandida) para permitir a soldagem com solvente durante a instalação. O processo de abocardamento utiliza um molde aquecido para alargar a extremidade do tubo e encaixar a próxima seção com segurança.
- A outra extremidade é mantida lisa (torneira).
Marcação e Impressão
Cada trecho de conduíte é marcado com informações obrigatórias, normalmente por meio de impressão jato de tinta ou hot stamp. Isso inclui:
Nome do fabricante ou marca registrada
Tamanho nominal
Designação de cronograma (Anexo 40)
Normas relevantes (por exemplo, UL 651)
Número do lote e data de fabricação
Classificações de uso (por exemplo, resistente à luz solar, se aplicável)
Controle de Qualidade e Testes
Os conduítes de PVC Schedule 40 passam por rigorosos controles de qualidade, incluindo:
Verificações dimensionais: Para garantir que os diâmetros interno e externo atendam às tolerâncias padrão.
Ensaios de resistência mecânica: Para confirmar se o conduíte pode suportar estresse mecânico sem rachar.
Testes de resistência à chama: Para verificar se ele atende aos requisitos de segurança contra incêndio, como UL 94 V-0 ou equivalente.
Durabilidade da marcação: Garante que a legibilidade permaneça durante o manuseio e armazenamento.
Alguns fabricantes também realizam testes de infravermelho (IR), análise termogravimétrica (TGA) ou calorimetria de varredura diferencial (DSC) para verificar a consistência do composto e garantir a formulação adequada em todos os lotes.
Embalagem e Envio
Após passar pela inspeção, os conduítes são agrupados e embalados usando:
- Tiras ou amarras de plástico
- Tampas nas extremidades para evitar sujeira ou umidade
- Etiquetas para rastreamento e inventário
Eles são então carregados para envio, geralmente em paletes ou caixas para distribuição nacional ou internacional.
Como instalar um conduíte de PVC Schedule 40? (9 etapas)
A instalação de conduítes de PVC Schedule 40 exige planejamento cuidadoso, ferramentas adequadas e o cumprimento dos códigos elétricos para garantir um sistema elétrico seguro, durável e em conformidade. Abaixo, você encontrará uma visão geral profissional do processo geral de instalação.
Planeje a rota do conduíte
Antes de começar, revise seu layout para determinar:
- O caminho do conduíte (acima do solo, subterrâneo, embutido no concreto ou escondido nas paredes).
- Pontos de entrada e saída para caixas, painéis e terminações.
- O número e o tipo de curvas e conexões necessárias.
Consulte as tabelas de preenchimento da NEC para garantir que o tamanho do conduíte acomode todos os condutores pretendidos.
Cortar e preparar o conduíte
Use uma serra de dentes finos, um cortador de conduíte ou uma serra de esquadria elétrica para cortar o conduíte no comprimento desejado.
Rebarbe e alise as bordas cortadas com uma ferramenta de rebarbação ou lima para evitar danos ao isolamento do fio.
Aplicar cimento solvente e montar
Primeiro, faça o ajuste a seco de todos os componentes para verificar o alinhamento.
Limpe tanto a extremidade do conduíte quanto o soquete do encaixe.
Aplique um solvente de cola para PVC aprovado uniformemente no tubo e na conexão.
Quickly insert the conduit into the fitting with a slight twist to evenly distribute the cement.
Hold together until set.
Support the Conduit Properly
Secure conduit at intervals as required by code.
Use corrosion-resistant straps or clamps that are compatible with PVC material.
Accommodate Thermal Expansion
PVC expands and contracts with temperature changes. For long runs or outdoor installations:
Install expansion joints as recommended by the manufacturer.
Leave room for slight movement within fittings.
Make Bends with Heat (If Needed)
Use factory-made elbows when possible.
If custom bends are needed, apply uniform heat with a heat blanket or conduit heater.
Bend slowly and evenly, avoiding kinks or flattening.
Install Conduit into Boxes and Enclosures
Use terminal adapters, female adapters, or conduit bodies as needed.
Ensure tight, secure connections and proper gasket seals in wet or outdoor locations.
Pull Conductors
Once the conduit system is complete and fully cured:
Use a fish tape or pulling line to route the conductors.
Apply wire-pulling lubricant if needed to reduce friction.
Test and Inspect
Check for continuity, grounding (if applicable), and physical integrity.
Comply with local electrical inspection requirements before energizing the system.
Proper installation not only ensures code compliance but also extends the life of the conduit and protects wiring from damage.
7 Commons Fitting for Schedule 40 PVC Conduit
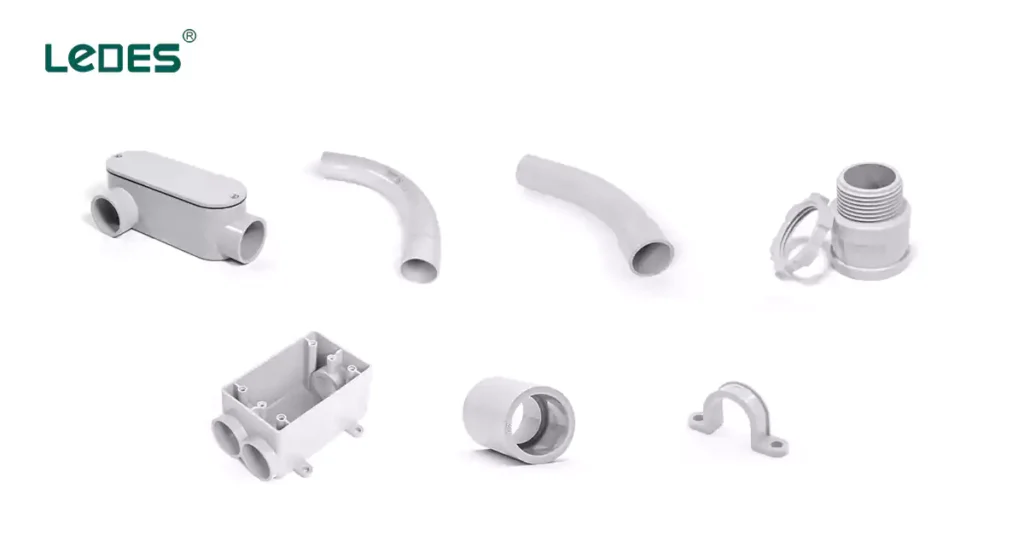

Fittings are essential components in any electrical conduit system. They allow Schedule 40 PVC conduit to connect, change direction, adapt to other systems, and safely terminate or support electrical wiring. Choosing the right fittings ensures a secure, code-compliant, and long-lasting installation. This section explores the most common types of fittings used with Schedule 40 PVC conduit, their applications, and installation considerations.
Conduit Couplings
Join two straight pieces of conduit end-to-end.
Tipos:
Standard Solvent Weld Couplings: Most common, joined with PVC cement.
Acoplamentos de expansão: Designed to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction.
Conduit Elbows
Change the direction of conduit runs.
Bend Angles: 90°, 45°, 30°, 22.5°, and 11.25° are commonly available.
Tipos:
Cotovelos Padrão: For general direction changes.
Sweep Elbows: Longer radius to ease wire pulling, often required for large or complex conduit runs.
Conduit Adapters
Transition from PVC conduit to boxes or other raceway systems.
Tipos:
Adaptadores femininos: It transitions the conduit to a threaded connection, typically to attach to a threaded male fitting, electrical box, or enclosure.
Terminal Adapters: Connect to electrical boxes; often come with a threaded end and a locknut.
Caixas Elétricas
Serve as junction points, pull points, or for housing electrical devices.
Tipos:
Caixas de junção: Available in square, round, or rectangular shapes.
Pull Boxes: Used to facilitate wire pulling in long conduit runs.
Device Boxes: Such as gang boxes, accommodate outlets, switches, and other fixtures.
Bushings and Caps
Bushings: Protect conductor insulation from abrasion at conduit ends.
End Caps: Seal unused conduit ends to prevent ingress of debris or moisture.
Straps and Clamps
Secure conduit runs to walls, ceilings, or other surfaces.
Materiais: Corrosion-resistant plastic or metal; must support conduit without causing deformation.
Conduit Bodies (Type LB, LL, LR, T, etc.)
Provide access to wiring for pulling, splicing, or inspection.
Conduit bodies must be clearly marked and listed for use with PVC systems.
Material and Compatibility
All fittings used with Schedule 40 PVC conduit must:
- Be UL Listed or CSA Certified, depending on local code.
- Be made from compatible PVC material to ensure uniform thermal and mechanical behavior.
- Support the conduit size and Schedule 40 wall thickness (although many are also compatible with Schedule 80).
Joining Methods
Schedule 40 PVC conduit and fittings are typically joined using:
Solvent Welding: A chemical bond formed by applying primer and cement to both the conduit and fitting surfaces. This creates a strong, watertight, and permanent connection.
Threaded or Mechanical Connections: Used with adapters or transition fittings to interface with metal conduit, boxes, or equipment.
Installation Considerations
Expansion Control: Use expansion fittings where temperature variations could lead to conduit movement.
Support: Install support straps within NEC specified distances (usually within 3 ft of boxes and every 3 or up to 8 ft for horizontal runs).
Weather Exposure: For outdoor applications, use fittings labeled as UV-resistant or sunlight-resistant.
Sealing: In wet or underground locations, ensure fittings and boxes are properly sealed against moisture ingress.
Schedule 40 PVC Conduit vs. Schedule 40 PVC Pipe

Although Schedule 40 PVC conduit and Schedule 40 PVC pipe look similar and even share the same outer diameter dimensions, they are not interchangeable and serve very different purposes. Understanding the key differences is essential for ensuring both code compliance and installation performance.
1. Application Purpose
Conduíte de PVC Anexo 40 is specifically designed for electrical wiring systems. It protects electrical cables from moisture, chemical exposure, and mechanical damage.
Schedule 40 PVC Pipe, on the other hand, is designed for plumbing systems, such as water supply, drainage, and irrigation.
2. Standards and Certifications
Conduíte is manufactured according to UL 651 or NEMA TC-2 standards, meeting NEC (National Electrical Code) requirements.
Pipe typically complies with ASTM D1785, ASTM D2665 and NSF standards for potable water or drain/waste/vent (DWV) applications.
3. Wall Thickness and Strength
- While both have the same nominal Schedule 40 wall thickness, conduits are optimized for pull strength and easier wire pulling rather than water pressure.
- Pipes are pressure-rated for hydraulic performance and durability under sustained fluid flow.
4. Sunlight Resistance
Electrical conduit is often made with UV-resistant additives, making it suitable for outdoor exposed applications.
Plumbing pipe is not always UV-rated and can degrade over time if installed in direct sunlight without protection.
5. Fittings and Connections
Conduit fittings are designed to accommodate wiring systems and are generally solvent-welded or threaded. They may also have special features to prevent water ingress.
Pipe fittings are designed for fluid-tight seals and may include pressure-rated couplings, tees, and elbows specific to plumbing.
6. Fire Performance and Color
- Schedule 40 PVC conduit is often gray in color and must meet flame and smoke performance requirements for electrical applications.
- Schedule 40 PVC pipe is usually white, and fire resistance is not a standard requirement for plumbing systems.
Using PVC pipe in place of conduit for electrical installations is not permitted by the NEC. Doing so can result in code violations, safety hazards, and potential system failure.
Tabela Resumo
Recurso | Conduíte de PVC Anexo 40 | Schedule 40 PVC Pipe |
Propósito | Proteção de fiação elétrica | Water/fluid transport |
Padrões | UL 651, NEMA TC-2 | ASTM D1785, ASTM D2665, NSF |
Resistência UV | Often UV-rated | Usually not UV-rated |
Classificação de pressão | Não classificado para pressão | Pressure-rated |
Resistência ao fogo | Must meet NEC, UL fire standards | Não é necessário |
Acessórios | Designed for wire pulling systems | Designed for hydraulic sealing |
Cor | Gray | Branco |
While Schedule 40 PVC conduit and pipe may look alike, they serve entirely different roles. For safe, compliant, and long-lasting electrical installations, always use Schedule 40 PVC conduit in accordance with NEC requirements—never substitute it with standard plumbing pipe.
Schedule 40 vs. Schedule 80 PVC Conduit (5 Different)

When choosing PVC conduit for an electrical installation, understanding the difference between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 is crucial. Both types are widely used in residential, commercial, and industrial applications, but each has unique features, strengths, and code-specific uses. Below is a comprehensive comparison to help you select the right conduit for your project.
1. Wall Thickness and Strength
- Schedule 40 PVC Conduit has thinner walls, making it lighter and easier to handle and cut. It is ideal for above-ground or underground installations in areas where physical damage is unlikely.
- Schedule 80 PVC Conduit has thicker walls, offering greater mechanical strength and resistance to impact. This makes it better suited for environments with potential for physical damage or high traffic, such as exposed installations in industrial areas.
Inner Diameter (ID)
The outer diameter of both Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 conduit is the same, ensuring compatibility with fittings.
However, due to its thicker wall, Schedule 80 has a smaller inner diameter, which reduces wire-pulling space and can affect conduit fill calculations.
2. Fire and UV Resistance
Both Schedule 40 and 80 conduits are available with UV-resistant formulations and must meet NEC flame performance requirements.
Neither is inherently flameproof like metallic conduit, but they are self-extinguishing and designed to resist spreading flames.
3. Chemical and Corrosive Resistance
Both types are nonmetallic and corrosion-resistant, making them suitable for chemical environments.
Schedule 80 is often preferred in more aggressive or corrosive locations due to its added thickness and toughness.
4. Use in Physical Damage Areas
According to NEC 352.10(K), Schedule 80 must be used “where subject to physical damage,” such as:
Exposed outdoor installations
Warehouses or factory floors
Locations with frequent equipment movement
5. Weight and Installation
Schedule 40 is easier to work with due to its lightweight and flexibility, reducing labor costs for large installations.
Schedule 80, while stronger, is heavier and more rigid, which can require more effort to cut, bend, and secure.
Comparison Table
Recurso | Conduíte de PVC Anexo 40 | Conduíte de PVC Schedule 80 |
Padrões | UL 651, NEMA TC-2 | UL 651, NEMA TC-2 |
Espessura da parede | Thinner | Thicker |
Peso | Lighter | Mais pesado |
Inner Diameter | Larger (more wire space) | Smaller (less wire space) |
Resistência mecânica | Moderado | Alto |
Custo | Mais baixo | Mais alto |
Instalação | Easier to cut and bend | Harder to work with |
Choosing between Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC conduit comes down to the environment and application demands. For most standard electrical work, Schedule 40 is sufficient. However, when installation sites demand higher impact resistance or face harsher conditions, Schedule 80 is the safer and code-compliant choice.
Ledes Schedule 40 PVC Conduit Solutions

As a professional electrical conduit products manufacturer, Ledes offers a premium line of Schedule 40 PVC conduit solutions designed to meet the demands of residential, commercial, industrial, and infrastructure projects. Built for durability, easy installation, and environmental resistance, Ledes Schedule 40 PVC conduits are trusted by electricians and contractors worldwide.
Product Features
- Standard Trade Sizes: 1/2″ through 6″ available.
- Bell-end design for easy solvent-welding installation.
- High impact resistance e crush strength for tough environments.
- Smooth inner wall for easy cable pulling and reduced friction.
Engineered to Perform
Ledes Schedule 40 PVC conduit is manufactured from high-quality, rigid polyvinyl chloride (PVC) materials that are:
- Resistente à corrosão, ideal for use in wet, damp, and underground environments.
- Não condutivo, ensuring safe isolation of electrical conductors.
- UV-resistant, with added stabilizers for superior outdoor performance.
- Fire-retardant, formulated to meet UL 651 standards for flame resistance.
Code-Compliant and Certified
Ledes conduits are rigorously tested to comply with international and regional standards:
- Listado na UL 651 for rigid PVC conduit and fittings.
- NEMA TC-2 compliant, meeting dimensional and performance specifications.
- Compliant with Artigo 352 da NEC for rigid PVC conduit use.
Comprehensive Conduit Systems
Ledes doesn’t just stop at conduit. To provide a full installation solution, they offer:
- Compatible Schedule 40 fittings, including couplings, elbows, adapters, boxes, and more.
- Custom lengths and packaging options for large-scale projects or distribution.
Por que escolher Ledes?
Choosing Ledes means choosing:
Certified quality
Proven performance
Global availability
Expert technical support
Whether you’re wiring a new home, upgrading a commercial facility, or building infrastructure for the future, Ledes Schedule 40 PVC conduit solutions offer the reliability and compliance your project demands.
PVC Conduit Buying Guide and Expert Advice
Choosing the right Schedule 40 PVC conduit isn’t just about picking a size—it involves evaluating compliance, compatibility, project needs, and supplier reliability. This guide breaks down what to consider before making a purchase, ensuring you get the right product for your electrical infrastructure.
8 Key Considerations Before Buying
1. Conduit Size (Diameter)
Choose the correct nominal trade size (e.g., ½”, ¾”, 1″, 2″) based on the number and type of conductors.
Follow NEC conduit fill tables and ensure adequate space for pulling and heat dissipation.
2. Wall Thickness
Ensure it’s Schedule 40 wall thickness as required—provides the appropriate strength for most residential and light commercial applications.
For areas subject to physical damage, consider upgrading to Schedule 80.
3. Compliance with Standards
Verify that the conduit is UL Listed (UL 651) or CSA certified, and meets NEC Article 352.
Check compliance with regional standards if outside North America
4. Material Quality
Use high-quality, virgin or certified reprocessed PVC materials.
Look for chemical resistance, UV resistance (if exposed outdoors), and heat tolerance.
5. Project Quantity Estimation
Calculate the total linear footage needed, including extra length for bends and waste.
Don’t forget accessories like couplings, adapters, and boxes.
6. Fittings Compatibility
Ensure fittings (elbows, adapters, boxes) are listed for use with Schedule 40 PVC conduit.
7. Transportation and Handling
Plan for safe transportation—PVC can be damaged by improper loading or impact.
Store in a dry, shaded area to prevent UV degradation and warping.
8. Reputable Brands and Manufacturers
Choose products from well-established manufacturers with quality control, technical documentation, and support.
Consider availability of compatible accessories and fittings.
Expert Advice
Tip 1: Don’t Mix Pipe and Conduit
Even if Schedule 40 PVC pipe and conduit look similar, PVC water pipe is not electrically rated. Use only UL-listed conduit for wire runs.
Tip 2: Plan for Expansion
PVC expands and contracts with temperature changes. Use expansion couplings in long runs, especially outdoors.
Tip 3: Use Primer and Solvent Cement for Watertight Seals
In wet or underground environments, follow best practices for gluing joints. Allow cure time before burial or pulling wires.
Tip 4: Match Temperature Ratings
Conductors must not exceed the maximum temperature rating of the PVC conduit—typically 90°C (194°F).
Conclusão
Schedule 40 PVC conduit stands out as one of the most widely used electrical conduit solutions in both residential and commercial applications. Its blend of durability, corrosion resistance, ease of installation, and cost-effectiveness makes it a trusted choice for protecting electrical wiring across a variety of environments—from underground systems to interior walls and exposed outdoor runs.
Throughout this guide, we’ve explored its core features, relevant NEC code permissions, manufacturing processes, fittings, and comparisons with other types like Schedule 80 and standard PVC pipe. We’ve also covered essential buying tips and practical installation guidelines to help ensure your project is both safe and compliant.
As with any electrical infrastructure product, choosing the right conduit involves more than just picking a size—it’s about understanding performance needs, environmental conditions, and code requirements. Whether you’re a contractor, builder, or engineer, Schedule 40 PVC conduit offers a flexible, reliable solution that continues to evolve with modern building demands.
Perguntas frequentes
Para que é usado o conduíte de PVC Schedule 40?
O conduíte de PVC Schedule 40 é usado principalmente para proteger e direcionar a fiação elétrica em aplicações residenciais, comerciais e industriais. É adequado para instalações acima do solo e subterrâneas, incluindo uso em paredes, tetos, pisos, enterramento direto e revestimento de concreto. Também é aprovado para ambientes úmidos e corrosivos quando instalado com conexões compatíveis.
Para que é usado o tubo de PVC Schedule 40?
O tubo de PVC Schedule 40 é normalmente utilizado em aplicações hidráulicas, como distribuição de água potável, irrigação e sistemas de drenagem. Embora possa parecer semelhante a um conduíte, ele é projetado para transporte de fluidos e não é classificado para uso elétrico.
O PVC Anexo 40 pode ser enterrado?
Sim, o conduíte de PVC Anexo 40 é aprovado para enterramento direto e para revestimento em concreto, desde que seja instalado de acordo com o Artigo 352 do NEC e os códigos locais. No entanto, em áreas sujeitas a danos físicos, o Anexo 80 pode ser necessário.
Qual deve ser a profundidade do conduíte de PVC sob o concreto?
Geralmente, conduítes não metálicos requerem 60 cm de profundidade de enterramento; se estiverem sob lajes de concreto em ambientes comerciais ou industriais, devem ser enterrados a pelo menos 45 cm de profundidade. Os requisitos de profundidade podem variar de acordo com a voltagem, a localização e a carga de tráfego, portanto, sempre confirme com as autoridades locais.
É possível misturar PVC Schedule 40 e Schedule 80?
Sim, os conduítes de PVC Schedule 40 e 80 podem ser conectados usando conexões padrão, pois ambos os tipos têm o mesmo diâmetro externo. No entanto, eles têm diferentes espessuras de parede e classificações de resistência, portanto, a combinação deve ser feita com cautela e, normalmente, apenas ao transitar entre áreas com diferentes requisitos de proteção.
É possível usar PVC Schedule 40 para fiação elétrica?
Somente conduítes de PVC Schedule 40 (marcados e listados para uso elétrico) podem ser usados em instalações elétricas. Tubos de PVC Schedule 40 comuns usados em encanamentos não devem ser usados como substitutos de conduítes, pois não atendem aos requisitos de proteção contra chamas e fumaça dos códigos elétricos.
Como dobrar um conduíte de PVC Schedule 40?
O conduíte de PVC Schedule 40 pode ser dobrado usando uma fonte de calor, como uma pistola de ar quente ou uma manta térmica de PVC especializada. Uma vez amolecido, pode ser moldado usando uma forma ou guia de dobra. Ele deve ser resfriado no local para manter sua forma. Mas evite o superaquecimento.
Quanto tempo dura um conduíte de PVC Schedule 40?
Quando instalado corretamente e protegido contra exposição extrema aos raios UV ou danos mecânicos, o conduíte de PVC Schedule 40 pode durar 50 anos ou mais. Sua resistência à corrosão, umidade e produtos químicos o torna altamente durável na maioria dos ambientes.
Qual é a diferença entre PVC branco e PVC cinza?
White PVC is typically used for plumbing and water systems and is not rated for electrical use.
Grey PVC is specifically manufactured for electrical applications, is UV-resistant, and complies with UL and NEC requirements for flame retardance and insulation.




