목차
In the world of electrical conduits, customers often ask about the distinctions between DB2 conduit and Schedule 40 conduit. While both are widely used for protecting electrical wiring, each has unique properties, compliance standards, and application benefits. Choosing the right conduit depends on a project’s specific needs, such as strength requirements, installation environment, and regulatory compliance. This article provides a comprehensive comparison of DB2 and Schedule 40 conduits, covering their definitions, standards, mechanical properties, fitting options, and applications, to help you choose the right conduit for your project.
DB2 conduit, or Direct Burial 2 conduit, is a type of rigid, non-metallic conduit specifically engineered for underground installations. It is designed to endure external pressures from soil and resist environmental corrosion. DB2 conduit complies with CSA C22.2 NO. 211.1, a Canadian standard that certifies its durability for direct burial in diverse soil conditions.
Schedule 40 conduits is a rigid PVC (polyvinyl chloride) conduits designed for both above-ground and below-ground installations. Known for its durability, it can be installed in exposed or concealed spaces and provides excellent protection for electrical wiring in both indoor and outdoor environments. Which appliable for Low-voltage cables are used for telephone, internet, television, and security system wiring protection. Schedule 40 conduit must meet the UL651 standard, which specifies the performance and safety requirements for plastic conduit.

DB2 Conduit: CSA C22.2 NO.211.1, this standard sets guidelines for direct burial use in underground applications in Canada.
일정 40 PVC 도관: UL651, the standard governs the performance, durability, and safety requirements for PVC conduit in the U.S.
These standards ensure that each conduit type meets specific mechanical and safety performance metrics, making them reliable choices for their intended applications.
Both DB2 and Schedule 40 conduits must adhere to a set of properties as outlined in their respective standards. Here are comes common required properties:

일정 40 도관
According to UL651, Schedule 40 rigid PVC conduit must meet a specific tensile strength requirement. It must not be less than 5000 psi (34.5 MPa) in unaged specimens. This strength ensures the conduit can withstand significant stress without elongation or breaking, making it suitable for both above-ground and underground applications where exposure to environmental variations, movement, or handling might introduce tensile stresses. In any case, tensile strength of conduit shall not be less than:
- a) 5,000 psi (34.5 MN/m2) (3.45 kN/cm2) (3515 gf/mm2) for Schedule 40 and 80 rigid PVC conduit
- b) 4000 lbf/in2 (27.6 MN/m2 or 2.76 kN/cm2 or 2812 gf/mm2) for Type A and EB rigid PVC conduit
To assess this requirement, three unaged specimens of Schedule 40 conduit are tested to determine their baseline tensile strength. These specimens are then aged, and the average tensile strength of the aged samples must equal or exceed 95% of the average tensile strength of the unaged specimens. This aging test follows procedures similar to those described in the Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics (ASTM D 638), ensuring the conduit retains its strength under different conditions.
These specifications make Sch 40 conduit an excellent choice for applications that require durable, high-strength conduits, even in environments where temperature fluctuations or potential exposure to stressors are more common.
DB2 Conduit Tensile Strength
For DB2 conduit, used primarily in direct burial applications, there is no specific tensile strength requirement defined by the CSA C22.2 NO. 211.1 standard. Since DBii conduit is installed underground, where the temperature remains relatively stable and protected from the above-ground elements, it experiences less exposure to stressors that might necessitate strict tensile strength benchmarks. This stability in the installation environment helps minimize thermal expansion and contraction issues, reducing the need for high tensile strength performance in DB2 conduit.
Schedule 40 Conduit Impact Resistance
According to UL651 (Article 6.6, Table 6.2), Schedule 40 conduit must undergo a specified impact test. During this test, a 20-pound (9.1 kg) weight is dropped onto the conduit from a set height, with the weight shaped as a cylinder with a 2-inch (51 mm) diameter. This requirement ensures that Schedule 40 conduit can handle physical impact, making it suitable for exposed installations where accidental impacts may occur, such as in above-ground applications.
거래 규모 | Height above the Specimen (Schedule 40) | |
피트 | (m) | |
1/2 | 2-1/2 | 0.762 |
3/4 | 4 | 1.22 |
1 | 5 | 1.52 |
1-1/4 | 6 | 1.83 |
1-1/2 | 7-1/2 | 2.29 |
2 | 9-1/2 | 2.90 |
2-1/2 | 10-1/2 | 3.20 |
3 – 6 | 11 | 3.35 |
DB2 Duct Impact Resistance
For DB2 conduit, CSA C22.2 NO. 211.1 (Clause 6.2) specifies a different impact testing method. DB2 conduit must withstand an impact energy of 61 joules at 23 ℃ (73.4 ℉) and 34 joules at –18 ℃ (0 ℉). This method ensures that DB2 conduit maintains its integrity under varying temperatures, particularly in colder conditions where the material may be more brittle. Given its direct burial application, DB2 conduit’s impact resistance is optimized for underground environments where it may encounter forces from soil or equipment.
If you are interested in the Impact Resistance section, you can click here to read the Impact Resistance performance insights of PVC conduit written by our technical team.
도관 유형 | Impact Test Method | Weight/Force | 온도 |
일정 40 도관 | UL651, Article 6.6, Table 6.2 | 20파운드(9.1kg) | 23.0 ± 2.0℃
|
DB2 덕트 | CSA C22.2 NO. 211.0, Clause 6.3.1, Method A | 1.36 kg ± 10 g 61 J at 23 ℃, 34 J at -18 ℃ | 23 ℃ and -18 ℃ |
Resistance to crushing is a critical property for conduits, ensuring they can withstand external pressures without deformation.
Schedule 40 Conduit Resistance to Crushing
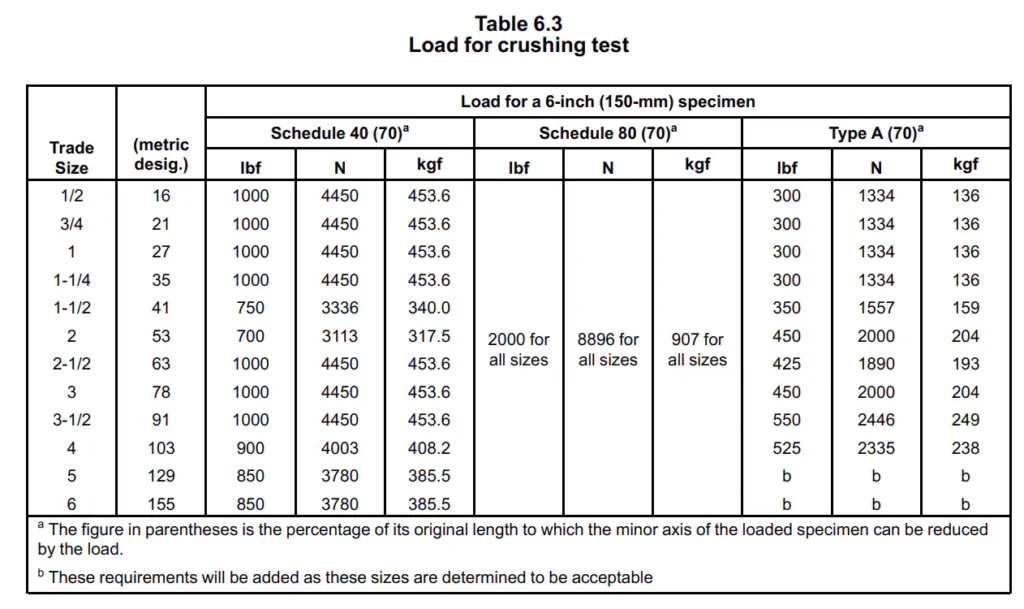
Under UL651 (Article 6.9), Schedule 40 conduit is subjected to a crush test to evaluate its resistance to deformation. And the conduit shall not flatten under the load indicated in table 6.3 to the point where they buckle, and the minor axis measured inside each loaded specimen shall not be less than 70 percent of the inside diameter of the specimen measured before loading.
- Plate Movement Rate: The plate is to be moved toward the other at the rate of rate of 1/2 ±1/8 inch (10.0 ±2.5 mm) per minute, until the load specified in Table 6.3 is applied as indicated on the dial on the machine.
The standard requires Sch 40 conduit to maintain its structural integrity up to a specific threshold, which simulates real-world conditions where the conduit may be exposed to weight or pressure from above-ground installations, such as traffic loads or heavy machinery. This ensures the conduit remains functional and safe even in environments where it might face significant physical compression.
DB2 Conduit Resistance to Crushing
For DB2 conduit, CSA C22.2 NO. 211.1 (Article 6.3) provides the specific requirements for crush resistance in direct burial applications. It requires the percentage decrease in diameter under and after recovery shall not exceed 10% on DB2, and shall not exceed 5% after recovery.
- 로드 응용 프로그램: A 90 kg mass (including the platen) is gradually applied and held for 60 ± 5 seconds.
- Diameter Measurement Under Load: While the mass is applied, the vertical inside diameter is remeasured.
- Recovery Measurement: After the load is removed, the conduit recovers for 300 ± 20 seconds before the diameter is measured again.
- Deformation Calculation: The percentage decrease in diameter is calculated, both under load and after recovery, indicating the conduit’s crush resistance.
This standard specifies that DBII conduit must endure a particular load per unit length to simulate the weight of soil or other materials that may be exerted on the conduit when buried underground. The CSA standard is designed to ensure DB2 conduit can withstand the unique stressors of buried installations, where it is not only protected from direct surface loads but also faces prolonged pressures from the surrounding soil.
Schedule 40 Conduit Stiffness
For Schedule 40 PVC conduit, pipe stiffness is assessed according to ASTM D 2412 (Standard Test Method for Determination of External Loading Characteristics of Plastic Pipe by Parallel-Plate Loading). Schedule 40 conduit used in directional boring applications must meet a minimum pipe stiffness of 120 psi (827 kPa) at 10% deflection. This ensures that Schedule 40 maintains structural integrity and resists deformation under external pressure.
DB2 Conduit Stiffness
DB2 conduit, tested per ASTM D 2412 as well, has stricter stiffness requirements given its direct burial application:
- Type EB1 Conduit: Must have a minimum pipe stiffness of 200 kPa at 5% deflection.
- Type DB2/ES2 Conduit: Must meet a higher threshold, with a minimum pipe stiffness of 300 kPa at 5% deflection.
These values ensure DB2 conduits withstand underground pressures more effectively, providing added resilience against soil loads and other environmental forces typical in burial applications.
도관 유형 | Minimum Pipe Stiffness | Deflection Percentage | Standard Test Method |
일정 40 | 120 psi (827 kPa) | 10% | ASTM D 2412 |
Type DB2/ES2 | 300kPa | 5% | ASTM D 2412 |

일정 40 도관
For Schedule 40 PVC conduit, sunlight resistance is essential to ensure long-term durability when exposed to UV radiation. According to UL651, Izod impact strength tests are conducted to measure how well the material withstands prolonged exposure to sunlight.
- Initial Impact Requirement: Unaged bar samples machined from Schedule 40 or Schedule 80 conduit must achieve an average Izod impact strength of at least 0.5 ft-lbf/inch (27 J/m) of notch width. This ensures that the conduit can handle mechanical impacts even before exposure to UV.
- Extended Sunlight Exposure Testing: Schedule 40 conduit specimens undergo conditioning for 720, 1080, and potentially 1440 hours to simulate extended UV exposure. After each time interval, the average Izod impact strength is measured to ensure compliance with values specified in Table 6.4 of UL651. This test uses a process similar to ASTM D 256 (Test Method for Determining the Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance of Plastics), ensuring that the material retains impact strength even after long-term sunlight exposure. The 1440-hour test is particularly rigorous, providing assurance for extended outdoor installations.
DB2 도관
Unlike Schedule 40, DB2 conduit is designed for direct burial applications, where it is typically not exposed to sunlight. Therefore, DB2 conduit has no specific sunlight resistance requirements under CSA C22.2 NO. 211.1, as its underground environment shields it from UV radiation, eliminating the need for sunlight testing.
There is always fire resistant requirement for electrical conduit, for Schedule 40 and DB2 conduit, there are different flammability requirements.
팁: The Sunlight Resistance and Fire Rating performance is the most important performance for electrical conduit durability, you can get more professional insights from this post for analyzing Sunlight and UV for electrical conduit.
일정 40 도관
- UL651: According to article 6.11 in UL651, Schedule 40 conduit shall not flame for longer than 5 seconds following any of three 60-second applications of flame, and the conduit shall not be capable of igniting combustible materials in its vicinity during, between, or after the three applications of the test flame.
- UL94: Beside the flammability requirements in UL651, most customers also require the conduit meeting V0 rate after testing in according to UL94. he UL 94 flammability rating is a standard developed by Underwriters Laboratories (UL) to measure how likely a plastic material is to ignite. Here are the flammability classifications included in UL94:
UL94 Rating | Orientation | 요구 사항 |
5VA | Vertical | Burning stops within 60 seconds after five applications of flame (each application 5 seconds), no flaming drips and specimens have no burn through hole; |
5VB | Vertical | Burning stops within 60 seconds after five applications of flame (each application 5 seconds), no flaming drips and specimens may have a burn though hole; |
V0 | Vertical | Burning stops within 10 seconds after two applications of flame (each 10 application seconds), no flaming drips; |
V1 | Vertical | Burning strops within 60 seconds after two application of flame (each 10 application seconds), no flaming drips; |
V2 | Vertical | Burning stops within 60 seconds after two applications of flame (each application 10 seconds), flaming drips are allowed; |
HB | Horizontal | Burning stops before 100mm. |
DB2 도관
DB2 conduit, designed primarily for direct burial applications, follows the standards in Canada, which includes flammability classifications like FT4 and FT6:
FT4 Flame Test
The FT4 certification is highly regarded due to its stringent testing requirements. The FT4 test subjects cables to a 70,000 BTU/hour flame in a vertical tray configuration. The test procedure is demanding:
- 테스트 설정: Cables are mounted on a vertical tray and exposed to a 70,000 BTU/hour flame for 20 minutes. This setup simulates the intense heat a cable or conduit might be exposed to in real-world industrial fires.
- 기준: For a cable or conduit to pass FT4, the charred material must not extend more than 1.5 meters (5 feet) from the lower edge of the burner face. This requirement is specified under CSA C22.2 No. 38 and is nearly identical to the IEEE 1202 flame test. Because of the reduced char height limits, the FT4 test is considered slightly more rigorous than the UL1685 vertical tray test.
- 응용 프로그램: FT4 certification is crucial for industrial and commercial spaces where vertical flame spread could pose a hazard. Passing the FT4 test ensures that the conduit will limit flame spread, enhancing fire safety in densely cabled environments.
FT6 Flame Test
The FT6 certification, often known as the Steiner Tunnel flame test (similar to the NFPA 262 in the U.S.), is even more rigorous, primarily assessing flame spread and smoke production in air-handling plenums. This is critical in HVAC systems and any environment with circulated air, where low smoke and limited flame spread are essential.
- 테스트 설정: The test uses a 25-foot Steiner Tunnel equipped with intake and exhaust ducts to control airflow. Cables or conduits are mounted in a tray within the tunnel, with two circular burners at the intake end. Methane is burned at 240 ft./min airflow through the tunnel for 20 minutes.
- 기준: To pass the FT6 test, the flame travel distance must not exceed 1.52 meters (5 feet). Additionally, the test monitors smoke density, requiring that the peak optical smoke density does not exceed 0.5, with an average optical density below 0.15. These criteria ensure that materials rated FT6 have excellent fire resistance and low smoke production, suitable for sensitive environments where air quality must be preserved.
- 응용 프로그램: FT6-certified materials are used in air plenums, HVAC systems, and other spaces where minimizing smoke and flame spread is essential for safety and air quality.
DB2 컨듀이트 피팅
DB2 conduit fittings are manufactured to be compatible with direct burial applications. These fittings are designed to form watertight seals, preventing moisture ingress and protecting the electrical wiring from underground elements.
Schedule 40 Conduit Fittings
Schedule 40 fittings offer flexibility in both above-ground and underground installations. They include elbows, couplings, adapters, and junction boxes that can adapt the conduit to various layouts. These fittings are easy to install and are compatible with most Schedule 40 conduit pipes.
Fittings’ Dimension Comparison
Commonly used solvent cement fittings for both conduit types, such as couplings and elbows and bends are offer the same functions, they may also have similar outlook, but dimensions requirements are quite different, here we take elbows for example to have a dimension comparison:
거래 규모 | 일정 40 도관 | DB2 도관 | ||
반지름 R (mm) | 길이 Ls (mm) | 반지름 R (mm) | 길이 Ls (mm) | |
1/2 | 100 | 38 | / | / |
3/4 | 114 | 38 | / | / |
1 | 146 | 48 | / | / |
1-1/4 | 184 | 50 | / | / |
1-1/2 | 210 | 50 | / | / |
2 | 241 | 50 | 241 | 38 |
2-1/2 | 267 | 76 | / | / |
3 | 330 | 79 | 330 | 38 |
3-1/2 | 380 | 83 | 381 | 44.5 |
4 | 400 | 86 | 406 | 50.5 |
4-1/2 | / | / | 508 | 57 |
5 | 600 | 92 | 610 | 63.5 |
6 | 760 | 95 | 762 | 82.5 |

DB2 컨듀잇 응용 분야: 직접 매설에 적합한 DB2는 공공 시설, 가로등, 공공 공사 등 지하 인프라 프로젝트에 널리 사용됩니다. 내식성과 내압성이 뛰어나 토양 조건이 다양한 장소에 적합합니다.
일정 40 도관 응용 프로그램: 스케줄 40 전선관은 주거, 상업 및 산업 시설에 사용되며, 다재다능하여 벽, 천장 및 옥외 공간에 설치할 수 있습니다. 햇빛에 노출될 수 있는 환경에 적합하여 건물 배선 시스템에 널리 사용됩니다.
무게:
일정 40 도관: 스케줄 40 도관은 DB2보다 두꺼운 벽체로 제작되어 내구성과 무게가 더욱 뛰어납니다. 이러한 구조 덕분에 스케줄 40은 지상 및 노출된 환경에서 모두 사용할 수 있습니다. 두꺼운 벽체로 인해 스케줄 40 도관은 DB2보다 무거워 견고성은 높지만, 특정 환경에서는 취급이 더 까다롭습니다. 이러한 추가 무게는 지하 및 노출된 환경 모두에서 내구성과 강도를 높이는 데 기여합니다.
DB2 덕트: DB2 도관은 Schedule 40과 같은 수준의 구조적 두께가 필요하지 않은 직접 매설 적용 분야에 맞게 설계되었습니다. 벽이 얇기 때문에 DB2 도관은 Schedule 40보다 가볍기 때문에 재료 무게와 취급이 중요한 고려 사항인 지하 설치 프로젝트에서 관리가 용이합니다.
벽 두께 및 소켓 치수
이들의 차원 요구 사항을 더 잘 이해하기 위해 여기서는 이들에 대한 몇 가지 중요한 차원 데이터를 비교해 보겠습니다.
크기 | 일정 40 도관 | DB2 도관 | ||||
최대 OD | 최소 평균 ID | 최소 T | 최대 OD | 최소 평균 ID | 최소 T | |
1/2 | 21.54 | 14.68 | 2.77 | / | / | / |
3/4 | 26.92 | 19.81 | 2.87 | / | / | / |
1 | 33.66 | 25.50 | 3.38 | / | / | / |
1-1/4 | 42.47 | 33.90 | 3.56 | / | / | / |
1-1/2 | 48.56 | 39.72 | 3.68 | / | / | / |
2 | 60.63 | 51.33 | 3.91 | 57.30 | 50.80 | 1.78 |
2-1/2 | 73.41 | 61.31 | 5.16 | / | / | / |
3 | 89.28 | 76.40 | 5.49 | 82.75 | 76.20 | 2.03 |
3-1/2 | 102.87 | 88.54 | 5.74 | 95.00 | 88.40 | 2.29 |
4 | 115.57 | 100.60 | 6.02 | 107.30 | 100.10 | 2.67 |
4-1/2 | / | / | / | 121.70 | 114.30 | 2.79 |
5 | 142.57 | 126.36 | 6.55 | 134.85 | 126.35 | 3.81 |
6 | 169.54 | 152.04 | 7.11 | 159.65 | 149.75 | 3.94 |
거래 규모 | 일정 40 | DB2 도관 | ||||
입구에서 | 맨 아래에 | 최소 소켓 깊이(mm) | 입구에서 | 맨 아래에 | 최소 소켓 깊이(mm) | |
1/2 | 21.64 | 21.23 | 16.56 | / | / | / |
3/4 | 27.03 | 26.57 | 18.26 | / | / | / |
1 | 33.78 | 33.27 | 22.22 | / | / | / |
1-1/4 | 42.60 | 42.04 | 23.83 | / | / | / |
1-1/2 | 48.72 | 48.11 | 26.97 | / | / | / |
2 | 60.78 | 60.17 | 28.58 | 57.53 | 57.02 | 18.92 |
2-1/2 | 73.41 | 72.85 | 37.31 | / | / | / |
3 | 89.28 | 88.70 | 40.49 | 83.08 | 82.42 | 37.97 |
3-1/2 | 101.98 | 101.40 | 42.85 | 95.38 | 94.51 | 38.10 |
4 | 114.68 | 114.07 | 44.45 | 107.57 | 106.91 | 43.94 |
4-1/2 | / | / | / | 122.43 | 121.06 | 50.80 |
5 | 142.06 | 141.05 | 49.20 | 135.38 | 134.47 | 62.99 |
6 | 169.11 | 168.00 | 53.98 | 160.15 | 159.26 | 74.93 |
UL 및 CSA 표준에 따라 Schedule 40 도관과 DB2 도관에는 서로 다른 표시 요구 사항이 있습니다. 아래는 CSA C22.2 No.211.1 및 UL651의 표시 요구 사항입니다.
체코
각 표준 길이의 도관과 각 엘보 및 굽힘은 읽기 쉽고 내구성 있게 표시되어야 합니다.
- a) 제조업체 이름, 상표 또는 기타 인정된 식별 기호;
- b) 제품 명칭;
- c) 거래 규모;
- d) 제조일자 또는 제조업체 코드
- e) CSA 표준 번호.
각 부속품은 외부 표면에 읽기 쉽고 내구성 있게 표시되어야 합니다.
- a) 제조업체 이름, 상표 또는 기타 인정된 식별 기호;
- b) 제품 명칭 및
- c) 거래 규모.
UL
8.1.3 제품, 포장 또는 라벨 표시에는 다음이 포함되어야 합니다.
- a) "강성 PVC 도관"이라는 문구“
- b) 도관 제품의 거래 규모,
- c) 제조업체의 이름 또는 상표 또는 기타 독특한 표시
제품을 담당하는 조직을 쉽게 식별할 수 있습니다.
- d) 제조일자 또는 기타 제조연도가 연속 3개월을 넘지 않는 경우.
엘보우의 경우 제조일은 다음 날짜로 합니다.
1) 압출과 굽힘이 같은 위치에서 발생하는 경우 도관은 압출됩니다.
2) 도관이 다른 위치로 돌출되어 엘보우가 형성되었습니다.

DB2와 Schedule 40 전선관을 선택할 때는 환경 조건, 예산, 설치 유형, 규제 요건 등의 요소를 고려해야 합니다. DB2 전선관은 추가적인 강도와 환경 보호가 필요한 지하 및 중부하 작업에 더 적합합니다. Schedule 40 전선관은 다재다능하고 비용 효율적이어서 일반적인 용도로 사용하기에 이상적입니다.
- 프로젝트 요구 사항
첫 번째 단계는 프로젝트의 전반적인 요구 사항을 평가하는 것입니다. 지상 설치는 견고한 구조적 특성과 옥외 노출 요건 준수로 인해 Schedule 40 전선관이 일반적으로 적합합니다. 그러나 프로젝트에 직접 매설하는 경우 DB2 전선관이 더 나은 선택입니다. DB2는 지하 설치용으로 특별히 설계되었으며 토양 조건 및 온도 안정성에 최적화된 기능을 갖추고 있습니다.
- 환경 고려 사항
도관을 설치할 환경은 선택에 큰 영향을 미칩니다. 예를 들어, Schedule 40 도관은 자외선 차단 기능이 있어 햇빛에 노출될 수 있는 옥외 지상 설치에 적합합니다. 반면 DB2 도관은 직접 매립하도록 설계되어 자외선 차단 기능이 필요하지 않습니다. 재료를 선택할 때는 극한 온도, 화학 물질 노출, 자외선 노출 등의 요소를 고려하십시오.
- 코드 준수
안전 및 품질 기준을 유지하려면 규정 준수가 필수적입니다. Schedule 40 전선관은 UL651 기준을 충족하는 반면, DB2 전선관은 CSA C22.2 No. 211.1 기준을 준수합니다. 이러한 기준은 가연성, 내충격성, 내압착성을 포함하여 각 전선관 유형에 대한 구체적인 요건을 명시하고 있습니다. 프로젝트 대상 지역의 지역 및 국가 건축 기준에 부합하는 전선관을 선택하십시오.
- 비용
DB2 도관은 일반적으로 무게가 가볍고 벽 두께가 얇아 비용이 저렴하여 지하 설치에 비용 효율적인 옵션입니다. 스케줄 40은 더 견고하기 때문에 일반적으로 비용이 더 많이 듭니다. 자재 예산을 책정할 때 초기 비용과 프로젝트의 장기적인 내구성 요건을 균형 있게 고려하는 것이 중요합니다.
- 설치 비용
스케줄 40 전선관은 더 무겁고 설치에 더 많은 인력과 자원이 필요할 수 있으며, 특히 지지대가 필요한 지상 설치 환경에서는 더욱 그렇습니다. DB2 전선관은 더 가볍고 매설에 최적화되어 있어 지하 설치가 더 용이하여 설치 비용을 절감할 수 있습니다. 전선관 무게, 접근성, 장비 요구 사항을 기준으로 설치 비용을 평가하면 예산이 중요한 프로젝트에 가장 적합한 옵션을 선택하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
- 다양성
Schedule 40은 다양한 부속품과 크기를 제공하여 다양한 용도와 구성에 유연하게 대응할 수 있습니다. 프로젝트에서 도관 직경, 부속품 또는 부속품 옵션에 대한 유연성이 필요한 경우, Schedule 40은 특정 설계 요구에 맞춰 더욱 다양한 옵션을 제공할 수 있습니다. DB2 도관은 일반적으로 간단한 지하 설치에 최적화되어 있어 크기 및 부속품 옵션이 제한적입니다.
- 전문가와의 상담
업계 전문가 또는 전선관 공급업체와 상담하면 귀사의 고유한 프로젝트 요구 사항에 맞는 귀중한 통찰력을 얻을 수 있습니다. 전문가들은 귀사의 프로젝트 사양과 환경 조건을 평가하여 가장 적합한 전선관 유형을 추천해 드립니다. 또한, 이러한 전문 지식을 바탕으로 예산 범위 내에서 규정 준수와 최적의 성능을 보장할 수 있습니다.
요약하자면, DB2와 Schedule 40 전선관 모두 전기 배선에 대한 안정적인 보호 기능을 제공하지만, 다양한 환경과 프로젝트 요구 사항에 맞게 최적화되어 있습니다. DB2 전선관은 더 두꺼운 벽 두께와 강력한 압착 저항성을 갖춰 지하 직접 매설 환경에서 내구성을 발휘하도록 설계되었습니다. 반면, Schedule 40 전선관은 범용 적용 분야에서 다재다능하고 저렴하며 설치가 용이합니다.
Ledes는 CSA 및 UL 표준을 모두 충족하는 고품질 인증 전선관 솔루션을 제공하기 위해 최선을 다하고 있으며, DB2 및 Schedule 40 유형의 옵션도 제공합니다. Ledes 제품은 내구성, 안전성 및 성능에 대한 산업 표준을 충족하는지 확인하기 위해 엄격한 테스트를 거쳤으며, 다양한 분야의 시공업체와 엔지니어에게 신뢰할 수 있는 선택입니다.
올바른 전선관을 선택하려면 각 프로젝트의 구체적인 요구 사항을 이해해야 하며, Ledes에서는 고객이 전기 인프라 요구 사항에 맞는 최적의 솔루션을 찾을 수 있도록 지원합니다.




