
목차
현대 세계를 묶는 보이지 않는 실
상상해 보세요. 세 대륙의 과학자들이 생명을 구하는 백신을 개발하기 위해 실시간으로 협력하고 있습니다. 시골 마을의 한 학생이 세계 명문 대학의 온라인 강의에 참석합니다. 여러 시간대에 걸쳐 흩어져 있는 가족이 사랑하는 사람의 중요한 순간을 기념하기 위해 화상 통화를 합니다. 현대 사회에 없어서는 안 될 이러한 순간들은 우리가 거의 생각하지 못하는 것, 바로 전 세계를 아우르는 광활하고 복잡한 통신 인프라와 통신망 덕분에 가능합니다.
이 인프라의 핵심은 다음과 같습니다. 통신 통로, 개인, 기업, 국가 간에 데이터가 원활하게 흐르도록 하는 물리적 채널입니다. 도시 도로 아래에 묻혀 있든, 바다를 가로지르든, 우뚝 솟은 빌딩 사이를 관통하든, 이러한 통로는 초연결 시대의 숨은 영웅입니다.
이 글에서는 우리의 삶, 업무, 그리고 상호작용 방식을 형성하는 데 있어 통신 수단이 갖는 혁신적인 역할을 살펴보겠습니다. 글로벌 비즈니스 운영의 원동력부터 문화적 격차 해소 및 혁신 촉진에 이르기까지, 통신 네트워크 인프라는 연결의 가능성을 새롭게 정의해 왔습니다. 오늘날 사회에서 통신 네트워크 인프라의 중요성을 살펴보고, 빠르게 디지털화되는 세상의 요구에 부응하기 위해 이 인프라가 어떻게 발전해 나갈지 살펴보겠습니다.

통신 도관(Comm Conduit)은 본질적으로 광대한 네트워크에서 데이터를 전송하는 케이블과 배선을 수용하고 보호하는 데 사용되는 물리적 경로입니다. 이러한 도관은 통신 네트워크 인프라의 필수 구성 요소로서 안정적이고 효율적인 정보 흐름을 가능하게 합니다. 일반적으로 PVC, HDPE 또는 금속과 같은 내구성 있는 소재로 제작된 통신 도관은 내용물을 환경적 요인, 물리적 손상 및 간섭으로부터 보호하여 현대 사회에 필수적인 데이터의 원활한 전송을 보장합니다.
통신 도관은 도시 광섬유망부터 농촌 광대역망 설비, 심지어 대륙을 연결하는 심해 인프라까지 다양한 용도로 사용됩니다. 이러한 도관은 지하에 매설되거나, 건물을 따라 설치되거나, 심지어 기둥에 매달릴 수도 있어 통신 인프라의 중추를 형성합니다.
커뮤니케이션 수단의 역할을 충분히 이해하려면 관련 산업 용어와 글로벌 연결을 지원하기 위해 함께 작동하는 주요 구성 요소를 이해하는 것이 필수적입니다.
더 자세한 내용을 알고 싶으시다면, 저희의 마지막 게시물을 읽어보세요. 통신 수단의 종류와 목적.
광섬유 케이블은 현대 통신망의 핵심입니다. 유리 또는 플라스틱 섬유 가닥을 빛의 펄스 형태로 전송하여 기존 구리 케이블에 비해 탁월한 속도와 용량을 제공합니다.
광섬유 케이블은 일반적으로 통신 도관에 둘러싸여 물리적 손상, 기상 조건, 전자기 간섭으로부터 보호됩니다. 광섬유와 도관의 이러한 조합은 데이터 전송을 위한 고속 고속도로를 형성합니다.
기지국은 무선 통신의 핵심 허브 역할을 합니다. 모바일 기기와 무선 신호를 송수신하여 음성 통화, 문자 메시지, 모바일 인터넷 접속을 가능하게 합니다.
이러한 타워는 종종 통신 도관을 통해 광섬유 케이블을 사용하여 더 넓은 통신 네트워크에 연결하고 타워와 핵심 네트워크 간에 고속 데이터 전송을 보장합니다.
해저 케이블은 전 세계 연결의 숨겨진 거인입니다. 바다와 바다를 가로지르는 이 케이블들은 국제 통신의 중추를 이루며, 모든 대양을 횡단하는 인터넷 데이터의 약 99%를 전송합니다.
여러 겹의 갑옷으로 보호되고 종종 해저의 특수 도관에 설치된 해저 케이블은 국가와 대륙을 연결하여 화상 통화부터 전자 상거래까지 모든 것을 가능하게 합니다.
해저 케이블이 장거리 데이터 전송의 대부분을 차지하는 반면, 위성은 원격 지역, 산악 지형, 재해 지역 등 물리적 인프라를 구축하기 어려운 지역에서 중요한 역할을 합니다.
위성은 통신 채널을 통해 연결된 지상국에 의존하여 데이터를 수신하고 전송하며, 궤도 네트워크와 지상 시스템 간의 다리 역할을 합니다.
라우터는 통신 네트워크의 트래픽 디렉터입니다. 장치와 네트워크 간의 데이터 흐름을 관리하여 정보가 의도한 목적지에 도달하도록 보장합니다.
주요 네트워크 노드에 위치한 라우터는 통신 도관에 있는 광섬유 케이블에 연결되어 데이터 전송 경로에서 중요한 교차점을 형성합니다.
통신 도관은 이러한 구성 요소들의 보호 채널 역할을 하여 최적의 기능을 보장합니다. 광섬유 케이블을 수용하고, 기지국을 연결하며, 다른 네트워크 장비의 경로를 형성함으로써 도관은 통신 시스템의 원활한 운영을 가능하게 합니다. 도관은 도시, 농촌, 수중 등 다양한 환경에 적응하고 증가하는 디지털 연결 수요를 지원하는 데 필요한 내구성과 확장성을 제공하는 데 있어 그 중요성이 있습니다.
디지털 시대로 접어들면서 견고하고 확장 가능한 통신 인프라에 대한 수요는 계속 증가할 것이며, 통신 채널은 이러한 발전의 초석으로 남을 것입니다.
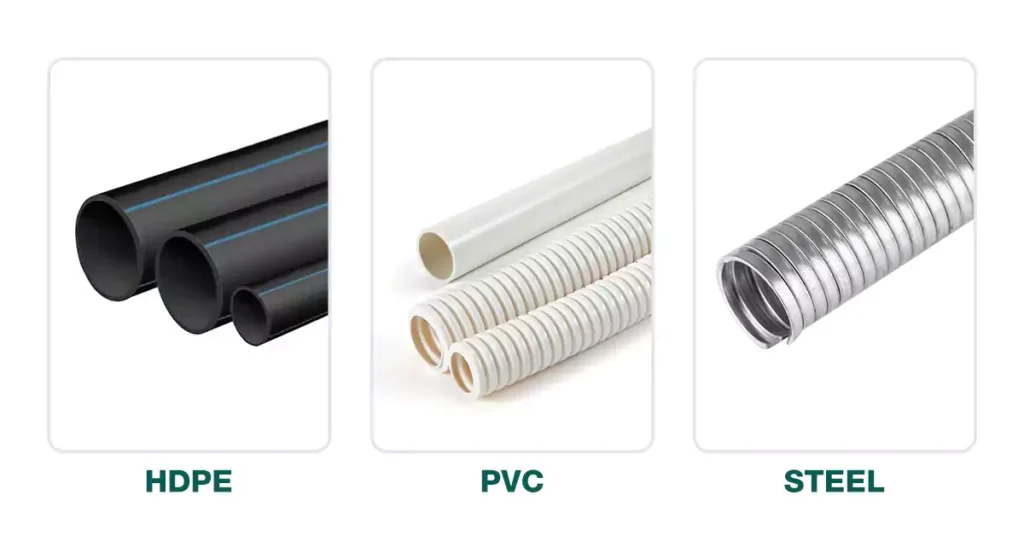
통신 도관(또는 덕트)은 현대 통신 인프라의 구조적 근간을 이루며, 광대한 네트워크에서 안전하고 효율적인 데이터 전송을 용이하게 합니다. 도관의 설계와 재질은 지역 표준, 환경 조건 및 의도된 용도에 따라 크게 달라집니다. 이 섹션에서는 미국, 캐나다, 호주의 세 주요 지역에서 통신 도관의 분류 및 용도를 자세히 살펴보고, 각 지역의 고유한 요구 사항, 재질 선호도 및 산업별 적용 사례를 중점적으로 다룹니다.

미국에서 통신관로는 직접 매설(DB) 및 매설 매설(EB) 기준과 사용 재료에 따라 분류됩니다. 이러한 관로는 지하 및 매설 시설 모두에서 통신 케이블을 보호하는 데 중요한 역할을 하며, 다양한 환경 및 기계적 응력 조건에 대한 솔루션을 제공합니다.
- EB20 및 EB35 덕트 일반적으로 콘크리트로 둘러싸인 배관이 있는 프로젝트에 사용됩니다.
- EB20은 벽이 얇고 가벼운 작업에 사용됩니다.
- EB35는 도로 아래와 교통량이 많은 지역 등 스트레스가 많은 환경에 적합한 두꺼운 벽을 가지고 있습니다.
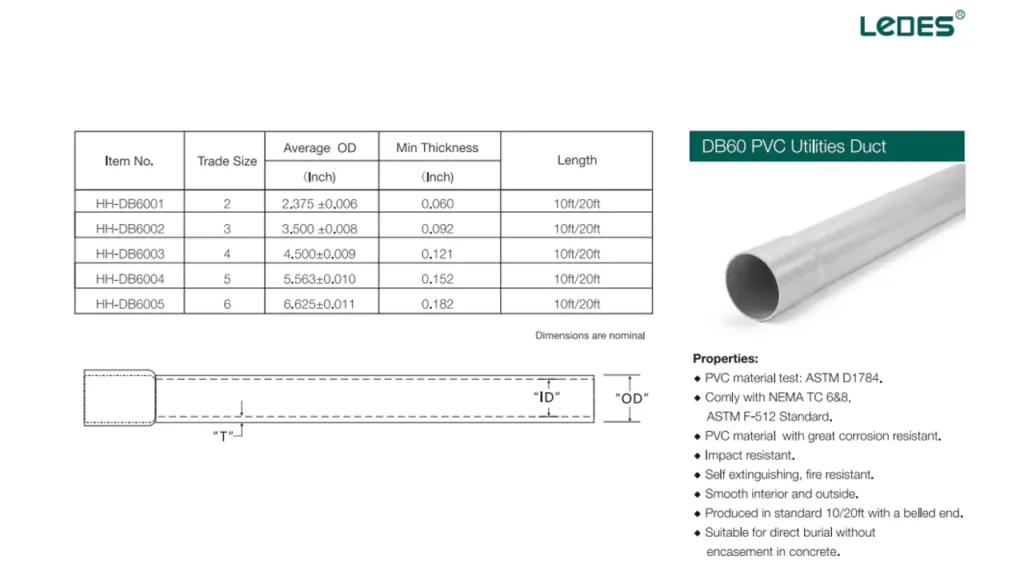
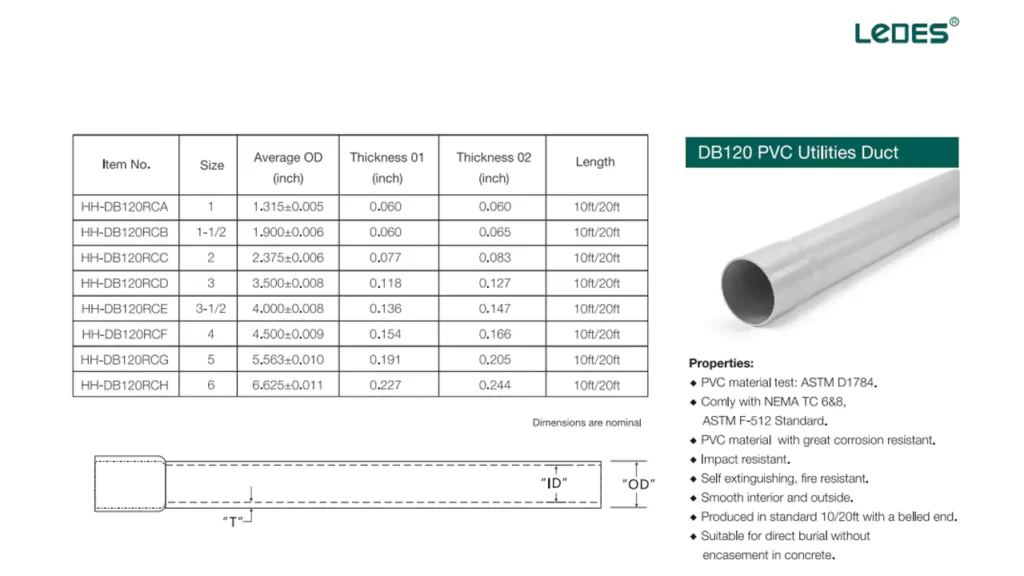
부식과 화학물질에 대한 저항성, 비용 효율성, 설치 용이성 때문에 널리 사용됩니다.
유연하고 충격에 강하기 때문에 장거리 광섬유 네트워크와 무굴착 설치에 일반적으로 사용됩니다.
내구성이 뛰어나고 보호성이 뛰어난 강철 도관은 최대 기계적 강도가 요구되는 산업이나 고위험 환경에서 사용됩니다.

도시 인프라: EB35와 같은 EB 덕트는 콘크리트 덮개로 추가적인 보호 기능을 제공하는 교통량이 많은 구역에 사용됩니다.
장거리 통신 네트워크: HDPE 도관은 특히 무굴착 응용 분야에서 유연한 지하 배치에 선호됩니다.
산업적 환경: 강철 도관은 기계적 응력이나 잠재적 손상에 대한 노출이 높은 곳에서 사용됩니다.
캐나다에서는, 통신관 표준 극한의 추위와 동상과 같은 캐나다의 까다로운 환경 조건에 맞춰 제작되었습니다. DB 시리즈는 캐나다 통신 전선관 표준을 선도하며 도시 및 오지 환경 모두에서 안정적인 보호 기능을 제공합니다.
DB2 도관은 얕은 매립지와 주거 지역에 사용되는 경량 도관입니다.
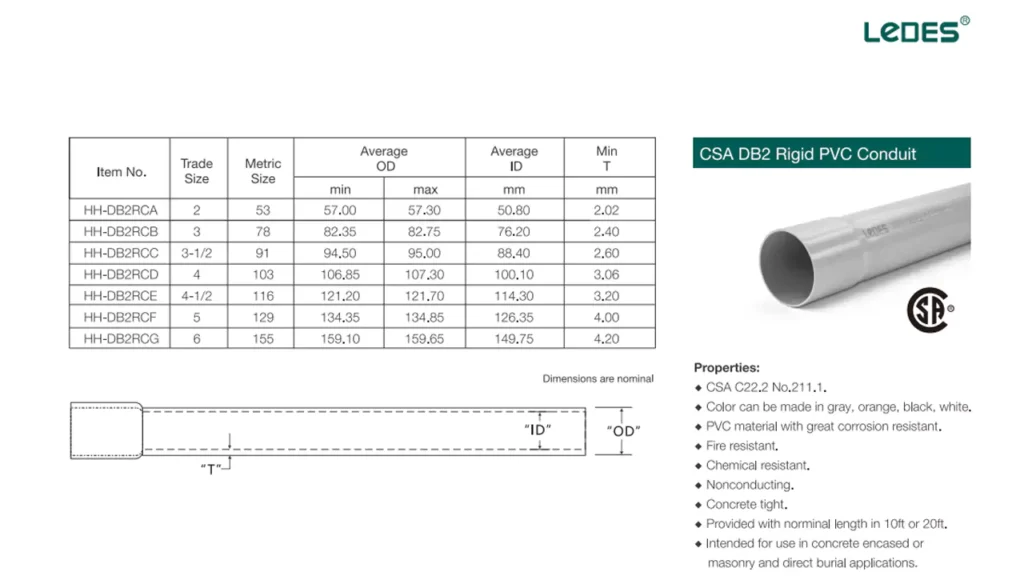
강철 전선은 특히 산업용 분야에서 추가적인 기계적 보호가 필요한 환경에서 캐나다에서도 사용됩니다.
지하 통신망: DB2와 같은 DB 정격 도관은 광섬유 및 데이터 케이블을 보호하기 위해 직접 매설하는 데 사용됩니다.
한랭 기후 설비: 도관은 동결 융기와 온도 변화에 견딜 수 있도록 설계되어 혹독한 환경에서도 내구성을 보장합니다.
산업 환경: 강철 도관은 중량물이나 고위험 구역에 사용되어 물리적 손상으로부터 최대한의 보호를 보장합니다.
호주는 광활한 지형과 도시 중심지부터 외딴 사막까지 다양한 환경 조건을 갖추고 있기 때문에 자외선 노출, 토양 이동 및 기타 문제를 견딜 수 있는 통신 도관이 필요합니다. 호주 통신 경로 준수하다 AS/NZS 표준, 내구성과 적응성에 중점을 둡니다.
MD 통신 도관(강성 도관 포함) 골판지 도관 옥외 및 지상 설치 시 자외선 저항성과 내구성이 뛰어나 널리 사용됩니다.
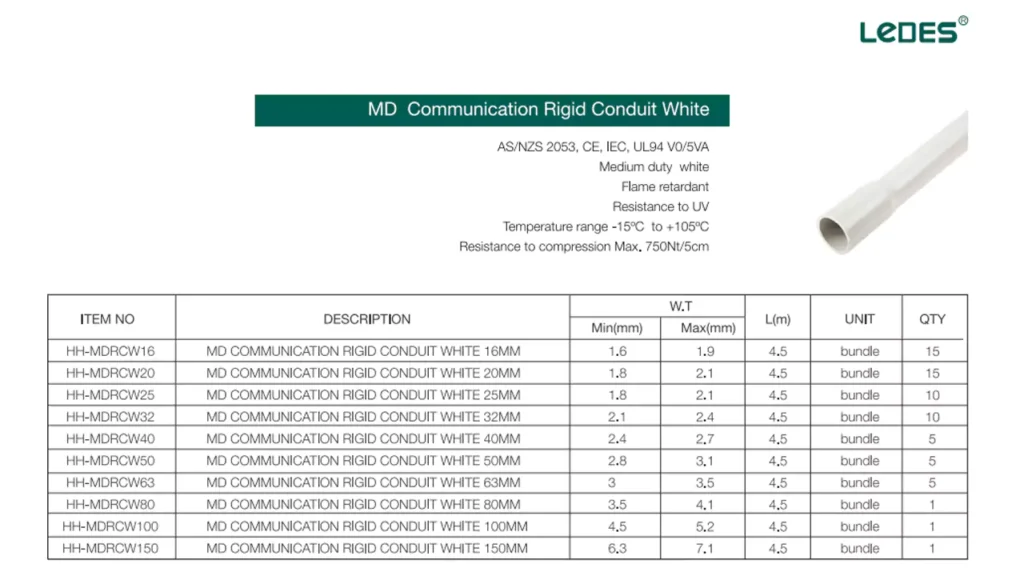
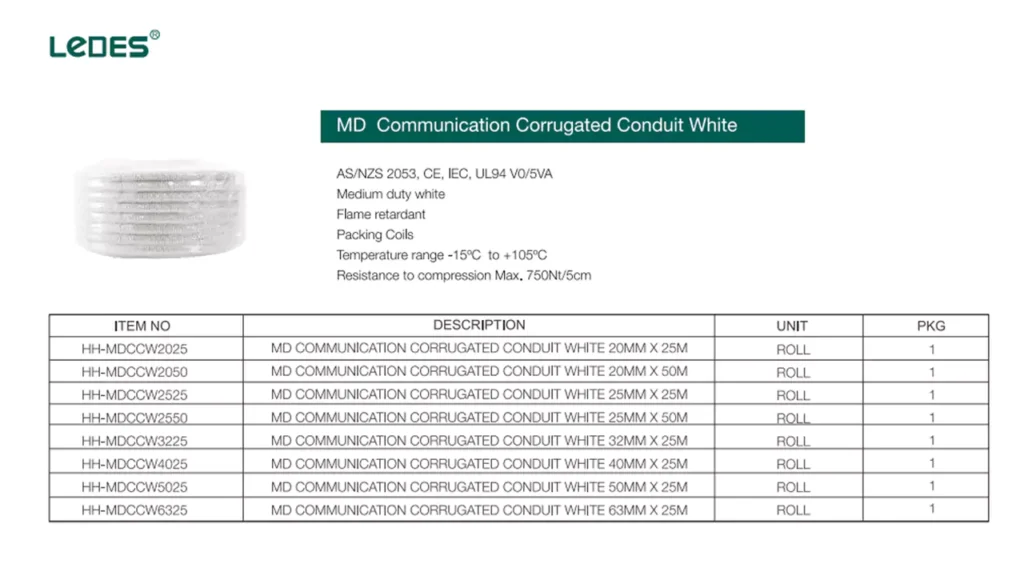
지하 시설에 사용되어 무굴착 방식에 유연성을 제공하고 토양 이동에 따른 보호를 제공합니다.
산업 현장이나 극한의 기계적 보호가 필요한 프로젝트에 사용됩니다.
호주에서는 설치 및 유지 관리 시 식별을 돕기 위해 통신관의 색상이 표준화되는 경우가 많습니다. AS/NZS 2053 및 AS 1345에 참조된 지침에 따르면, 다양한 색상은 특정 용도에 따라 사용됩니다.
하얀색: 데이터 및 통신 통로.
회색: 지상에 설치된 전기 배선.
주황색: 지하에 설치된 전기 배선.
이러한 색상 코드는 다양한 환경에서 배관을 쉽게 식별하여 용도에 맞는 적절한 배관을 사용할 수 있도록 합니다. 예를 들어, 흰색 배관은 데이터 및 통신용으로 명시적으로 사용되므로 복합 용도 시설의 전기 배관과 쉽게 구분할 수 있습니다.
AS/NZS 2053 표준은 전기 및 통신 도관에 대한 색상 사양을 명시적으로 의무화하지 않지만 AS 1345 및 PIPA 지침 POP203과 같은 다른 지침은 설치 위치 및 유형에 따라 색상 코딩에 대한 실질적인 권장 사항을 제공합니다.

통신 도관은 본질적으로 간단하지만 중요한 역할을 합니다. 바로 통신 케이블을 보호하고 정리하는 것입니다. 지하에 매설하든, 지상에 설치하든, 건물 내부에 설치하든, 이러한 도관은 케이블을 물리적 손상, 환경적 스트레스, 그리고 간섭으로부터 보호합니다.
통신 통로가 없다면 통신 인프라는 잦은 장애, 증가된 유지 보수 비용, 그리고 저하된 효율성에 직면하게 될 것입니다. 고속 인터넷의 안정성, 중단 없는 모바일 서비스, 그리고 안정적인 데이터 센터 운영은 통신 통로의 적절한 배치에 크게 좌우됩니다.
통신 도관은 통신 인프라 운영에 중요한 역할을 합니다.,
- 보호 및 내구성:
전선관은 민감한 광섬유 케이블, 동축 케이블, 전력 케이블을 물리적 손상, 습기 및 환경적 마모로부터 보호합니다. 지하 매설, 해저 매설, 또는 도심 지역에 설치 등 어떤 방식으로든 전선관은 통신 시스템의 무결성을 보호합니다.
- 케이블 관리:
효율적인 케이블 정리는 현대 네트워크에 필수적입니다. 통신관은 설치를 간소화하고, 향후 업그레이드를 지원하며, 유지 보수 또는 수리 시 네트워크 중단을 최소화합니다.
- 확장성 및 성장:
통신 네트워크는 증가하는 수요를 충족하기 위해 발전해야 합니다. 전선관은 케이블 추가 또는 교체를 위한 체계적인 시스템을 제공하여 네트워크를 손쉽게 확장할 수 있도록 합니다.
- 다양한 적용 분야:
PVC, HDPE 또는 강철 등 어떤 재질로 제작되든 통신 도관은 다양한 요건을 충족하도록 설계되었습니다. 교통량이 많은 도시 환경, 극한의 기상 조건, 또는 해저 케이블을 통한 장거리 데이터 전송 등 어떤 환경에서도 안정적으로 작동할 수 있습니다.
통신 수단은 물리적 역할을 넘어 통신 산업에 혁신적인 영향을 미칩니다.
- 사업 성장 지원:
기업에게 안정적인 통신 인프라는 운영에 필수적입니다. 컨듀잇은 빠른 데이터 전송, 안전한 전자상거래, 원활한 화상 회의, 클라우드 기반 서비스를 지원합니다. 또한, 기업이 원격 근무 모델을 도입하고, 글로벌 인재 풀에 접근하며, 생산성을 향상시킬 수 있도록 지원합니다.
- 디지털 경제에서 혁신을 주도하다:
커뮤니케이션 채널은 온라인 플랫폼, 핀테크 서비스, 그리고 이러닝 시스템을 구축하여 디지털 경제를 뒷받침합니다. 빠르고 안전한 연결을 지원함으로써, 채널은 스타트업과 기업이 경쟁이 치열한 시장에서 혁신하고, 확장하고, 성공할 수 있도록 지원합니다.
- 글로벌 연결성 강화:
소통의 통로는 거리를 좁혀 개인과 기업이 전 세계로 연결될 수 있도록 합니다. 이를 통해 경제적 협력, 문화 교류, 그리고 아이디어 공유가 촉진되어 사회·경제적 발전이 촉진됩니다.
- 디지털 격차 해소:
연결성이 제한적인 소외 지역에서는 안정적인 인터넷 및 통신 서비스를 제공하는 데 있어 통신망이 중요한 역할을 합니다. 정부와 민간 부문은 이러한 통신망을 활용하여 네트워크를 확장하고 더 많은 사람들에게 교육, 일자리, 의료 서비스를 제공합니다.
- 신기술 활성화:
통신 도관은 5G 네트워크, 스마트 시티, 사물 인터넷(IoT)의 인프라 요구를 충족하는 데 필수적입니다. 이러한 혁신은 도관이 제공하는 보호 기능과 효율성을 통해 가능해진 고속, 저지연 연결을 기반으로 합니다.
- 네트워크 보안 개선:
데이터 유출 위협이 증가하는 세상에서, 컨듀잇은 주요 통신 회선에 물리적 보호 계층을 추가합니다. 컨듀잇은 변조, 환경적 위험, 그리고 우발적 손상으로부터 데이터를 보호하여 안전하고 안정적인 데이터 전송을 보장합니다.
전력선과 통신선은 구조와 재질이 유사해 보일 수 있지만, 용도, 설계 및 요구 사항은 상당히 다릅니다. 두 가지 모두 현대 인프라에서 중요한 역할을 하지만, 특정 용도에 적합한 솔루션을 선택하려면 두 가지의 차이점을 이해하는 것이 필수적입니다.
전력선:
전력선은 전기를 전달하는 전기 배선을 수용하고 보호하도록 설계되었습니다. 주로 주거, 상업 및 산업 환경에서 안전하고 효율적인 전기 분배를 위해 사용됩니다. 일정 40 도관 예를 들어, 는 전형적인 전력선입니다.
응용 프로그램 예시:
건물, 기계, 가로등에 전력 공급
Electrical systems in factories and large facilities
Communication Conduits:
Communication conduits protect low-voltage cables used for transmitting data, signals, and communication. These conduits ensure the integrity of fiber optic, coaxial, or Ethernet cables in telecom networks. The types EB, DB (USA and Canada) and medium-duty white PVC conduit (Australia) are typical communication conduits.
응용 프로그램 예시:
Fiber optic networks for high-speed internet
Telephone, television, and data transmission systems
Undersea data cables

전력선:
Power conduits handle high-voltage electrical wires, typically carrying alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). These voltages range from low residential power (120-240V) to industrial levels exceeding 10kV.
Communication Conduits:
Communication conduits carry low-voltage signals or optical data pulses, typically below 60V. These signals are more sensitive to interference, making proper shielding and separation essential.
전력선:
Governed by electrical codes such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the U.S. and Canadian Electrical Code (CEC) in Canada.
Must meet specific safety standards for voltage capacity, grounding, and insulation.
Communication Conduits:
Governed by telecommunications standards like ANSI/TIA or specific guidelines for fiber optic and data cabling.
Often installed in separate pathways from power conduits to reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI).
전력선:
Since they carry high voltage, power conduits require insulation and must be placed at safe distances from sensitive electronic equipment to prevent electrical hazards.
Communication Conduits:
Because data signals are sensitive to interference, communication conduits are typically installed away from power conduits. Shielding and grounding are used to reduce EMI and maintain signal quality.
The common applications of power and communication conduits are different,
Different Application Between Power and Communication Conduits
특징 | Power Conduits | Communication Conduits |
Primary Purpose | Transmitting electrical power | Transmitting data and communication signals |
Common Locations | Buildings, factories, outdoor power lines | Data centers, telecom towers, undersea cables |
재료 | PVC, steel, aluminum | PVC, HDPE, composite polymers |
Key Standards | NEC, CEC, IEC | ANSI/TIA, ISO/IEC for telecom systems |
Voltage Levels | High-voltage | Low-voltage or data signals |
To ensure safety and performance, power and communication conduits are kept separate during installation:
Safety Concerns:
High-voltage cables in power conduits can cause electrical hazards if not properly isolated. Separation prevents accidents and equipment failures.
Signal Quality:
Power lines can generate electromagnetic fields, causing interference with low-voltage communication cables. Dedicated communication conduits maintain the integrity of data signals.
규정 준수:
Electrical and telecom codes mandate separation distances and shielding to ensure compliance and operational efficiency.
Understanding the codes and standards for communication conduits is essential for ensuring compliance, safety, and optimal performance in telecom infrastructure. These regulations govern everything from the materials used to the installation techniques, ensuring the protection and efficiency of the telecom network. Here, we will explore the key standards and codes for communication conduits in Australia, the United States, and Canada, focusing on some of the most significant ones, including the NEMA TC-10, NEC, and other relevant national standards.

Australia’s communication conduit standards are outlined in several key documents that provide guidelines for the construction, installation, and use of conduits in telecom and data applications. Key Australian standards include:
AS/NZS 2053: This standard covers the installation of communication cables and provides specifications for telecommunication conduit systems, ensuring their safety, durability, and effective operation. The AS/NZS 2053 series includes guidelines on the installation of both indoor and outdoor conduit systems and defines their compatibility with various cable types.
AS/NZS 4296: This standard is concerned with the installation of telecommunications cabling and the physical protection of cables, including the use of conduits. It provides requirements for pathways, supports, and conduit systems to ensure safe operation and long-term reliability of telecommunication installations.
AS/NZS 5033: This standard primarily addresses the installation of photovoltaic (solar) systems, including the requirements for communication cables that may be part of the solar power systems. The conduits used in these installations must meet both safety standards and compatibility with the electrical systems.
AS 4702: This standard defines the requirements for communication cables used in optical fiber installations, including conduit protection against external forces. It ensures that cables are properly shielded from mechanical damage.

In the United States, a comprehensive set of codes and standards governs telecommunication conduit systems. These standards define the physical requirements, performance specifications, and installation methods for communication conduits to ensure safety, reliability, and effectiveness. Key standards include:
NEMA TC-6 & TC-8: The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) provides these standards for telecommunication conduits. NEMA TC-6 is for non-metallic conduits such as PVC and HDPE, while NEMA TC-8 is for corrugated conduit systems. These standards focus on the material, design, and performance of the conduits used in the telecom industry.
NEMA TC-10: This standard, issued by NEMA, is widely used in telecommunications conduit installations. NEMA TC-10 focuses on underground conduit systems that need to provide extra protection for cables and communications equipment. The standard covers the design, construction, and testing methods for communication conduit, with an emphasis on reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI) and providing mechanical protection. It also addresses fire resistance and moisture resistance, ensuring that installations are safe and durable over time.
UL Standards (e.g., UL 651A): Underwriters Laboratories (UL) provides certifications for conduits that meet certain fire-resistance and safety criteria. For example, UL 651A covers the requirements for rigid HDPE conduit used in telecommunication applications, ensuring that the conduit material and design comply with safety standards.
ASTM F-512: This ASTM standard specifies the requirements for non-metallic electrical and telecommunication conduit, mainly PVC and HDPE. It establishes the minimum performance criteria, including mechanical strength, resistance to environmental factors, and the installation practices for safe, efficient operation.
NEC(국가 전기 규정): Chapter 8 of the NEC governs the installation of telecommunications wiring and communication conduit systems. It includes rules for conduit routing, grounding, bonding, and separation from power lines to minimize risk of fire or electrical interference. This chapter also defines the safety measures necessary for telecommunication wiring in commercial, industrial, and residential applications.
EIA/TIA 569: The Electronics Industries Alliance (EIA) and the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) provide guidelines for the design and installation of telecommunications pathways and spaces, including conduits. TIA 569 covers both the physical installation and environmental factors that affect conduit performance, ensuring that data cabling systems are safe and efficient.
In Canada, telecommunication conduits are regulated by a combination of CSA standards and national codes that ensure safety and functionality. Key Canadian standards include:
CSA C22.2 NO. 211.1: This standard defines the construction and performance requirements for direct burial conduit that used for underground communication installation. The CSA standard includes specifications for both metallic and non-metallic conduits, addressing their ability to withstand environmental stresses and ensuring they provide safe pathways for communication cables. This standard ensures that conduits meet strict performance criteria for:
Material composition to resist chemical corrosion and degradation.
기계적 특성 such as impact resistance and crush strength.
Temperature tolerance for both high and low extremes.
가연성 to reduce risks in fire-prone environments.
캐나다 전기 규정(CEC):
The CEC establishes the foundational rules for designing, installing, and maintaining electrical and communication systems. Among its many sections, Section 12 (Wiring Methods) 그리고 Section 60 (Electrical Communication Systems) provide critical guidance for communication conduit installations, ensuring safety, reliability, and compliance. Together, these sections offer a comprehensive framework for protecting communication cables and enabling modern connectivity.
- Section 12 – Wiring Methods: Section 12 of the CEC is dedicated to wiring methods, covering the installation of conductors, cables, and raceways in diverse applications. It emphasizes versatility and safety, offering detailed rules for everything from exposed wiring on building exteriors to specialized raceways like conduits. The overarching goal of Section 12 is to ensure that wiring systems are durable, efficient, and adaptable to future needs.
When it comes to communication conduits, Section 12 highlights:
재료 요구 사항: Conduits must meet high standards for durability, with specific attention to resisting environmental and mechanical stress.
Compatibility with Cables: Properly sized conduits are essential to house cables securely, allowing for smooth installation and future upgrades.
Separation and Routing: Ensures that communication conduits are installed with adequate separation from power wiring to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI).
This section underscores that raceways, including rigid and flexible conduits, are not merely protective pathways but integral components of a safe and efficient electrical infrastructure.
- Section 60 – Electrical Communication Systems: Section 60 focuses exclusively on communication systems, addressing the unique challenges of routing and protecting cables used for data, voice, and signaling. With the increasing reliance on fast and reliable connectivity in residential, commercial, and industrial settings, this section ensures that communication conduits meet modern performance and safety demands.
Key aspects of Section 60 include:
Tailored Protection: Communication conduits must shield cables from physical damage, environmental exposure, and signal interference.
Adaptability for Emerging Technologies: Recognizing the growth of high-speed internet and IoT systems, Section 60 ensures that communication conduits are suitable for advanced applications.
Compliance with Installation Standards: From underground to aerial installations, this section ensures that conduits maintain long-term performance and safety under various environmental conditions.
Section 60 builds on the principles of Section 12, applying them specifically to communication systems. It ensures that these systems are not only functional but also future-ready and aligned with Canada’s growing demand for digital infrastructure.
When it comes to installing fiber optic systems, choosing between conduit and direct-buried cables involves weighing factors like protection, scalability, installation, and maintenance requirements. Each method has its advantages, but conduit offers notable benefits in terms of longevity, flexibility, and reduced operational complexity.
Direct-buried fiber cables typically require metallic armor for physical protection and detection, as well as grounding and bonding to guard against electrical hazards. These steps can add complexity, time, and cost to the installation process. Additionally, when it’s time to terminate the cable, removing the armor introduces further challenges.
By contrast, conduit eliminates the need for metallic armor and its associated grounding requirements. Conduits provide a permanent protective pathway for fiber cables, simplifying the overall installation process. Maintenance also becomes more manageable, as technicians can easily access the conduit to repair or replace damaged cables without disturbing the surrounding environment.
The risk of damage to communication cables during construction or ground disturbances is significant, particularly in urban or high-traffic areas. Conduits act as a robust protective barrier, safeguarding cables from environmental stresses like moisture, soil shifts, and external mechanical forces, including accidental strikes during excavation.
Direct-buried cables, while equipped with durable outer sheaths, are inherently more vulnerable to such risks. Repairing these cables is not only costly but also time-sensitive, particularly when service disruptions lead to penalties under service-level agreements. Conduits mitigate these risks by physically separating cables from potential hazards, offering peace of mind in high-stakes installations.
One of the most significant advantages of conduit systems is their inherent scalability. Installing conduits creates a protected pathway that can accommodate additional fiber cables as network demand grows. This flexibility eliminates the need for repeated excavation or new permits, saving both time and resources. Conduits also allow for the possibility of leasing spare capacity to other service providers, offering a secondary revenue stream for operators.
In contrast, upgrading a direct-buried fiber network requires reopening trenches and laying new cables—a costly and time-intensive process. As technologies like 5G and Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) drive the need for expanded bandwidth, conduit systems provide the adaptability needed to meet evolving demands efficiently.
Advancements in conduit technology, such as microduct systems, have further enhanced the appeal of using conduits. Microducts are smaller-diameter conduits designed to optimize space and allow for multiple fiber pathways within a single protective structure. These systems offer:
Space Optimization: More cables in a smaller footprint, ideal for dense urban networks.
Ease of Routing: Simplified installation for distributed applications like 5G backhaul.
Cost-Effective Upgrades: The ability to add or replace cables without disturbing the overall infrastructure.
Conduit Vs. Direct-Buried Cable
측면 | 도관 | Direct-Buried Cable |
설치 | Structured and streamlined | Simpler initial setup but with added steps |
보호 | High level of mechanical and environmental safety | Moderate, relying on cable construction |
Repair Accessibility | Accessible without excavation | Requires trenching for repairs |
Scalability | Future-ready, supporting additional capacity | Limited and costly to upgrade |
환경 조건 | Ideal for unstable or high-risk areas | Suitable for stable, low-risk environments |
비용 | Higher upfront cost; lower long-term expenses | Lower initial cost; higher maintenance and repair costs |
The installation of communication conduit systems must adhere to various requirements that ensure both safety and reliable performance. Here are the primary considerations and installation guidelines drawn from NEC, ASTM, and other standards:
재료 호환성: The conduit must be compatible with the type of cable being used, ensuring protection against physical damage, moisture, and electromagnetic interference.
Separation from Power Lines: In many codes, such as the NEC Chapter 8, conduits carrying communication cables must be installed separately from high-voltage power lines to reduce the risk of electrical hazards and signal interference.
접지 및 본딩: Communication conduit systems must be properly grounded and bonded to avoid electrical shock hazards and to ensure signal integrity.
Temperature and Environmental Resistance: Communication conduits must be able to withstand environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations, moisture, and UV exposure. This is particularly important in outdoor or underground installations, as per standards like NEMA TC-10.
내화성: Conduits must meet specific fire-resistance standards, such as those outlined in UL 651A and other relevant fire codes, to prevent the spread of fire and protect telecom infrastructure.

Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elittellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
The telecom industry has always been in a state of constant evolution, adapting to the increasing demand for faster, more reliable connections and the emergence of new technologies. As the backbone of global communications, communication conduits have undergone significant transformations to meet the ever-growing needs of both consumers and businesses. From the early days of copper wire and basic protection systems to today’s advanced fiber optic networks and smart conduits, the evolution of the comms conduit is closely tied to the technological advances shaping the world.
The demand for faster internet speeds, low-latency communication, and the ability to handle massive amounts of data is at an all-time high. This is due in part to the expansion of 5G networks, which promise to revolutionize connectivity. With ultra-fast speeds and minimal delay, 5G technology is expected to support cutting-edge applications such as autonomous vehicles, virtual reality, and real-time data analytics. As these technologies require more advanced communication systems, the role of comms conduit systems in enabling them becomes even more critical.
Similarly, the expansion of fiber optic networks continues to provide the bandwidth needed for applications like seamless cloud computing, streaming, and the proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT). Fiber optic cables, which use light to transmit data, require specialized conduits that protect the delicate fibers while maintaining high performance. Over time, fiber optic conduits have evolved to offer enhanced durability, flexibility, and easy installation, helping telecom networks keep pace with the demand for high-speed data transfer.
One of the most promising developments in the telecom world is the rise of satellite internet solutions. These networks are bridging the digital divide by providing internet access to remote and underserved areas. Through the use of advanced satellite technology, communication conduits are extending their reach far beyond urban centers, ensuring that even the most geographically isolated communities can benefit from reliable internet connections. This is particularly important for rural areas and developing nations, where traditional cable-based infrastructure may be cost-prohibitive or impractical.
The future of communication conduits goes beyond physical protection to include smart technology. Smart conduits integrate sensors and monitoring systems that can detect issues such as cable damage, temperature fluctuations, or moisture ingress in real time. This allows telecom companies to proactively maintain their networks, preventing outages and minimizing downtime. As telecom systems become more complex and interconnected, the role of smart conduits in maintaining the integrity of the network becomes increasingly important.
These innovations not only improve the efficiency and longevity of telecom infrastructure but also align with the growing demand for sustainability. The push for environmentally friendly materials is driving the development of more sustainable conduits made from recycled plastics or biodegradable materials. As the world becomes more conscious of its environmental impact, the materials used in telecom conduit systems are evolving to reflect these concerns.
The evolution of the comms conduit is a testament to the rapidly changing telecom landscape. From simple protective tubes to advanced systems capable of supporting cutting-edge technologies like 5G, fiber optics, and satellite internet, communication conduits are more critical than ever. As we move toward a future where information flows seamlessly across the globe, the role of these conduits will only grow, ensuring that our networks remain fast, reliable, and capable of supporting the innovations of tomorrow
The comms conduit plays a crucial role in our modern world, providing the connections that make everything from video calls to online shopping possible. Although it’s often hidden, it is essential to the way we communicate, do business, and innovate. This network of communication conduits is what connects people, powers economies, and helps new technologies thrive.
We’ve discussed how communication conduits come in different types, like fiber optic cables, HDPE ducts, and steel conduits, each serving specific needs. These conduits ensure fast, reliable connections that support the growth of industries, especially with the rise of 5G networks and satellite internet bringing connectivity to remote areas.
Looking to the future, advancements in smart conduits and sustainable materials will continue to improve telecom infrastructure, enabling new technologies like IoT and AI. As these systems grow, it’s important that everyone has access to the benefits they bring.
We’d love to hear your thoughts on the future of comms conduits and how they might impact your life. And if you have any questions or requirements for communication conduit, contact us at any time.




