
목차
Have you ever wondered whether you should use conduit or trunking for your next wiring job? Many people get confused by these two electrical systems, and choosing the wrong one can lead to costly problems or installation headaches.
In this article, we’ll explain the key differences between conduit and trunking in simple terms. You’ll learn when to use each system, how they protect your wires, and which one is best for different types of projects. By the end, you’ll be able to make the right choice with confidence and ensure your installation is both safe and efficient.
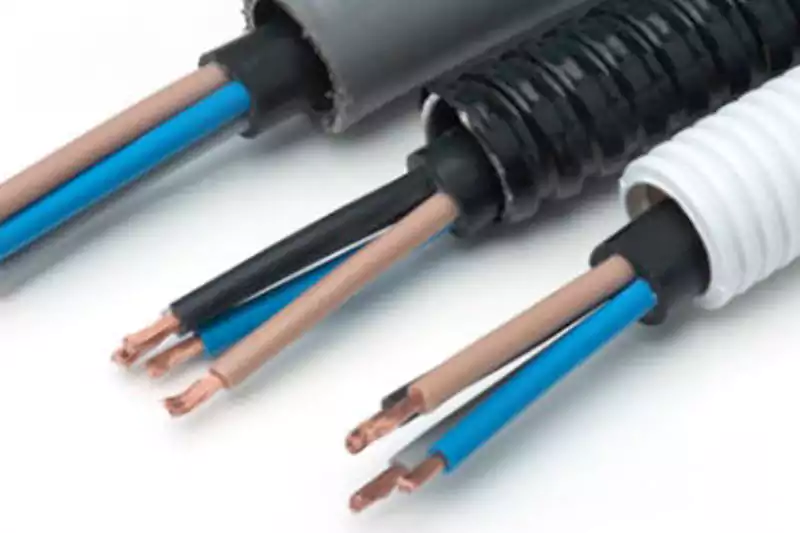

전선관은 전기 케이블을 감싸는 보호 채널 또는 튜빙을 의미하며, 외부 요소로부터 보호하고 전선과의 우발적인 접촉을 방지합니다. 경성 전선관과 연성 전선관 등 다양한 유형으로 제공됩니다. 경성 전선관은 일반적으로 금속이나 PVC로 제작되며, 기계적 강도가 높아 산업 현장에서 널리 사용됩니다. 반면, 연성 전선관은 일반적으로 PVC 또는 금속 코팅 재질로 제작되며, 굴곡이나 진동이 심한 곳에서도 유연하고 설치가 용이합니다.
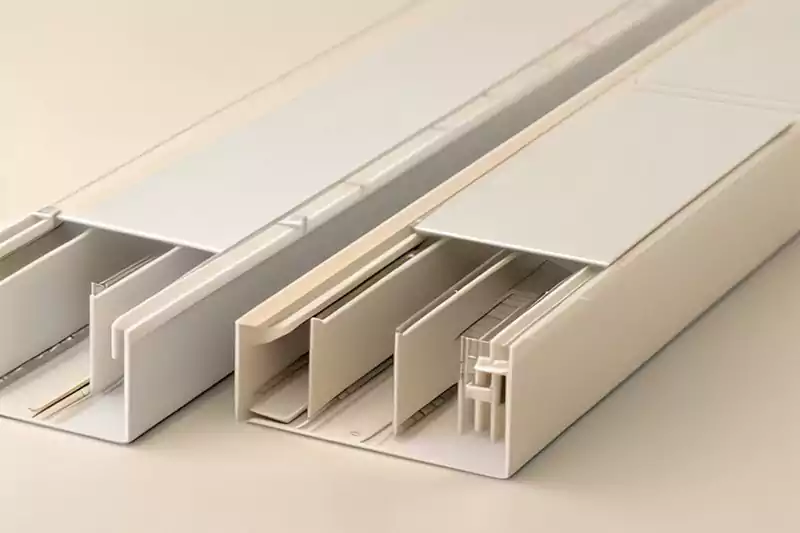

트렁킹(케이블 트렁킹 또는 와이어웨이라고도 함)은 전기 케이블을 수용하는 밀폐형 경로 시스템으로, 체계적인 배선 및 보호 기능을 제공합니다. 트렁킹은 베이스와 덮개로 구성되어 있으며, 케이블 설치 또는 유지 보수를 위해 쉽게 열 수 있습니다. 트렁킹은 다양한 크기와 수량의 케이블을 수용할 수 있도록 직사각형, 정사각형, 원형 등 다양한 크기와 모양으로 제공됩니다. 일반적으로 PVC나 금속과 같은 재질로 제작되어 내구성과 전기 절연성을 제공합니다.
배선 보호: 전선관과 트렁킹의 주요 목적 중 하나는 전기 배선을 물리적 손상, 습기, 화학 물질 및 기타 외부 요인으로부터 보호하는 것입니다. 케이블을 보호 하우징 안에 넣음으로써 이러한 구성 요소는 단락이나 감전과 같은 사고 위험을 최소화하여 개인의 안전과 전기 시스템의 무결성을 보장합니다.
조직과 깔끔함: 전선관과 트렁킹은 정돈되고 미관적으로 아름다운 전기 설비에 기여합니다. 케이블의 체계적인 배선을 통해 복잡하고 혼란스러운 배선을 방지할 수 있습니다. 이러한 체계적인 관리는 향후 유지 관리 또는 문제 해결 작업을 간소화하여 시간과 노력을 절약해 줍니다.
표준 준수: 전선관과 트렁킹은 전기 관련 법규 및 산업 표준을 충족하는 데 중요한 역할을 합니다. 이러한 표준은 전선관과 트렁킹의 종류, 크기 및 설치 방법을 명시하여 전기 설비의 균일성과 일관성을 보장합니다. 이러한 표준을 준수하는 것은 규정 준수와 전기 시스템의 안전 및 신뢰성 확보에 필수적입니다.
유연성과 적응력: 전선관 및 트렁킹 시스템은 전기 시스템의 변경이나 추가에 유연하게 대응할 수 있습니다. 대규모 수정 없이도 배선을 쉽게 재연결하거나 확장할 수 있습니다. 이러한 유연성 덕분에 전선관 및 트렁킹은 개조 및 업그레이드가 잦은 주거 및 상업 시설 모두에 적합합니다.
전선관은 전기 케이블을 감싸는 보호 채널 또는 튜브로, 안전한 통로와 절연을 제공합니다. 전선관의 주요 목적은 전기 배선을 물리적 손상, 습기 및 환경 요인으로부터 보호하는 것입니다. 전선관은 케이블을 감싸고 차폐함으로써 전기 시스템의 안전성과 수명을 보장합니다.
도관은 다양한 재질로 제공되며, 각 재질은 서로 다른 특성과 용도에 대한 적합성을 제공합니다. 일반적인 재질은 다음과 같습니다.
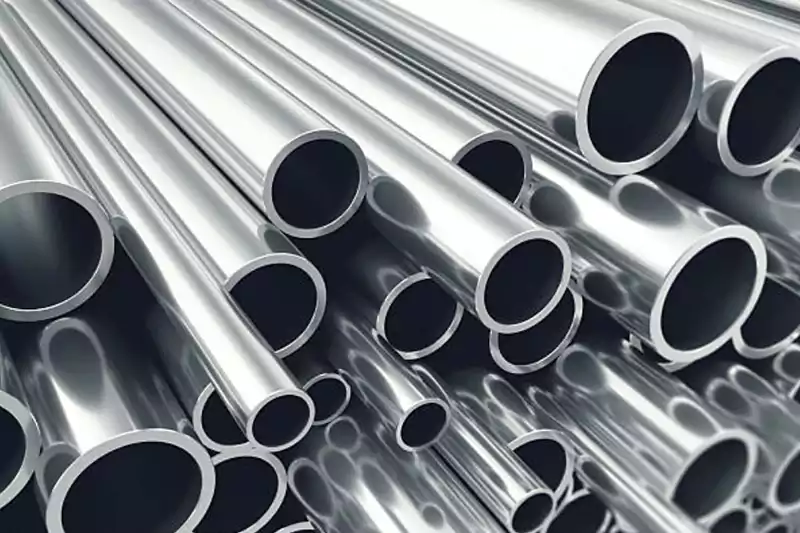

강성 금속 도관(RMC): 강철로 제작된 RMC는 높은 기계적 강도와 내구성으로 유명합니다. 견고한 보호가 필요한 산업 및 상업 분야에서 일반적으로 사용됩니다.
전기 금속 튜브(EMT): EMT는 아연 도금 강철 또는 알루미늄으로 제작되어 가볍고 비용 효율적인 옵션을 제공합니다. 주거 및 상업 분야에서 일반적으로 사용됩니다.
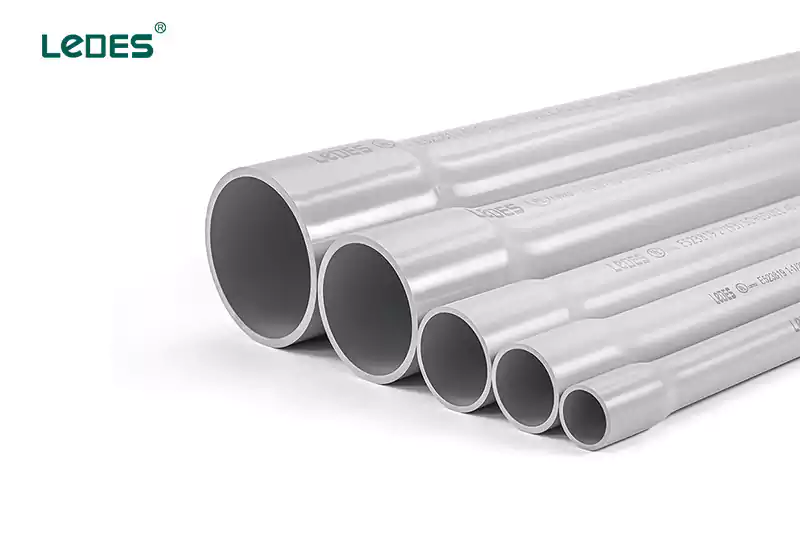

폴리염화비닐(PVC) 도관: PVC 도관 뛰어난 내식성, 합리적인 가격, 그리고 간편한 설치로 인해 많은 사랑을 받고 있습니다. 다양한 두께로 제공되며, 주거, 상업, 산업 분야에서 널리 사용됩니다.
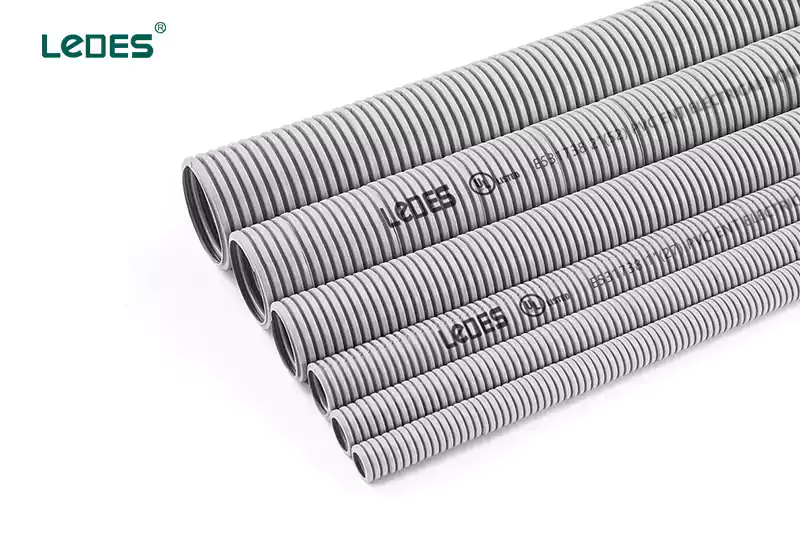

유연 금속 도관(FMC): FMC는 유연한 PVC 코팅이 된 나선형 금속 스트립으로 구성되어 있습니다. 급격한 굽힘이나 진동과 같이 유연성이 필요한 곳에 설치가 간편하고 다재다능합니다.
액체가 새지 않는 유연 전선관(LFMC): LFMC는 액체 저항성 코팅이 된 유연한 도관으로, 액체나 습기에 노출되는 것이 우려되는 곳에 적합합니다.
전기 비금속 튜빙: PVC로 만든 전기 비금속 튜빙(ENT)은 다음과 같이 알려져 있습니다. 유연한 도관 플라스틱 도관은 건물의 전기 배선을 보호하고 연결하는 데 사용되는 일종의 전기 도관입니다.
미국과 캐나다에서는 전선관, 특히 PVC 전선관 설치 시 특정 표준 및 규정을 준수해야 합니다. 미국의 국가전기규정(NEC)과 캐나다의 캐나다전기규정(CEC)은 전선관 크기, 배선, 지지대, 접지 요건 등의 측면을 포함하는 전선관 설치 지침을 제공합니다. 이러한 규정은 전기 규정의 통일성, 안전성 및 준수를 보장합니다.
PVC 도관은 시중에서 가장 인기 있는 제품이며, 강성 PVC 도관 및 비금속 튜빙과 같은 가장 많이 사용되는 PVC 유형은 다음 사항을 준수해야 합니다.
미국에서는 UL651, UL1653, NEMA TC-2
캐나다: CSA C22.2 No.211.2, CSA C22.2 No.227.1

Conduit은 다음을 포함한 다양한 전기 설비에 적용됩니다.
벽, 천장, 바닥에 숨겨진 배선.
조명기구, 콘센트, 스위치의 배선.
조경 조명과 같은 야외 전기 설비.
상업용 건물, 사무실, 소매 공간의 배선.
산업용 기계 및 장비 배선.
가연성 또는 폭발성 환경으로부터 도관이 추가적으로 보호해주는 위험한 장소입니다.
- 물리적 손상, 습기, 환경적 요인으로부터 보호합니다.
- 감전이나 단락 위험을 줄여 안전성을 강화했습니다.
- 체계적이고 깔끔한 정리로 유지관리와 문제 해결이 간소화됩니다.
- 향후 전기 시스템을 수정하거나 업그레이드할 수 있는 유연성이 있습니다.
- 전기 관련 규정 및 기준을 준수하여 안전과 규정 준수를 보장합니다.
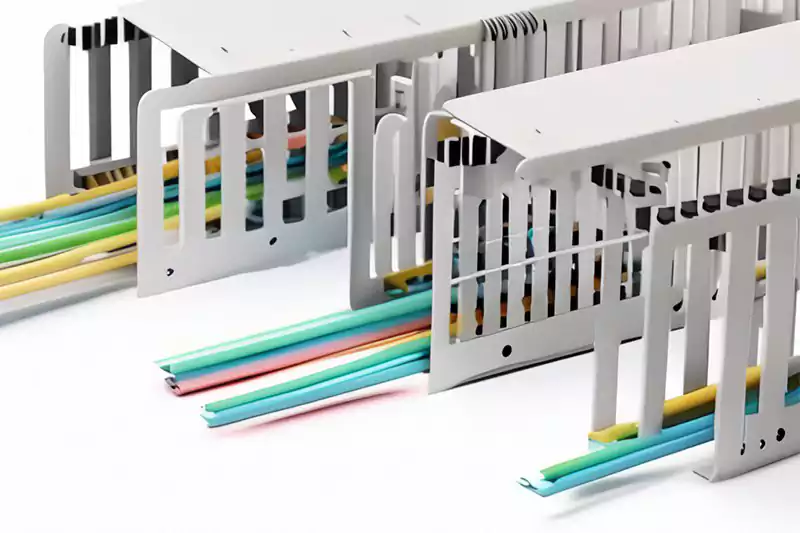
트렁킹(케이블 트렁킹 또는 와이어웨이라고도 함)은 전기 케이블의 보호 도관 역할을 하는 밀폐형 경로 시스템입니다. 대부분의 경우 직사각형 또는 정사각형 모양이며, 덮개는 분리할 수 있습니다. 트렁킹의 주요 목적은 케이블을 깔끔하고 효율적으로 정리하고 배선하여 전기 시스템의 설치, 유지 보수 및 문제 해결을 용이하게 하는 것입니다. 트렁킹은 케이블에 안전하고 정돈된 환경을 제공하여 손상, 엉킴 또는 우발적인 접촉 위험을 최소화하는 데 중요한 역할을 합니다.
케이블 트렁킹(케이블 덕팅이라고도 함)은 전기 케이블을 보호하고 배선하기 위해 특별히 설계된 트렁킹의 한 유형입니다. 다양한 크기와 재질(PVC, 금속, 복합 소재 등)로 제공되어 다양한 케이블 용량과 환경 조건에 대응할 수 있습니다. 케이블 트렁킹은 일반적으로 주거, 상업 및 산업 환경에서 전력, 데이터 또는 통신 케이블의 체계적인 경로를 구축하는 데 사용됩니다.
조명 트렁킹은 조명 기구 설치를 위해 특별히 설계되었습니다. 여러 조명 지점으로 전원 및 제어 케이블을 연결하는 편리하고 체계적인 솔루션을 제공합니다. 조명 트렁킹은 조명 기구를 위한 통합 장착 옵션이 있는 조립식 섹션을 특징으로 하는 경우가 많아 설치 및 유지 관리가 간편합니다. 상업용 건물, 소매점, 그리고 대규모 조명 시설에 널리 사용됩니다.
버스바 트렁킹(BBT) 건물 및 산업 시설의 전력 분배에 사용되는 트렁킹 시스템입니다. 이 시스템은 전력 전송에 사용되는 도체인 여러 개의 버스 바(bus-bar)를 수용하는 금속 외함으로 구성됩니다. BBT는 전력 분배를 위한 작고 효율적인 솔루션을 제공하여 긴 케이블 설치와 개별 배선의 필요성을 줄입니다. 조명, 기계 또는 HVAC 시스템과 같이 고전력 부하를 공급해야 하는 애플리케이션에 일반적으로 사용됩니다.

다중 구획 트렁킹은 단일 인클로저 내에 별도의 구획 또는 채널을 갖추고 있습니다. 각 구획은 전원 케이블, 데이터 케이블, 통신 케이블 등 다양한 유형의 케이블을 분리된 상태로 수용하도록 설계되었습니다. 이러한 설계는 단일 트렁킹 시스템 내에서 다양한 서비스를 분리하여 깔끔하고 체계적인 솔루션을 제공하는 동시에 다양한 유형의 케이블 간 간섭이나 혼선 위험을 줄입니다. 다중 구획 트렁킹은 여러 서비스를 효율적으로 라우팅하고 관리해야 하는 사무실 건물, 데이터 센터 및 기타 시설에서 일반적으로 사용됩니다.
네트워킹에서 트렁킹은 여러 개의 물리적 네트워크 연결을 결합하여 전체 용량과 안정성을 높이는 링크 통합(link aggregation) 개념을 의미합니다. 이 기술은 더 높은 대역폭과 향상된 네트워크 성능을 제공합니다. 트렁킹은 트래픽을 통합된 링크에 분산시키는 로드 밸런싱과 하나의 링크에 장애가 발생하더라도 중단 없는 네트워크 연결을 보장하는 이중화를 가능하게 합니다. 트렁킹은 네트워크 용량을 향상시키고 내결함성을 제공하므로 데이터 센터나 기업 네트워크와 같이 수요가 높은 환경에서 특히 유용합니다.

전기 및 네트워킹 환경에서 트렁킹 기술은 호환성과 상호운용성을 보장하기 위해 표준과 프로토콜을 준수하는 경우가 많습니다. 일반적인 표준 및 프로토콜은 다음과 같습니다.
IEEE 802.3ad: 이 표준은 이더넷 트렁킹을 위한 LACP(Link Aggregation Control Protocol)를 정의하여 동적 집계 링크 생성 및 관리를 가능하게 합니다.
가상 라우터 중복 프로토콜(VRRP): VRRP는 여러 라우터가 공유할 수 있는 가상 IP 주소를 생성하여 라우팅에서 자동 장애 조치 및 중복성을 제공하는 네트워크 프로토콜입니다.
IEEE 802.1Q: IEEE 802.1Q 표준은 VLAN(Virtual Local Area Network) 태깅으로도 알려져 있으며, 컴퓨터 네트워크에서 가상 LAN을 구현하는 데 사용되는 프로토콜입니다. 네트워크 인프라 내에서 서로 다른 VLAN을 식별하고 구분하는 방법을 제공합니다.
트렁킹은 다양한 애플리케이션에서 수많은 이점을 제공합니다.
케이블 관리: 트렁킹 시스템은 케이블의 체계적이고 구조화된 경로를 제공하여 엉킴, 손상 또는 우발적인 단선 위험을 최소화합니다. 이를 통해 설치, 유지 관리 및 문제 해결 프로세스가 간소화됩니다.
보호: 트렁킹은 먼지, 습기 또는 물리적 충격과 같은 외부 요소로부터 케이블을 보호하여 전기 또는 네트워크 인프라의 수명과 안정성을 보장합니다.
확장성: 트렁킹 시스템을 사용하면 케이블을 쉽게 확장하고 수정할 수 있어 향후 시스템 확장이나 변경에도 대응할 수 있습니다.
안전 및 규정 준수: 트렁킹은 전기 코드와 규정을 준수하여 케이블을 위한 안전한 환경을 제공하고 전기적 위험의 위험을 줄여줍니다.
능률: 트렁킹은 케이블 라우팅을 간소화하고, 설치 시간을 절약하며, 네트워킹 컨텍스트에서 링크 집계 및 부하 분산을 통해 시스템 성능을 향상시킵니다.
트렁킹 시스템은 효율적인 케이블 관리, 향상된 조직화, 향상된 시스템 성능을 제공하므로 전기 및 네트워크 설비에 필수적인 구성 요소입니다.
도관은 금속이나 PVC와 같은 재료로 만들어진 단단하거나 유연한 관 모양의 구조물입니다.
일반적으로 원형 단면을 갖지만 직사각형이나 정사각형 도관도 사용 가능합니다.
전선관은 개별 케이블이나 전선을 둘러싸고 보호하도록 설계되었습니다.
노출된 설치나 숨겨진 설치 모두에 사용할 수 있습니다.
트렁킹은 일련의 상호 연결된 구획이나 구획으로 구성된 폐쇄형 경로 시스템입니다. 일반적으로 직사각형이나 정사각형 모양입니다.
PVC, 금속 또는 합성물과 같은 재료로 만들어질 수 있습니다.
트렁킹은 여러 케이블을 수용하고 케이블을 연결하고 보호하기 위한 경로를 제공하도록 설계되었습니다.
트렁킹은 일반적으로 표면 장착형이나 가공 설치에 사용됩니다.

전선관 설치에는 전선관에 개별 케이블을 꿰거나 미리 배선된 케이블을 끌어당기는 작업이 포함됩니다.
원하는 경로에 맞게 도관을 구부리고 자르는 작업이 필요합니다.
전선은 클램프나 브래킷으로 고정해야 할 수도 있습니다.
전선관 구간을 연결하려면 종종 피팅, 커넥터 또는 커플링이 필요합니다.
트렁킹 설치에는 브래킷, 클립 또는 나사를 사용하여 트렁킹 섹션을 벽, 천장 또는 바닥에 부착하는 작업이 포함됩니다.
케이블은 트렁크 칸에 깔거나 삽입됩니다.
트렁킹을 사용하면 분리형 커버나 액세스 포인트를 통해 케이블에 쉽게 접근할 수 있습니다.
트렁킹 섹션은 호환되는 커넥터나 커플링을 사용하여 연결하거나 확장할 수 있습니다.

전선관은 일반적으로 주거 및 상업 환경에서 모두 사용됩니다.
전기 배선, 통신, 데이터 케이블 등 개별 케이블 보호 및 분리가 필요한 설비에 적합합니다.
전선관은 종종 벽, 바닥 또는 천장 내부의 은폐된 설치에 사용됩니다.
트렁킹은 상업, 산업, 기관 등에서 널리 사용됩니다.
전력 분배, 데이터 센터, 오디오/비디오 설치 등 여러 개의 케이블이나 전선이 필요한 설치에 이상적입니다.
트렁킹은 케이블 라우팅이 눈에 띄고 쉽게 접근 가능해야 하는 표면 장착 설치에 일반적으로 사용됩니다.
전선관은 자재비, 부속품비, 노동집약적 설치비 등으로 인해 비용이 더 많이 들 수 있습니다.
비용은 도관 유형(강성, 유연성)과 재료(금속, PVC)에 따라 달라질 수 있습니다.
트렁킹은 특히 여러 개의 케이블이 있는 설비의 경우 도관에 비해 비용 효율성이 높은 경우가 많습니다.
비용은 트렁킹 재질, 크기, 설치의 복잡성에 따라 달라질 수 있습니다.
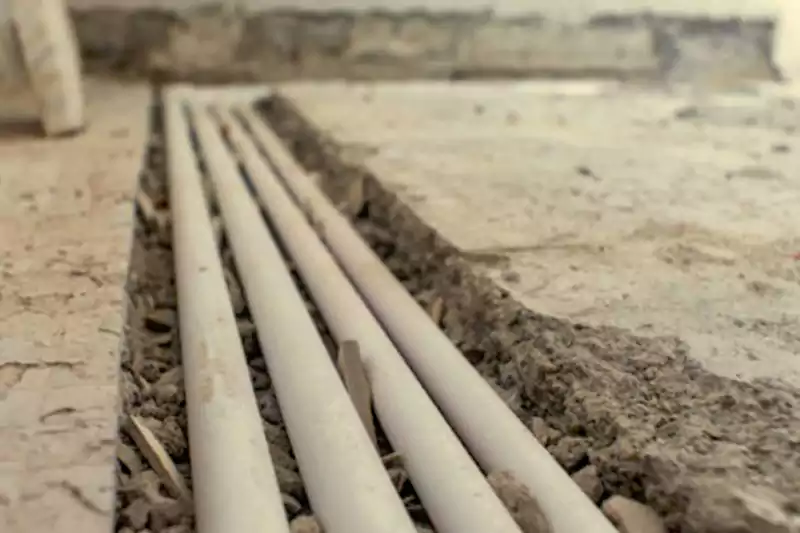

도관은 설치 후 케이블에 대한 접근이 제한적이어서 개조나 수리를 위해 분해나 절단이 필요합니다.
배관은 밀폐된 구조로 되어 있어 유지관리나 문제 해결에 더 많은 노력과 시간이 필요할 수 있습니다.
트렁킹은 분리형 커버나 액세스 포인트를 통해 케이블에 쉽게 접근할 수 있게 하여 유지관리, 개조 및 문제 해결을 간소화합니다.
트렁킹을 사용하면 전체 시스템을 중단하지 않고도 케이블을 쉽게 재구성하거나 추가할 수 있습니다.
도관은 물리적 손상, 습기, 환경적 위험으로부터 더 나은 보호 기능을 제공합니다.
금속 도관과 같은 더 높은 내화 등급의 재료를 사용하여 내화성이 더욱 향상되었습니다.
트렁킹 역시 케이블 보호 기능을 제공하지만 도관에 비해 물리적 손상에 대한 저항력이 떨어질 수 있습니다.
내화성은 사용된 트렁크 재료에 따라 달라질 수 있습니다.
전선관과 트렁킹 중 어떤 것을 선택할지 결정할 때는 구체적인 프로젝트 요건, 규정 및 예산을 고려하는 것이 중요합니다. 케이블 수량, 설치 위치, 접근성, 화재 안전 요건 등의 요소가 의사 결정에 영향을 미칩니다. 전기 전문가와 상담하거나 프로젝트 요건을 면밀히 분석하면 전선관과 트렁킹 중 적절한 것을 선택할 수 있습니다.
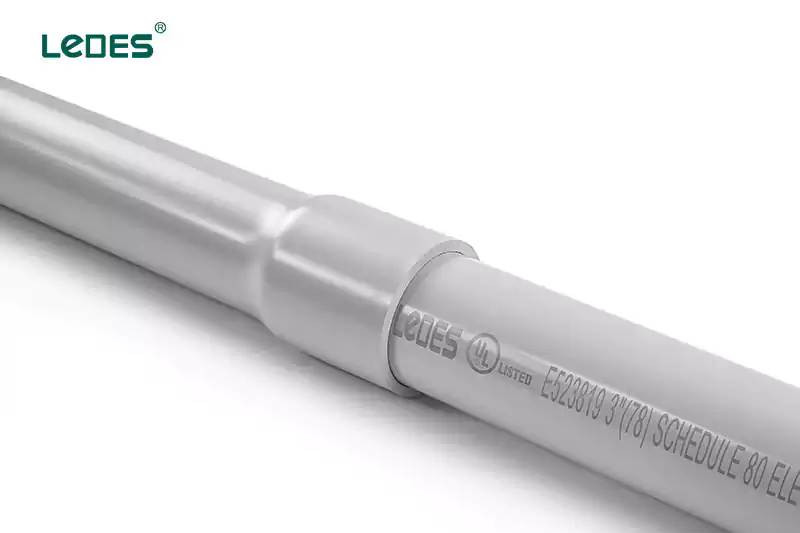

- Planning: Determine the conduit size, type (rigid or flexible), and material based on the application and local electrical codes.
- 경로 계획: Map out the desired conduit path, considering obstacles, bends, and required access points.
- 표시: Use a pencil or marker to mark the conduit’s path on the walls, floors, or ceilings.
Mounting: Install conduit clamps or brackets at regular intervals along the marked path to secure the conduit.
- Cutting and Bending: Cut the conduit sections to the required lengths using a hacksaw or conduit cutter. Use a conduit bender to create bends where necessary.
- Threading or Pulling: Thread individual cables through the conduit or use pre-wired cables and pull them through the conduit sections.
- Joining: Use appropriate fittings, connectors, or couplings to join conduit sections together securely.
- 접지: Ensure proper grounding of the conduit system by connecting grounding wires to each conduit section and to the grounding system.
- Securing and Fastening: Secure the conduit system firmly in place using clamps, straps, or fasteners.
- Testing: Conduct necessary tests to ensure proper installation, such as continuity, insulation resistance, or voltage drop tests.
- Covering: Install conduit covers or fittings to protect the exposed ends of the conduit and ensure safety.
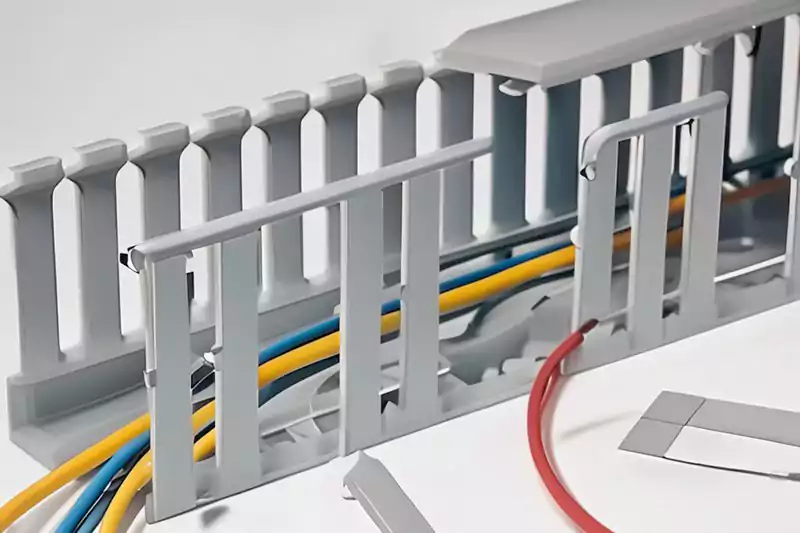
- Planning: Determine the trunking size, material, and configuration based on the number and types of cables to be accommodated.
- Route Planning: Decide on the trunking path, considering accessibility, cable management, and aesthetics.
- 설치: Attach trunking brackets, clips, or screws to the walls, ceilings, or floors at suitable intervals along the planned path.
- Cutting: Cut trunking sections to the desired lengths using appropriate cutting tools, following manufacturer guidelines.
- Joining: Connect trunking sections together using compatible connectors or couplings.
- Cable Placement: Lay or insert the cables into the trunking compartments, ensuring proper organization and segregation.
- Covering: Install trunking covers or access points, providing easy access to the cables while ensuring their protection.
- Fixing: Secure the trunking system firmly in place using the provided fasteners or clips.
- Testing: Conduct necessary tests, such as continuity or cable integrity checks, to ensure proper installation.
- 라벨링: Label the trunking sections or compartments to aid identification and maintenance activities.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct routine inspections of the conduit or trunking system to identify any signs of damage, wear, or loose connections. Check for corrosion, dents, or physical impacts.
- 청결: Keep the conduit or trunking system clean, removing any dust, debris, or obstructions that may accumulate over time.
- 케이블 관리: Ensure cables are properly organized and secured within the conduit or trunking system, avoiding excessive bending, twisting, or strain.
- Repair and Replacement: Promptly repair or replace damaged conduit or trunking sections, fittings, or covers to maintain system integrity.
- 습기 보호: Take measures to prevent water or moisture ingress into the conduit or trunking system, such as sealing entry points or using waterproof gaskets.
- Grounding Integrity: Regularly inspect and maintain proper grounding connections within the conduit or trunking system to ensure electrical safety.
- Labeling and Documentation: Maintain accurate labeling of cables and document any changes or additions to the conduit or trunking system for future reference and troubleshooting purposes.
- 법규 및 표준 준수: Ensure that the installation and maintenance practices adhere to relevant electrical codes, regulations, and industry standards.
Regular maintenance and adherence to proper installation procedures will help ensure the longevity, safety, and performance of both conduit and trunking systems.

Conduit is commonly used in outdoor and damp environments, offering protection against moisture and chemicals. It is ideal for installations that may undergo future changes and can be easily altered or removed. Conduit is also effective in minimizing electromagnetic interference when using metal conduit systems.
Trunking is often used for power distribution in buildings, equipment, and switching yards where multiple electrical cables are involved. It excels in cable management, providing easy accessibility and organization of cables. Trunking systems are suitable for applications that require high current distribution and where aesthetic considerations are important.

Trunking efficiency refers to the effectiveness and utilization of trunking systems in efficiently managing and distributing cables. It measures how well the trunking system optimizes the available space and resources while maintaining effective cable management.
Here are some factors that contribute to trunking efficiency:
Cable Capacity: Trunking efficiency is influenced by the capacity of the trunking system to accommodate the number and size of cables required for a specific application. A well-designed trunking system should have sufficient capacity to handle the current and future cable requirements without overcrowding or excessive cable congestion.
Cable Organization: Efficient trunking systems ensure proper organization and bundling of cables. This includes using appropriate cable management accessories such as cable ties, clips, or trays to neatly arrange and route cables within the trunking. Well-organized cables minimize the risk of tangles, twists, or obstructions, making maintenance and troubleshooting easier.
공간 활용: Trunking efficiency is also related to how effectively the available space is utilized. A well-designed trunking system maximizes the use of available space while considering factors such as cable bend radius, ventilation requirements, and access for maintenance. Efficient use of space ensures that the trunking system can accommodate the required cables without unnecessary wastage or overcrowding.
Scalability and Future Expansion: Trunking efficiency includes the ability of the system to scale and accommodate future cable additions or modifications. A flexible trunking system can easily adapt to changing needs, allowing for the seamless integration of new cables or the removal of obsolete ones. This scalability minimizes disruption and the need for extensive rework in the future.
접근성 및 유지 관리: An efficient trunking system provides easy access to cables, allowing for quick and convenient maintenance, repairs, or modifications. Trunking systems with removable covers or access points simplify the process of adding or removing cables, reducing downtime and minimizing disruption to the overall network or infrastructure.

The choice between cable tray and conduit as a wiring system design depends on various factors and the specific requirements of the project. Both systems have their advantages and considerations. Cable trays are typically more suitable for managing large cable volumes, providing flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. On the other hand, conduit offers superior cable protection, EMI shielding, and compliance with certain regulations. In some cases, a combination of both cable tray and conduit systems may be used, leveraging the strengths of each system for different sections of the installation. It is recommended to consult with electrical professionals and consider the specific requirements and constraints of the project before making a decision.
Conduit and trunking systems play a vital role in managing electrical cables by providing protection, organization, and routing. This article covered key points about these systems. Conduits enclose and safeguard cables, while trunking systems facilitate neatness and easy identification. Both contribute to safety by minimizing electrical hazards. Conduit options include rigid metal, intermediate metal, and flexible conduits, each with specific applications. Trunking systems are typically made of PVC or metal. Factors to consider when choosing between conduit and trunking include required protection levels, environmental factors, ease of installation, cost, and compliance with regulations. Seeking professional advice from electricians or engineers is strongly advised for proper system selection and installation. Professionals ensure adherence to safety standards and regulations, resulting in a reliable and secure electrical infrastructure.
Any more questions about cable or wiring systems, Ledes is here for helping resolving the wiring problems. Send us an email 또는 submit a filled form at any time.
자주 묻는 질문
What is the main difference between conduit and trunking?
Conduit is a round, typically rigid or flexible tube that protects individual cables, while trunking is a rectangular or square enclosure that organizes and routes multiple cables for neatness and easy future access.
In what situations should I use conduit vs. trunking?
Choose conduit for installations needing superior protection against physical damage or moisture (e.g., outdoor or industrial), and trunking for managing many cables in accessible, organized runs, such as in offices or data centers.
What materials are commonly used for conduit and trunking?
Conduits are often metal (steel, aluminum) or PVC, while trunking is generally made from PVC, metal, or composite materials.
How do installation methods differ for conduit and trunking?
전선관은 밀폐된 파이프를 통해 케이블을 끼워 넣거나 당겨야 하며, 종종 굴곡부와 부속품이 필요합니다. 반면 케이블 트렁킹은 탈착식 덮개를 통해 쉽게 접근할 수 있고 여러 케이블을 신속하게 설치할 수 있도록 해줍니다.
What are the advantages of using trunking in large installations?
Trunking simplifies cable management, enables easy modifications, reduces clutter, and provides clear separation among power, data, and communication lines.
Does conduit or trunking offer better fire or electrical safety?
Metal conduit offers superior fire and EMI (electromagnetic interference) protection. Trunking fire safety varies by material; always check local regulations for compliance.
Are there standards or codes for using conduit and trunking?
Yes. Installation must follow national and local electrical codes (e.g., NEC in the US, IEC, CSA), covering type, sizing, routing, supports, and materials used.
How does cost compare between conduit and trunking installations?
Conduits are usually costlier due to material and labor, especially in complex runs. Trunking is more economical for managing multiple cables in accessible environments.
Is maintenance easier with trunking or conduit?
Trunking offers easier maintenance – just remove the cover for cable access. Conduits often require more time to access or replace individual wires.
Can conduit and trunking be combined in a single project?
Yes. Many installations combine conduit (for protection where needed) and trunking (for cable management), leveraging the advantages of both systems as required by the project.




