
Tabla de contenido
In modern electrical infrastructure, durability and safety are non-negotiable. That’s where Conducto de PVC Schedule 80 comes in. Known for its thick walls and high impact resistance, Schedule 80 conduit is a go-to choice for demanding environments where mechanical protection is critical. Whether referred to as schedule 80 electrical conduit, sch 80 conduit, or schedule 80 PVC electrical conduit, this material stands out for its robust performance across industrial, commercial, and utility applications.
In this article, we’ll explore the purpose of Schedule 80 PVC conduit, its available sizes, how it meets key code compliance requirements and installations. If you’re designing or installing electrical systems that demand extra protection, understanding the advantages of sch 80 PVC conduit can help ensure long-term system reliability and safety.
¿Qué es el conducto de PVC Schedule 80?
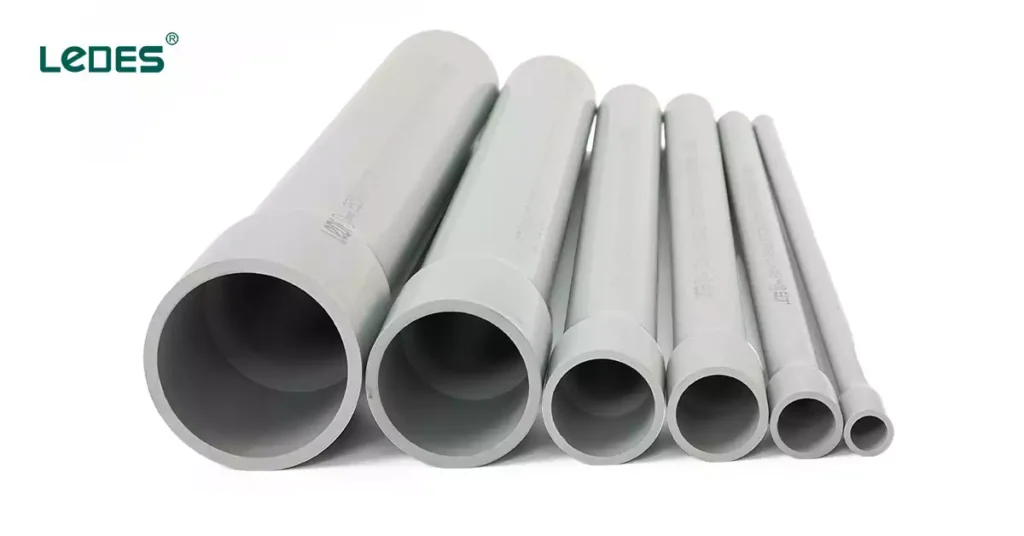

Definición
Schedule 80 PVC conduit, commonly labeled as sch 80 PVC conduit, schedule 80 electrical conduit, SCH 80 or Sch 80 PVC conduit. It is a type of nonmetallic raceway made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) that specifically designed for high-stress environments. The “Schedule 80” term refers to the wall thickness of the conduit, not the physical size of the conduit or its pressure capacity, which are sometimes confused.
Compared to Schedule 40, Schedule 80 conduit features a significantly thicker wall, providing greater impact resistance, crush resistance, and mechanical strength. This structural upgrade makes it a preferred choice for environments where the conduit is subject to physical abuse or where enhanced protection is required for critical electrical systems.
The Role of SCH 80 PVC Conduit
The primary function of Schedule 80 PVC electrical conduit is twofold:
Protección mecánica
- It shields electrical wires and cables from physical hazards such as impact, crushing, and environmental stresses (UV exposure, corrosion, vibration, etc.). It’s particularly valuable in:
- Instalaciones industriales
- Outdoor installations
- Underground wiring systems
- High-traffic or heavy-equipment zones
Efficient Wire Routing
As a rigid raceway, it offers a reliable and code-compliant pathway for running and pulling conductors, simplifying wire replacement and inspection during future maintenance or upgrades.
When conduit is exposed to mechanical risk and high stress, the durability of Schedule 80 conduit becomes a necessity, not an option. Its thicker wall helps comply with National Electrical Code rules regarding protection against physical damage.
Consejos profesionales: Want to learn more about electrical raceways and how to choose the right one? You can read this comprehensive guide to the electrical raceway to learn more.
SCH 80 PVC Conduit Sizes and Dimensions
Schedule 80 PVC conduit is available in a wide range of sizes to accommodate various wiring demands, from light residential circuits to complex industrial systems. Understanding the available sizes and specifications is essential for selecting the right conduit size for your project.
Tamaño comercial (pulgadas) | Designador métrico (mm) |
1/2 | 16 |
3/4 | 21 |
1 | 27 |
1-1/4 | 35 |
1-1/2 | 41 |
2 | 53 |
2-1/2 | 63 |
3 | 78 |
3-1/2 | 91 |
4 | 103 |
5 | 129 |
6 | 155 |
These are nominal trade sizes, and the actual outer diameter (OD) is the same as that of Schedule This wide selection allows contractors and engineers to select the most suitable size for specific conductor quantities, environmental conditions, and installation locations.
Outer Diameter Consistency of Sch 80 Conduit
The outer diameter (OD) of Schedule 80 PVC conduit is the same as that of Schedule 40 conduit of the same nominal size. This ensures compatibility with standard fittings and accessories across conduit types. However, due to the thicker wall of Schedule 80, the inner diameter (ID) is smaller, which affects internal capacity.
Dimensions and Wall Thickness of Sch 80 Conduit
According to UL651, the dimensions of SCH 80 PVC conduit are as follows:
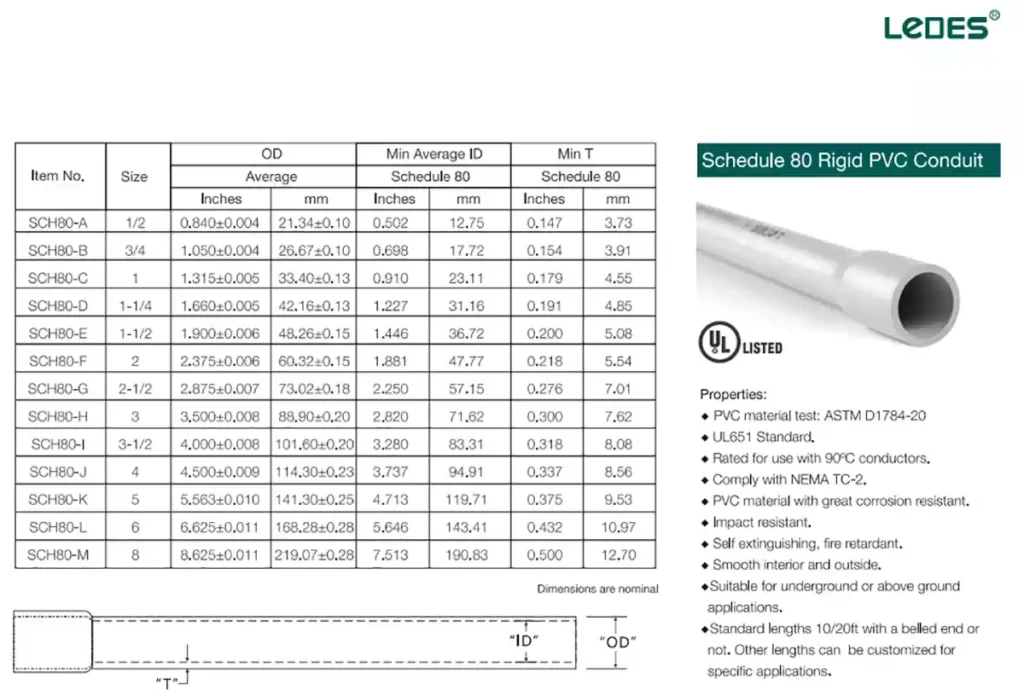
Smaller sizes (½” to 1″) are frequently used in residential and light commercial installations, while larger sizes (2″ and above) are often seen in industrial, utility, or infrastructure projects, where larger conductor bundles or higher levels of physical protection are required.
Length and Configuration of Sch 80 Conduit
Most Schedule 80 PVC electrical conduit is supplied in:
- 10 feet or 20 feet lengths as standard
- With one end plain and the other bell-end for solvent welding joining, or both ends in plain.
Conduits can be bent with heat (could be hard due to thick walls) or joined with PVC elbows, couplings, and fittings, which are also rated for Schedule 80 wall thickness.
Pros and Cons of Schedule 80 PVC Conduit

Schedule 80 PVC electrical conduit is known for its enhanced durability and protection capabilities, especially in environments where mechanical impact or exposure to harsh elements is a concern. However, as with any conduit type, it comes with both benefits and trade-offs. Understanding these advantages and disadvantages helps engineers, contractors, and electricians make informed choices for each application.
Schedule 80 PVC Conduit Advantages
Thicker Wall for Greater Strength
The most prominent feature of SCH 80 PVC conduit is its thicker wall compared to Schedule 40, which results in:
- Improved resistance to physical impact
- Higher compression strength
- Better protection against crushing or deformation in buried or exposed applications
This makes it ideal for demanding installations like industrial plants, utility substations, or direct burial in high-traffic zones.
Enhanced Protection in Harsh Environments
Due to its robust wall structure, SCH 80 offers better protection for electrical wires and cables against:
- Mechanical abrasion
- Accidental puncture
- Rodents or debris in underground installations
It is frequently used in outdoor and corrosive environments, especially when conduit integrity is critical.
Long-Term Durability and Corrosion Resistance
As with all PVC conduits, SCH 80 is non-metallic and corrosion-resistant, making it suitable for:
- Ambientes húmedos o corrosivos
- Chemical plants or wastewater facilities
- Marine or coastal installations
Its added thickness further extends its life cycle in aggressive settings.
UV Resistance (with Additives)
Most manufacturers offer Schedule 80 conduits with UV-resistant formulations, making them suitable for extended outdoor use when exposed to sunlight.
Schedule 80 PVC Conduit Disadvantages
Reduced Internal Space (Smaller ID)
The thicker wall of SCH 80 reduces its internal diameter, resulting in:
- Less space for conductors
- Potentially higher conduit size requirements for the same wire count compared to Schedule 40
- More frequent fill calculations to ensure code compliance
This can be a limitation in space-constrained designs or projects aiming to minimize material volume.
Increased Weight and Harder for Installation
Schedule 80 conduit is heavier and less flexible, which can lead to:
- More difficult handling during installation
- Greater labor or equipment needs, especially for large-diameter conduits
- Higher shipping and transport costs
Higher Material Costs
Due to its increased wall thickness and resin content, SCH 80:
- Costs more per foot than Schedule 40 or DB-rated conduit
- Might impact project budgets for large-scale installations if not absolutely necessary
Understanding these pros and cons allows professionals to determine when Schedule 80 PVC conduit is the best choice, not just based on strength, but also on project efficiency and cost.
Sch 80 PVC Conduit Code Compliance
Schedule 80 PVC conduit is widely used in electrical systems where enhanced mechanical protection is required. To ensure safety, performance, and regulatory compliance, this type of conduit must meet several industry standards. The most relevant are UL 651, ASTM D1784, and the National Electrical Code (NEC). This section breaks down each of these in detail, with a focus on how they apply specifically to Schedule 80 conduit.
ASTM D 1784: PVC Compound Material Classification
ASTM D1784 is the standard specification that governs the physical and mechanical properties of the polyvinyl chloride (PVC) compound used in manufacturing Schedule 80 rigid PVC conduit. This specification ensures that the material can perform reliably under mechanical, thermal, and electrical stress over time.
Required Cell Classification of SCH 80
According to UL651, the compound of Schedule 80 PVC conduit must have cell class equal to or greater than 12123, ensuing minimum thresholds in five property categories:
Property Category | What It Describes |
Base Resin | Type of PVC resin used (e.g., homopolymer or copolymer) |
Resistencia al impacto | Resistance to sudden force or impact (lzod impact value) |
Resistencia a la tracción | Maximum stress the material can withstand when stretched, indicates structural strength under pulling forces. |
Modulus of Elasticity | Flexibility or stiffness of the material, reflects rigidity |
Deflection Temperature Under Load (DTUL) | Temperature at which material deforms under a load, important for high-temperature installations |
These characteristics are critical for ensuring long-term performance of rigid conduits in both indoor and outdoor electrical systems, especially where higher mechanical strength is necessary.
Why ASTM D1784 Matters
Compliance with ASTM D1784 helps manufacturers and specifiers ensure that:
- The PVC compound is rigid, durable, and weather-resistant
- The material performs reliably across a wide temperature range
- The conduit maintains structural integrity under mechanical load
- The product can meet UL 651 testing without failure
In essence, ASTM D1784 forms the material foundation upon which performance standards like UL 651 and installation standards like the NEC are built.
UL651: Safety Standard for Rigid PVC Conduit and Fittings
UL 651 is the principal standard for both Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 PVC conduit. Since Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 share most of the same test criteria, we’ll briefly summarize the key points here. For a detailed review of UL 651 testing, see our article of introducing Schedule 40 PVC Conduit.
UL 651 Test Requirements
Both Schedule 40 and 80 rigid PVC conduits must meet the following performance criteria, detailed testing method and requirements, check on the previous article of Schedule 40 conduit introduction:
Requisitos | Descripción |
Resistencia a la tracción | Must meet a minimum of 5,000 psi, ensuring adequate resistance to pulling forces. |
Extrusion Quality | PVC must be uniformly extruded, free from cracks, blisters, or voids to maintain structural integrity. |
Low-Temperature Handling | Conduit is tested for flexibility and durability at low temperatures to avoid brittleness and cracking. |
Water Absorption Resistance | Material must resist absorbing water, ensuring long-term mechanical and dielectric performance. |
Deflection Under Load | Assesses how much the conduit deforms under mechanical load, simulating real-world stresses. |
Resistencia a las llamas | Tested to ensure the conduit self-extinguishes and limits flame spread per UL safety standards. |
Resistance to Specified Reagents | Conduit must resist degradation when exposed to chemicals like acids and oils, suitable for industrial use. |
Resistencia a la luz solar | To be suitable for outdoor and exposed environments, the Schedule 80 should made of UV-resistant formulations to pass the UV-resistant test. |
Rated for 90°C Conductors | Certified for use with conductors rated up to 90°C, suitable for modern electrical wiring loads. |
Schedule 80 Vs Schedule 40 Codnuit Specific Differences
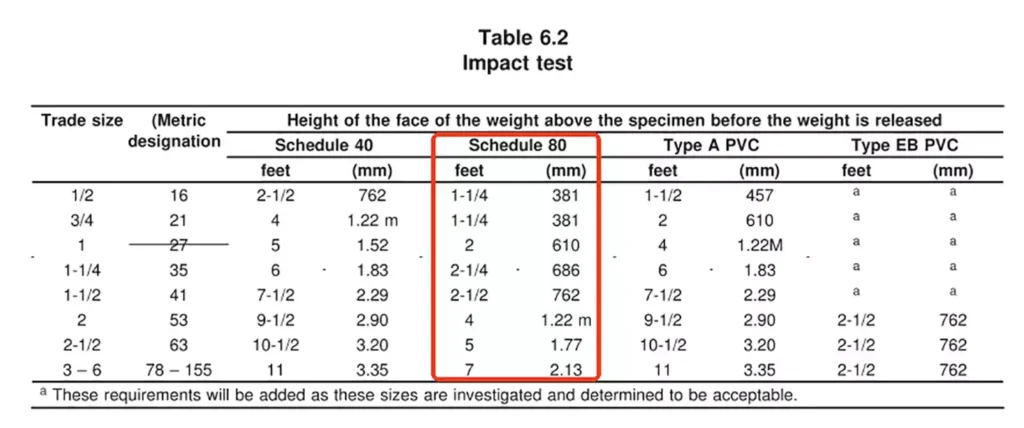
While many test methods are identical to those for Schedule 40, UL 651 specifies stricter mechanical requirements for Schedule 80 conduit in two main areas:
- Resistencia al impacto:
Conducto de PVC Schedule 40: 20 lb (9.7 kg) weight, 2 in (51 mm) diameter cylinder
Schedule 80 PVC Conduit: 75 lb (34 kg) weight, 6 in (150 mm) diameter cylinder
Drop height varies by size, as defined in Table 6.2 of UL 651.
- Resistencia al aplastamiento:
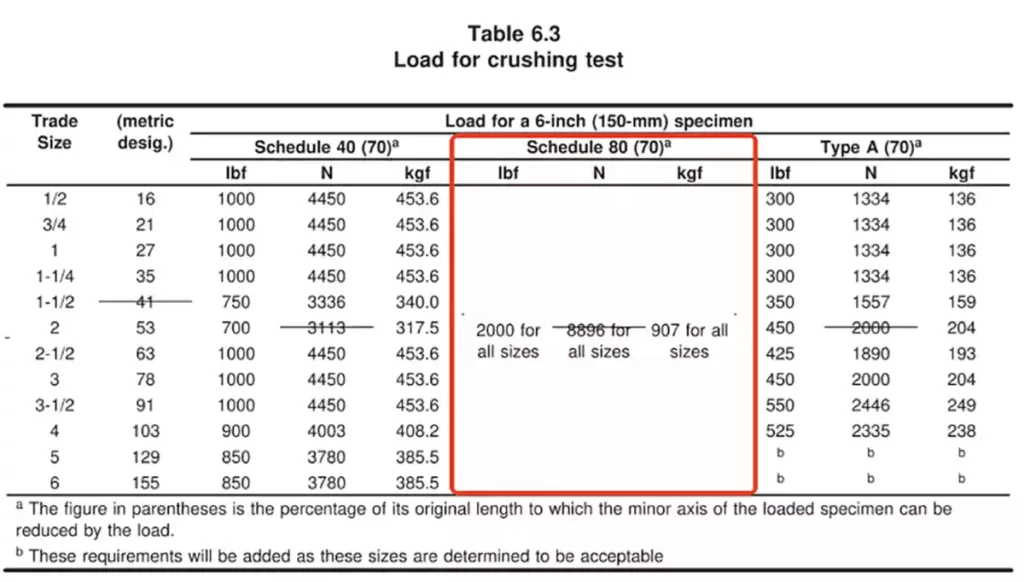
El mismo método de prueba que el Schedule 40, pero con requisitos de carga más elevados, como se detalla en la Tabla 6.3 de UL 651.
Estas mejoras garantizan que el conducto Schedule 80 sea más robusto y adecuado para aplicaciones con mayor estrés mecánico.
Código Eléctrico Nacional (NEC) - Artículo 352
El Código Eléctrico Nacional (NEC) es el documento que rige las instalaciones eléctricas en Estados Unidos. El Artículo 352 aborda específicamente los conductos rígidos de cloruro de polivinilo (PVC).
352.10(K) - Uso donde esté expuesto a daños físicos
El NEC exige el uso del Cédula 80 en lugares donde el conducto esté sujeto a daños físicos, como áreas en entornos comerciales o industriales con tráfico pesado de maquinaria.
352.12 - Usos no permitidos
Los conductos de PVC (tanto SCH 40 como 80) no se pueden utilizar en lugares peligrosos o áreas sujetas a temperaturas ambiente superiores a 50 °C, a menos que estén listados o protegidos adecuadamente.
353.22 - Número de conductores
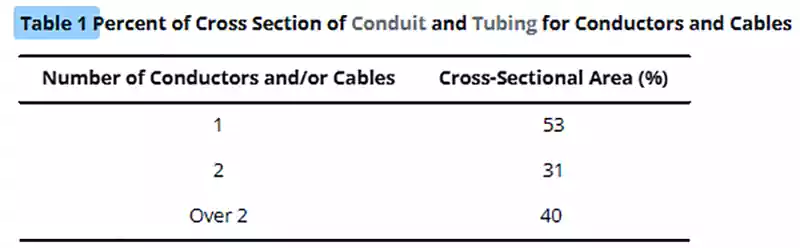
La cantidad permitida de conductores en un conducto se determina según la Tabla 1 del Capítulo 9 y el espacio interno del conducto, que es más pequeño en Sch 80 que en Sch 40. Esto da como resultado una capacidad de llenado de cable reducida para el mismo tamaño nominal.
Anexo C - Relleno de conductos
El relleno de conductos se refiere a la cantidad de espacio dentro de un conducto que ocupan los conductores eléctricos. Un relleno adecuado es esencial para garantizar una disipación térmica segura, facilitar la instalación de los conductores y la fiabilidad del sistema a largo plazo.
Anexo C La Tabla C.10(A) proporciona tablas de llenado de conductores para conductos de PVC Schedule 80.
Tipo | Tamaño del comercio (designador métrico) | |||||||||||||
3/8 | 1/2 | 3/4 | 1 | 11/4 | 11/2 | 2 | 21/2 | 3 | 31/2 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
CONDUCTORES | ||||||||||||||
RHH, RHW, RHW-2 | 14 | — | 3 | 5 | 9 | 17 | 23 | 39 | 56 | 88 | 118 | 153 | 243 | 349 |
12 | — | 2 | 4 | 7 | 14 | 19 | 32 | 46 | 73 | 98 | 127 | 202 | 290 | |
10 | — | 1 | 3 | 6 | 11 | 15 | 26 | 37 | 59 | 79 | 103 | 163 | 234 | |
8 | — | 1 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 8 | 13 | 19 | 31 | 41 | 54 | 85 | 122 | |
6 | — | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 11 | 16 | 24 | 33 | 43 | 68 | 98 | |
4 | — | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 12 | 19 | 26 | 33 | 53 | 77 | |
3 | — | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 11 | 17 | 23 | 29 | 47 | 67 | |
2 | — | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 9 | 14 | 20 | 25 | 41 | 58 | |
1 | — | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 9 | 13 | 17 | 27 | 38 | |
1/0 | — | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 11 | 15 | 23 | 33 | |
2/0 | — | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 10 | 13 | 20 | 29 | |
3/0 | — | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 11 | 17 | 25 | |
4/0 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 15 | 21 | |
250 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 11 | 16 | |
300 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 10 | 14 | |
350 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 9 | 13 | |
400 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 8 | 12 | |
500 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 10 | |
600 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 8 | |
700 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | |
750 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | |
800 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 7 | |
900 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 6 | |
1000 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 | |
1250 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 4 | |
1500 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 | |
1750 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
2000 | — | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | |
352.44(A)- Expansión y contracción térmica
Cuando se instala en entornos con grandes variaciones de temperatura, pueden requerirse accesorios de expansión para cumplir con las pautas NEC Tabla 352.44(A) y evitar la tensión o deformación del conducto.
Al garantizar el cumplimiento de las normas UL, ASTM y NEC, el conducto de PVC Schedule 80 ofrece una solución altamente confiable y aprobada por el código para entornos eléctricos exigentes.
NEMA TC 2: Requisitos para conductos eléctricos de PVC
La norma NEMA TC-2, establecida por la Asociación Nacional de Fabricantes Eléctricos (NEMA), describe las especificaciones para los conductos rígidos de cloruro de polivinilo (PVC) utilizados en sistemas eléctricos. Los conductos de PVC cédula 80, conocidos por sus paredes más gruesas y mayor resistencia mecánica, deben cumplir los criterios definidos en esta norma para garantizar una calidad, un rendimiento y una seguridad consistentes en una amplia gama de aplicaciones.
NEMA TC-2 cubre aspectos clave como:
Composición del material
Garantiza el uso de compuesto de PVC virgen o reprocesado de calidad con propiedades aislantes y mecánicas confiables.
Consistencia dimensional
Define el diámetro exterior, el espesor de la pared y las tolerancias de longitud para garantizar la compatibilidad con accesorios estándar y un rendimiento uniforme.
Color
El conducto de PVC rígido Schedule 80 debe ser de color gris; otros colores pueden ser aceptables si se acuerda con los terceros involucrados.
Prueba de deflexión
Para verificar la capacidad del conducto para soportar la compresión y volver a su forma casi original.
El conducto se comprime a un ritmo uniforme mediante placas de acero rígidas.
El diámetro interior debe conservar al menos 70% de su tamaño original bajo la carga especificada (según la Tabla 4-1 de la norma).
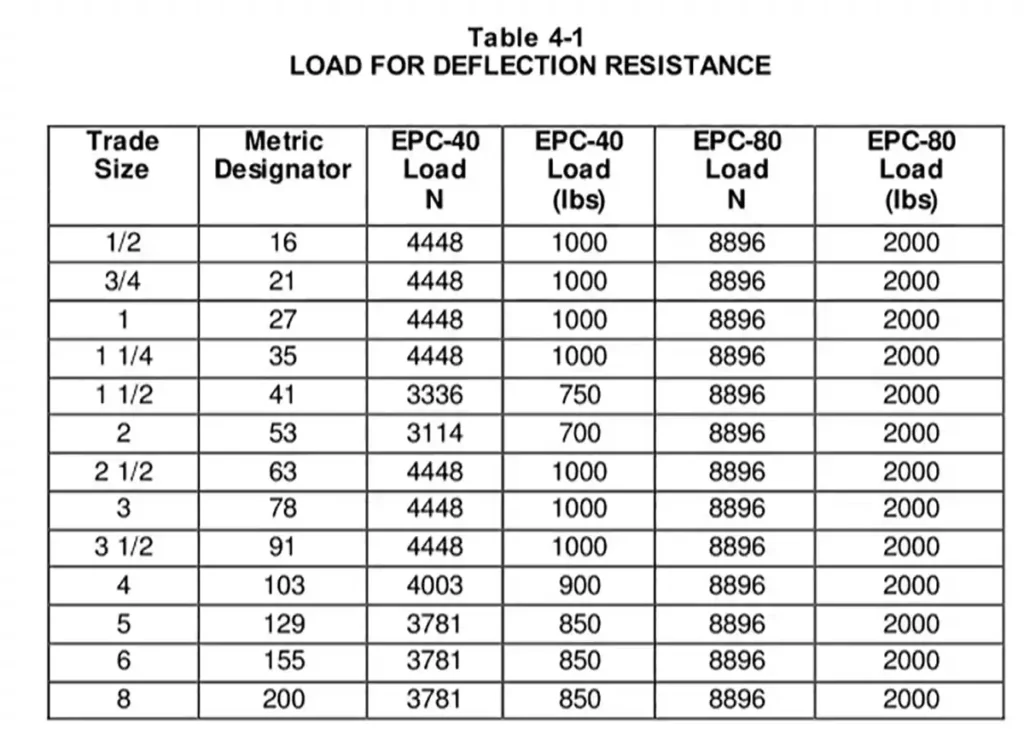
Fugas en juntas cementadas con solvente
Para confirmar la estanqueidad de las uniones de conductos adheridos bajo presión.
Las juntas cementadas con disolvente se someten a pruebas de presión de agua.
Las juntas deben soportar 25 psi (172,4 kPa) durante una hora sin fugas.
Aplastamiento
Para evaluar la resistencia del conducto al aplastamiento o agrietamiento bajo carga de compresión.
El conducto se comprime entre placas planas hasta 40% de su diámetro exterior original.
No se permite ninguna división ni desgarro en la pared durante o después de la compresión.
Resistencia al impacto
Para evaluar la tenacidad del conducto y su capacidad para resistir fracturas por impactos externos.
Se deja caer un peso de 75 lb ± 12 oz (igual que UL651) sobre el conducto sostenido por una base de acero.
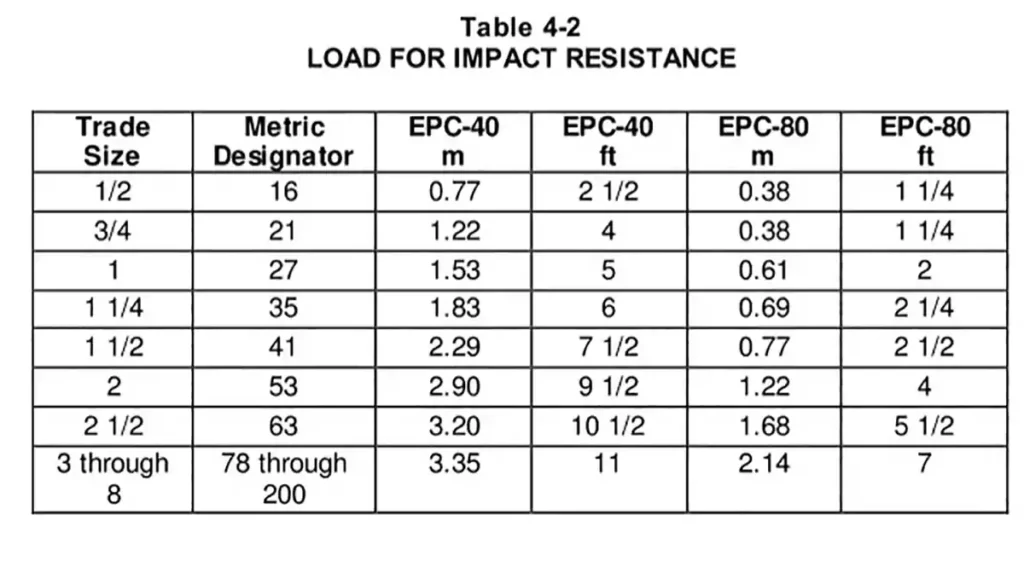
Un mínimo de 7 de 10 muestras analizadas no deben presentar grietas ni rasgaduras durante la inspección.
Las alturas de caída de peso son las especificadas en la Tabla 4-2:
Requisitos de marcado para conductos de PVC Sch 80
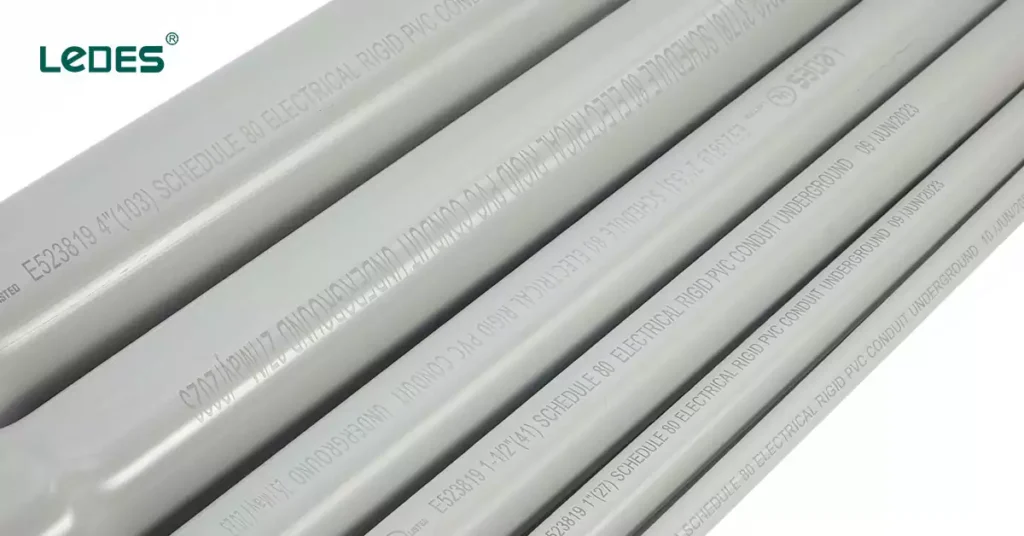

El marcado correcto en los conductos de PVC Schedule 80 es esencial para la identificación del producto, el cumplimiento de la normativa y una instalación segura. Este marcado se rige principalmente por la norma UL 651 y garantiza que los usuarios puedan verificar fácilmente especificaciones clave como el tipo de producto, el fabricante y la idoneidad para determinadas aplicaciones.
Elementos clave de marcado necesarios:
- Nombre o marca registrada del fabricante
- Tamaño comercial del conducto
- Tipo de producto: Conducto eléctrico rígido de PVC, cédula 80
- Cumplimiento de normas: como UL651
- Fecha de fabricación
- CABLE RESISTENTE A LA LUZ SOLAR o MÁXIMO 90 °C si está clasificado
Importancia de un marcado adecuado
Las marcas adecuadas en los conductos de PVC Schedule 80 cumplen múltiples propósitos:
- Verificación de campo por electricistas e inspectores.
- Controles de cumplimiento durante las etapas de aprobación o inspección del proyecto.
- Validación de la garantía y trazabilidad de la fabricación.
El no incluir o seguir estos requisitos de marcado puede resultar en el rechazo de la instalación por parte de los inspectores o las autoridades encargadas del cumplimiento del código y puede afectar la confiabilidad o seguridad del sistema.
7 aplicaciones del conducto de PVC Schedule 80
El conducto de PVC cédula 80 está diseñado para entornos exigentes que requieren protección eléctrica y durabilidad mecánica. Gracias a su mayor espesor de pared en comparación con el cédula 40, suele ser el conducto predilecto para instalaciones industriales, comerciales y de alto impacto.
A continuación se presentan los escenarios de aplicación comunes en los que se prefiere o se requiere el conducto eléctrico de PVC Schedule 80 (conducto de PVC Sch 80):
1. Instalaciones expuestas sobre el suelo
En entornos donde el conducto está expuesto a posibles impactos, como en almacenes, salas mecánicas o áreas industriales al aire libre, las paredes más gruesas del Schedule 80 ofrecen una protección superior contra:
Daño físico
Impacto accidental de vehículos o herramientas
Vandalismo
2. Instalaciones subterráneas
Si bien los conductos con clasificación Schedule 40 y DB se utilizan comúnmente para cableado subterráneo, el Schedule 80 a menudo se especifica en áreas donde:
La presión del suelo es alta (por ejemplo, debajo de carreteras o caminos de acceso)
Existe potencial de carga pesada sobre el suelo.
La profundidad de instalación es baja y carece de refuerzo externo.
Su alta resistencia al aplastamiento y al impacto lo hacen confiable en sistemas críticos de canales subterráneos.
3. Ambientes corrosivos
Gracias a la resistencia química inherente del material de PVC, el conducto Schedule 80 es adecuado para entornos expuestos a:
Aire salado (instalaciones costeras)
Productos químicos y ácidos (plantas de procesamiento químico)
Plantas de tratamiento de aguas residuales
Áreas agrícolas o de manejo de fertilizantes
A diferencia de los conductos metálicos, el PVC no se corroe ni se oxida, lo que lo hace ideal para una durabilidad a largo plazo.
4. Lugares peligrosos (cuando estén permitidos)
En ubicaciones clasificadas como peligrosas, se pueden utilizar sistemas de conductos no metálicos como Schedule 80 si:
Debidamente sellado
Aprobado por la Autoridad competente (AHJ)
Instalado de conformidad con el NEC y cualquier accesorio listado por UL aplicable
Confirme siempre con los códigos eléctricos locales.
5. Instalaciones industriales y de fabricación
Las fábricas y los entornos de trabajo pesado suelen presentar maquinaria y riesgos operativos. El conducto cédula 80 se utiliza para:
Enrutar la energía a los motores y paneles de control
Proteger el cableado de comunicaciones o fibra óptica
Mantener limpios los caminos de cables en las líneas de producción
Su alta resistencia a la tracción y al impacto reducen el tiempo de inactividad causado por daños en los conductos.
6. Edificios institucionales y comerciales
En espacios públicos o comerciales como:
Hospitales
Escuelas
Estadios
Cuartos de servicio
El Schedule 80 se instala donde se requiere protección adicional de conductos debido al alto tránsito peatonal o acceso a equipos de mantenimiento.
7. Proyectos de energía renovable y servicios públicos
En sistemas de energía solar y eólica, particularmente en instalaciones a gran escala:
Los conductos están expuestos a los rayos UV, al viento y al desgaste físico.
El Schedule 80 se especifica a menudo para tramos verticales y contrahuellas expuestos.
Las variantes resistentes a la luz solar garantizan un rendimiento a largo plazo
Guía de instalación de conductos de PVC Sch 80 (9 pasos)
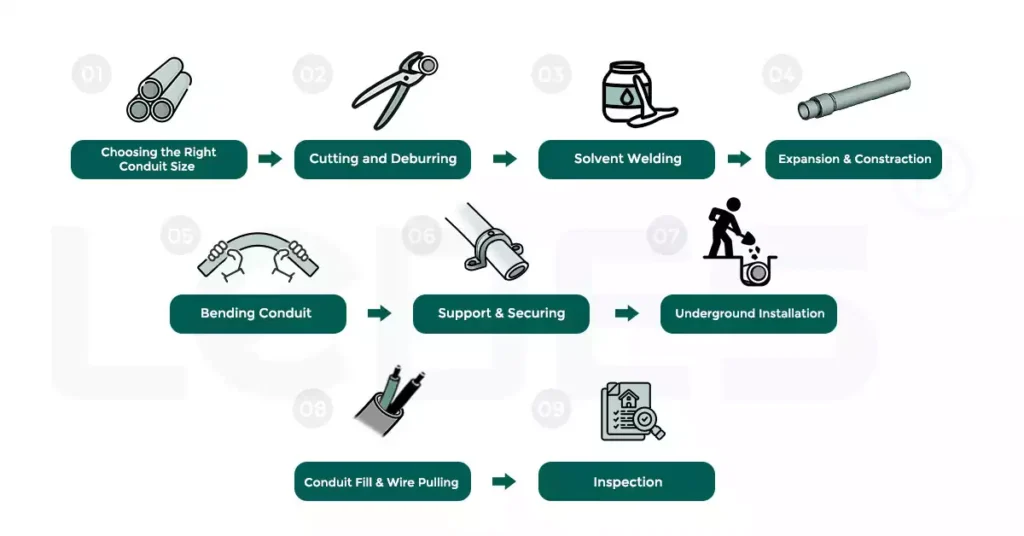
Una instalación correcta es esencial para maximizar el rendimiento, la seguridad y el cumplimiento normativo del conducto de PVC cédula 80 (conducto Sch 80). Si bien su pared más gruesa proporciona una mayor durabilidad, también requiere una manipulación y preparación cuidadosas, especialmente en entornos exigentes.
Notas: Leer más sobre Consejos para la instalación de conductos, Requisitos de cumplimiento y consideraciones en nuestro asesoramiento de expertos en instalación de conductos eléctricos.
Aquí se describen las mejores prácticas y consideraciones esenciales para instalar conductos eléctricos Schedule 80 de acuerdo con los estándares de la industria y el NEC.
1. Elección del tamaño de conducto adecuado
Seleccionar el tamaño correcto de conducto de PVC Schedule 80 es crucial para garantizar un sistema eléctrico seguro, eficiente y que cumpla con la normativa. El tamaño que elija dependerá de los siguientes factores:
Requisito del proyecto
Número y tipo de conductores
Capacidad de llenado del conductor
2. Corte y desbarbado
Las paredes gruesas del Schedule 80 requieren un poco más de esfuerzo para cortarlas que las del Schedule 40. Por lo tanto, es mejor utilizar una sierra de dientes finos para cortar; también se puede utilizar un cortador de conductos para tamaños pequeños, pero puede ser difícil.
3. Soldadura con solvente
Las secciones de conductos de PVC generalmente se unen mediante soldadura con cemento solvente:
Limpie ambas superficies: dentro del accesorio y fuera del conducto.
Aplique imprimación para ablandar el plástico y mejorar la adhesión (requerido para la mayoría de las instalaciones que cumplen con el código).
Aplique el cemento solvente mientras la imprimación aún esté húmeda.
Inserte el conducto en el conector con un giro de 1/4 para distribuir el cemento de manera uniforme.
Manténgalo así durante 30 segundos y luego deje que se endurezca adecuadamente (consulte las instrucciones del fabricante del cemento).
4. Gestión de la expansión y la contracción
PVC expands and contracts significantly with temperature changes.
For outdoor or long runs:
Use expansion fittings to accommodate movement (required when temperature variation exceeds 25°F/13.9°C).
Refer to NEC Table 352.44(A) for guidance on expansion fitting spacing.
5. Bending Conduit
Unlike ENT or flexible conduit, Schedule 80 PVC must be heat bent if custom angles are required:
But due to it’s thick wall, it’s not that easy for heat bending, factory-made elbows and sweeps are often recommended for consistency and code compliance.
6. Support and Securing
Schedule 80 conduit must be properly supported according to NEC 352.30:
Horizontal runs: Secure within 3 feet (0.91 m) of each box or fitting and at intervals not exceeding 10 feet (3.05 m).
Vertical runs: Use straps or clamps rated for PVC, considering expansion/contraction movement.
7. Underground Installation
Schedule 80 is ideal for direct burial without additional encasement. Installation must comply with:
NEC 300.5 for minimum burial depths
Soil compaction and backfill without sharp rocks or debris
Use of bushings to protect conductors at entry/exit points
8. Conduit Fill and Wire Pulling
Follow NEC Chapter 9, Table 1 and Annex C for conduit fill calculations.
Use fish tape to help the wire pulling and avoid pulling at high tension to prevent insulation damage.
9. Inspection
Check and ensure all installed conduit is properly supported, sealed, and compliant with applicable codes.
Installations are reviewed by the Authority Having Jurisdiction (AHJ) when required.
Each manufacturer may provide specific guidance based on their Schedule 80 product formulation and listings (e.g., temperature ratings, pressure resistance, fire performance). Always consult their documentation in addition to national codes.
Burial Depth for Sch 80 PVC Conduit
Schedule 80 PVC conduit is often used underground, when used underground, the burial depth mush comply with NEC Table 300.5, which outlines minimum cover requirements based on voltage, installation location, and protection level.
Location & Application | Profundidad mínima de enterramiento |
All locations not specified | 18 in. (450mm) |
In trench below 50mm thick concrete | 12 in. (300mm) |
Under a building | 0 |
Under streets, highways, roads | 24 in. (600mm) |
Under min. 102mm thick concrete slab with no vehicle traffic | 4 in. (100mm) |
In or under airport runways | 18 in. (450mm) |
Always verify with local code enforcement or utility provider as local amendments may require deeper installation or additional protection methods.
Schedule 80 vs. Schedule 40 PVC Conduit
Schedule 80 PVC conduit and Schedule 40 PVC conduit are two commonly used types of rigid nonmetallic conduit, each with different wall thicknesses, mechanical properties, and application focuses. Understanding their differences is essential for choosing the right one based on environmental conditions, load-bearing needs, and regulatory compliance.
Característica | Anexo 80 | Anexo 40 |
Espesor de la pared | Thicker | Thinner |
Outside Diameter | Same as SCH 40 | Same as SCH 80 |
Inside Diameter | Smaller | Larger |
Conductor Fill Capacity | Más bajo | Más alto |
Peso | Más pesado | Encendedor |
Costo | Más alto | Más bajo |
Resistencia mecánica | Alto | Más bajo |
Facilidad de instalación | Harder to cut and install | Easier to cut and install |
Aplicaciones típicas | Industrial, direct burial, exposed to physical damage | Residential, above-ground, light duty environments |
SCH 80 PVC Conduit vs. DB Conduit
When planning an underground installation, both Schedule 80 PVC conduit and DB conduits can be used, then which one to choose and what are their differences?
What Is DB Conduit?
“DB” stands for Direct Burial, and DB conduits are specifically designed for underground use. These conduits are not intended to be exposed above ground and are often used by power utilities and telecom companies. DB conduit is categorized by wall thickness ratings, such as:
- DB60 – Light-duty wall, used where minimal protection is acceptable.
- DB100 – Medium-duty wall, suitable for many utility applications.
- DB120 – Heavy-duty wall, but still thinner than Schedule 40 and 80.
They are manufactured to NEMA TC 6 & 8 standard.
Característica | Conducto de PVC Schedule 80 | DB PVC Conduit |
Uso principal | Exposed or underground wiring subject to physical damage | Underground only – direct burial in trenches |
Espesor de la pared | Thicker then SCH 40 and DB conduits | Thinner then SCH 40 and 80, even at DB120 rating |
Estándar | UL 651 | NEMA TC 6 y 8 |
Resistencia mecánica | High impact and crush resistance | Menor resistencia mecánica |
UN Resistance | Yes if rated, suitable for above-ground exposure | No, for underground use |
Bendability | Less flexible, more rigid | More flexible, easier to handle |
Costo | Higher (due to thicker wall and UL listing) | Lower (more economical for buried-only installations) |
When to Use
Use SCH 80 PVC Conduit for:
Above-ground runs
Underground runs exposed to physical damage
Harsh environments requiring added protection
Use DB Conduit (DB60/100/120) for:
Underground-only electrical and communication ducting
Long-distance trenching
Projects where cost efficiency and physical damage risk is low
Consejos profesionales: Still confused about the direct burial conduit type and code compliance? You can click the link above to read our newest guide.
Why Choose Schedule 80 PVC Conduit?
Among the various options available, Schedule 80 PVC conduit stands out as a top-tier choice when high mechanical strength and code compliance are essential. And why choose it over other alternatives?
Superior Wall Thickness and Strength
The most defining characteristic of Schedule 80 PVC conduit is its thicker wall, which provides:
- Greater impact resistance – ideal for locations prone to mechanical abuse, such as warehouses, garages, or commercial risers.
- Higher crush resistance – suitable for installations under roadways or in areas with potential soil pressure or heavy equipment traffic.
- Compliance with more demanding installation environments.
Code Compliance in High-Risk Areas
Schedule 80 PVC conduit is often required by the NEC and local authorities when wiring systems are:
Exposed to potential damage
Installed on posts, risers, or exterior walls
Transiting from underground to above-ground systems
Its UL 651 listing and robust test performance give inspectors and engineers confidence in its use for demanding applications.
Versatility Across Applications
Unlike DB conduit which is limited to underground use, Schedule 80 PVC conduit is suitable for:
Instalaciones sobre el suelo y subterráneas
Indoor and outdoor environments
Wet, dry, and corrosive areas
Transition points in residential, commercial, industrial, and utility projects
Sunlight and Corrosion Resistance
Schedule 80 PVC conduit is designed for UV exposure and corrosive atmospheres:
Gray coloring includes UV inhibitors, allowing long-term outdoor installation without degradation.
Excellent chemical resistance makes it ideal for water treatment plants, agricultural facilities, or coastal regions.
Smooth Interior for Easier Pulling
Despite its thicker walls, Schedule 80 still offers:
A smooth bore that reduces friction
Easier wire pulling compared to metal conduit
Non-conductive material that eliminates the need for grounding in many cases
Broad Size Availability
Schedule 80 conduit is available in a wide range of diameters, from ½ inch to 6 inches, accommodating everything from branch circuits to large-scale service entrances. With matching fittings, couplings, boxes, and adapters, it supports end-to-end solutions in even the most complex wiring designs.
Cost-Effective Alternative to Metal
While more expensive than Schedule 40 or DB conduit, Schedule 80 is still significantly more affordable and easier to install than rigid metal conduit (RMC). It provides a high-performance and corrosion-proof alternative without the need for cutting oils, special tools, or grounding.
Specialized Schedule 80 PVC Conduit
While standard Schedule 80 PVC conduit is already a durable and versatile solution, but modern electrical systems, especially in solar energy and sensitive environments often demand more specialized materials.
Schedule 80 Solar Conduit
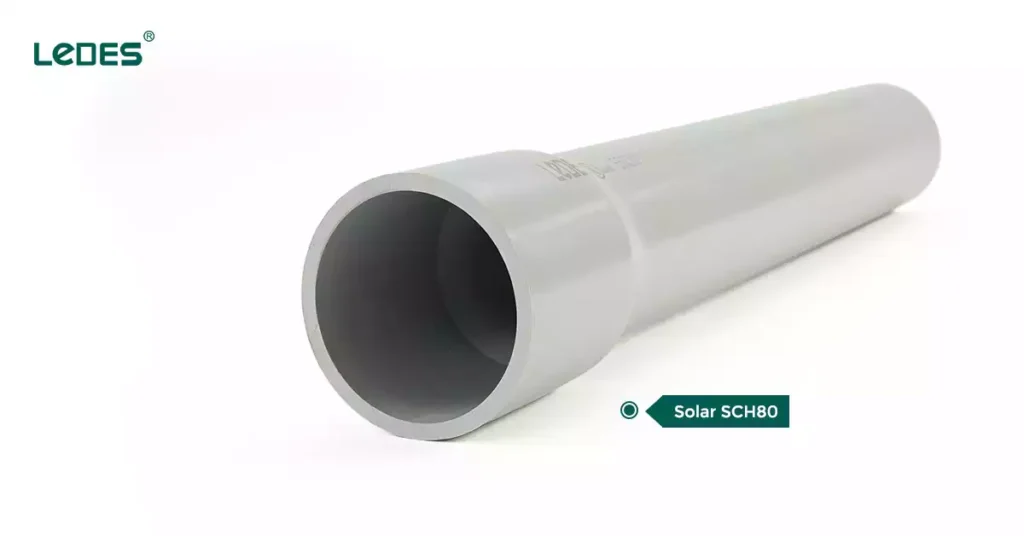

Solar installations, particularly those exposed to harsh environmental conditions, require conduits that can withstand:
- Intense UV exposure
- Wide temperature fluctuations
- Mechanical stresses from wind and other environmental factors
Schedule 80 solar conduits specifically designed for solar applications feature:
- Enhanced UV resistance: Tested for prolonged exposure to sunlight without degradation.
- High mechanical strength: Withstands outdoor harsh environments, ensuring durability under mechanical stress.
- Fire rating: Ensures self-extinguishing properties for added safety.
Such conduits are ideal for rooftop solar arrays, ground-mounted systems, and other installations where long-term durability and safety are paramount.
LSZH Schedule 80 Conduit
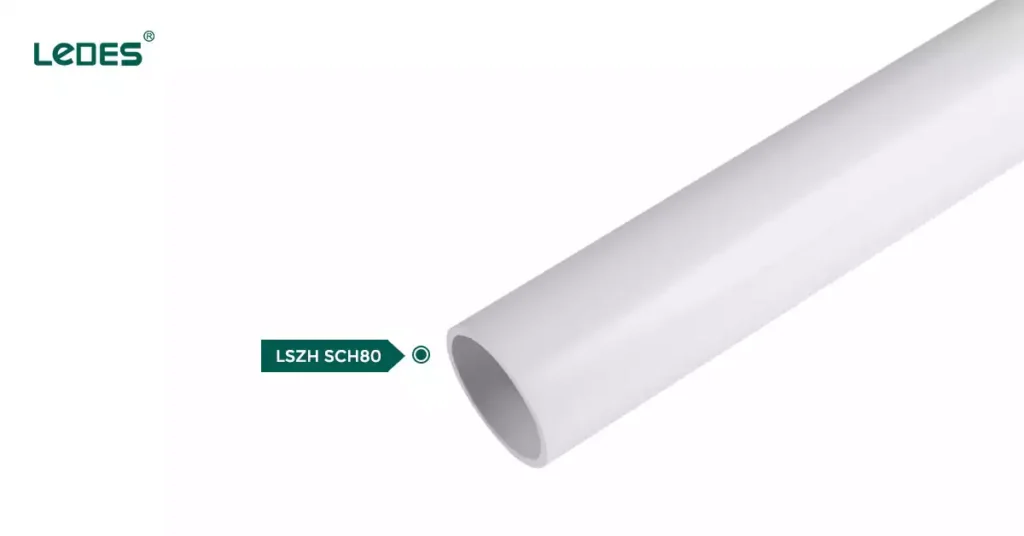

In settings like hospitals, data centers, tunnels, and transportation hubs, minimizing smoke and toxic emissions during a fire is crucial. Low Smoke Zero Halogen Sch 80 conduits address this need by:
- Reducing smoke emissions: Facilitates safer evacuation and reduces damage to equipment.
- Eliminating halogens: Prevents the release of toxic gases when exposed to fire.
- Maintaining mechanical strength: Offers tensile strength comparable to standard Schedule 80 conduits.
This type of SCH 80 is ideal for application where not only exposed to physical damage but also have strict fire safety requirement.
Trends in Schedule 80 PVC Conduit Use
As construction practices evolve and industries demand more resilient, sustainable, and safer infrastructure solutions, the use of Schedule 80 PVC conduit continues to adapt. Here are several key trends shaping its development and adoption:
1. Rising Demand in Renewable Energy Projects
With the global shift toward solar, wind, and battery storage systems, there’s an increased need for conduit systems that can withstand UV exposure, harsh climates, and mechanical stress. Schedule 80 PVC conduit, due to its rigidity and durability, is often used in exposed environments, especially when paired with proper UV-rated formulations.
2. Growing Focus on Fire Safety and Emissions
More industries, especially data centers, transportation hubs, and healthcare facilities are prioritizing low-smoke, halogen-free alternatives to traditional PVC. Although standard Schedule 80 conduit is not inherently LSZH, demand is growing for similar products that meet fire safety and toxicity standards without compromising mechanical strength.
3. Increasing Use in Industrial and Urban Infrastructure
Urbanization and heavy industrial development are pushing the need for more robust conduit systems that can endure vibration, mechanical wear, and frequent maintenance activity. Schedule 80 PVC’s thicker wall structure makes it a favorable choice in such settings, particularly in manufacturing plants and utility systems.
4. Advancements in Material Engineering
Material improvements are leading to enhanced UV resistance, improved impact tolerance, and longer service life, even in extreme climates. Manufacturers are innovating PVC compounds to better meet specific application requirements-resulting in more application-specific Schedule 80 products.
5. Integration with Smart Infrastructure
While traditionally rigid conduits aren’t associated with smart technologies, they’re now being integrated into broader “smart city” infrastructure plans. For instance, Schedule 80 conduit is increasingly used to house and protect fiber optics, sensor cables, and control systems in utility corridors that demand higher mechanical protection.
6. Regulatory Pressure and Environmental Standards
Governments and regulatory agencies are raising standards for conduit materials, requiring compliance with environmental and safety directives. Schedule 80 PVC continues to evolve to meet stricter building codes, UL listings, and ASTM classifications, ensuring long-term market relevance.
Ledes Schedule 80 PVC Conduit Solution

When reliability, strength, and compliance are top priorities, Ledes Schedule 80 PVC Conduit offers a premium solution for demanding electrical installations. Designed to meet the needs of both commercial and industrial projects, Ledes UL listed SCH 80 conduit combines high mechanical durability with consistent code compliance, making it a trusted choice for professional worldwide.
Product Overview
Ledes Schedule 80 PVC conduit is a rigid nonmetallic conduit that exceeds industry requirements in strength and longevity.
- Sizes Range: 1/2” to 8” trade size
- Lengths: 10 feet or 20 feet with belled ends or without belled end
- Custom lengths and chamfer design are available upon request
Features and Benefits
- Thick-Walled Protection: Superior wall thickness offers enhanced resistance to physical damage and external pressure, perfect for exposed and underground use.
- High Impact Resistance: Compliant with UL 651 standards, Ledes SCH 80 withstands higher impact loads compared to Schedule 40 (75 lb impact weight with 6-inch drop cylinder).
- Interior liso: Ensures easy wire pulling and reduced cable abrasion.
- Corrosion-Free & Non-Conductive: Unlike metallic conduits, it resists corrosion and is safe to use around sensitive electrical and communication systems.
Codes Compliance and Certifications
Ledes Schedule 80 PVC conduit is:
- Listado UL 651
- Marked for 90°C rated conductors
- Flame tested and classified as UL94 – V0 rating
Ledes Schedule 80 PVC conduit is more than a product, it’s a complete solution built for performance, compliance, and durability in today’s most challenging environments.
Conclusión
Schedule 80 PVC conduit is a high-strength electrical conduit designed to meet the demands of rigorous environments. Its thicker walls, compared to Schedule 40 and DB-rated conduits, provide increased resistance to impact, crushing, and mechanical damage, making it ideal for exposed installations, industrial settings, and areas with high traffic or physical stress.
In this article, we’ve covered the full scope of what professionals and installers need to know about Schedule 80 PVC conduit—including its definition and purpose, available sizes, advantages and disadvantages, and installation guidelines. We’ve also explored the relevant code and standard requirements like UL 651, ASTM D1784, and NEC provisions, and explained how to choose the right size based on conductor fill and project requirements.
Ultimately, Schedule 80 PVC conduit is a durable, code-compliant, and versatile solution that serves both general-purpose and specialized needs, especially when mechanical strength and long-term safety are priorities.
Preguntas frecuentes
¿Qué es el conducto de PVC Schedule 80?
El conducto de PVC cédula 80 es un conducto rígido no metálico con una pared más gruesa que la cédula 40, diseñado para sistemas eléctricos que requieren protección mecánica adicional. Cumple con la norma UL 651 y es apto tanto para instalaciones superficiales como subterráneas.
¿Qué es la tubería de PVC cédula 80?
La tubería de PVC cédula 80 es similar en apariencia y espesor de pared al conducto cédula 80, pero se utiliza generalmente para sistemas de plomería y agua a presión, no para cableado eléctrico. Si bien ambas están hechas de cloruro de polivinilo (PVC), no son intercambiables debido a diferencias en la aplicación, las normas y el acabado interior.
¿De qué color es el conducto de PVC Schedule 80?
Las tuberías y conductos de PVC de calibre 80 suelen ser de color gris.
¿Dónde se requiere el conducto de PVC Schedule 80?
Schedule 80 PVC conduit is required in locations where extra strength and impact resistance are needed, such as:
Exposed outdoor environments (subject to damage or UV exposure)
Underground in high-traffic areas (under driveways or roads)
Industrial settings with mechanical hazards
Utility installations where deeper burial or load-bearing is required
¿Cuándo utilizar conductos de PVC Schedule 80 frente a Schedule 40?
Use Schedule 80 when:
You need higher mechanical protection
Installing in harsh environments
Codes mandate extra durability
Use Schedule 40 in typical indoor or low-risk underground runs where heavy-duty protection isn’t essential.
¿Se pueden enterrar los conductos de PVC Schedule 80?
Sí. El conducto de PVC cédula 80 es apto para enterramiento directo y suele preferirse al cédula 40 en zonas con mucho tráfico o tráfico intenso, como entradas de vehículos o locales comerciales. Consulte siempre el NEC y los códigos locales para conocer los requisitos de profundidad de enterramiento.
¿El conducto de PVC Schedule 80 tiene clasificación contra incendios?
El conducto de PVC estándar Schedule 80 no está clasificado para aplicaciones de fuego a alta temperatura. Sin embargo, debe superar la prueba de llama de la norma UL 651, lo que garantiza una resistencia básica al fuego.
¿Cuál es la diferencia entre los conductos de PVC Schedule 40 y Schedule 80?
The primary difference lies in wall thickness and strength.
Schedule 80 PVC has thicker walls than Schedule 40, offering greater mechanical protection and crush resistance.
However, this comes with a smaller internal diameter, affecting conduit fill capacity.
Both schedules are made from the same PVC material and offer the same chemical resistance and temperature ratings.
¿El código exige el uso de conductos de PVC Schedule 80?
Yes, in certain applications.
The National Electrical Code (NEC) may require Schedule 80 when the conduit is subject to:
Physical damage (e.g., exposed areas in garages, warehouses, or outdoors)
Heavy-duty environments where extra protection is needed
Refer to NEC 352.10(F), which mandates Schedule 80 for above-ground installations where physical damage is likely.
¿A qué profundidad debo enterrar el conducto de PVC Schedule 80?
Burying depth depends on location, voltage, and usage.
For residential electrical circuits:18 inches minimum burial depth is typically required.
If unprotected or under driveways, deeper burial is required—up to 24 inches.
Always check local amendments to the NEC for regional depth requirements.
¿Existen opciones de conductos de PVC respetuosos con el medio ambiente?
Yes. Some manufacturers offer:
Low-smoke, halogen-free (LSZH) PVC conduits
Conduits made with recycled PVC or eco-friendly stabilizers
These options reduce toxic emissions during fire and support sustainable construction goals, especially in green-certified buildings (e.g., LEED projects).
¿Puede utilizarse el PVC Schedule 80 en exteriores?
Absolutely if the conduit is made with additives.
UV-resistant (when marked “sunlight resistant” per UL 651)
Suitable for wet, damp, or corrosive outdoor environments
It performs well in above-ground or buried outdoor installations when properly rated.
¿Cuál es la clasificación de temperatura máxima del conducto de PVC Schedule 80?
Schedule 80 PVC typically used at a 50°C (122°F) and lower ambient temperatures, use with 75°C (167°F) wiring, but it can use with 90°C (194°F) if rated.
¿Es necesario el Anexo 80 para el uso subterráneo?
Not always.
Schedule 80 is not strictly required for all underground installations.
Schedule 40 PVC is permitted if buried or encased in concrete.
Schedule 80 is required where the conduit emerges from the ground and may be exposed to physical damage (NEC 352.10(F)).
But DB conduit is required for underground use.
Reference




