
Tabla de contenido
En las instalaciones eléctricas, el sistema de conductos desempeña un papel fundamental como componente crucial. Este sistema, que consta de conductos y accesorios, tiene como finalidad proteger y organizar el cableado eléctrico. De este modo, evita posibles peligros y garantiza un flujo de energía sin interrupciones. Entre los numerosos accesorios disponibles, un tipo en particular, conocido como codos para conductos, tiene una importancia significativa en cualquier proyecto de instalación eléctrica. En esta guía completa, exploraremos todos los aspectos esenciales de los codos para conductos para ayudarle a comprender mejor este accesorio para conductos.

Un codo para conducto eléctrico es un tipo de accesorio que se utiliza en instalaciones eléctricas para cambiar la dirección de un sistema de conductos. Está diseñado para conectar dos secciones de conducto en ángulo, lo que permite que el cableado pueda pasar por esquinas, curvas o cambios de dirección. Los codos para conductos suelen estar hechos de materiales metálicos o no metálicos y están disponibles en varios tamaños para adaptarse a diferentes diámetros de conductos.
Estos codos son esenciales para enrutar el cableado eléctrico de manera segura y organizada. Garantizan que el cableado esté protegido contra daños y brindan una apariencia ordenada y profesional a la instalación. Al permitir que el sistema de conductos supere obstáculos y cambie de dirección sin problemas, los codos de conductos ayudan a mantener la integridad del cableado eléctrico y evitan posibles peligros como tensión en los cables, curvas cerradas o daños accidentales.
Hay muchos tipos de codos para conductos eléctricos, cada uno diseñado para aplicaciones específicas, y los codos utilizados en diferentes países pueden ser un poco diferentes; aquí se muestran algunos tipos utilizados comúnmente.
Codos de 90 grados: Este tipo de codo se utiliza ampliamente en situaciones en las que se requiere una dirección cerrada dentro de un sistema de conductos eléctricos. Proporcionan un ángulo recto preciso de 90 grados, lo que permite que el conducto pueda sortear esquinas y cambios de dirección con una eficiencia óptima.
Codos de 45 grados: Este tipo se utiliza generalmente cuando se necesita un giro más gradual, en lugar de un ángulo rígido, inclinando el conducto a 45 grados.

Codos de 30 grados: Este tipo de codo crea un giro moderado de 30 grados, proporcionando un cambio de dirección más gradual en comparación con ángulos más pronunciados como 45 o 90 grados.
Codo de 22,5 grados: Los codos de 22,5 grados se utilizan principalmente cuando un sistema de conductos necesita hacer una ligera curva o navegar por un ángulo específico que no es tan pronunciado como un giro de 45 o 30 grados.
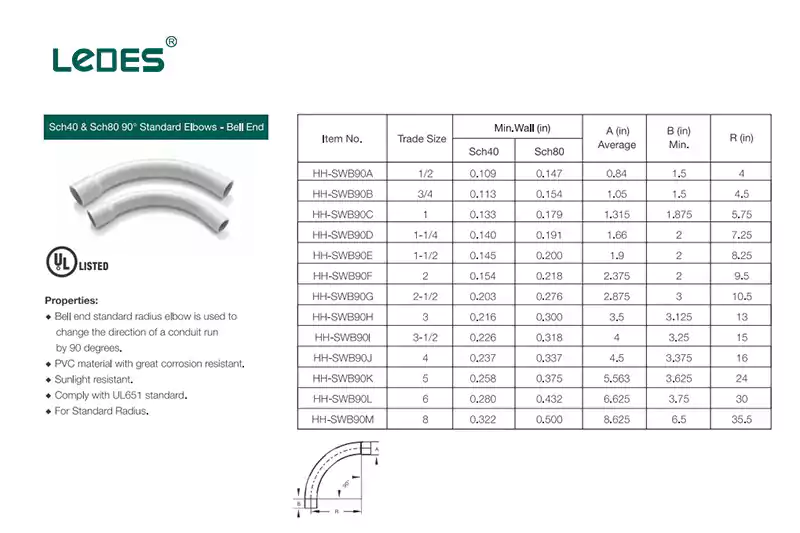
En Estados Unidos y Canadá, se utilizan ampliamente estos tipos de codos para ayudar a realizar diferentes ángulos de giro en el sistema de conductos, pero las dimensiones y algunos de los requisitos de rendimiento son ligeramente diferentes en comparación con los codos estándar UL de Estados Unidos y CSA de Canadá.
Aquí están las dimensiones para los estándares UL y CSA.
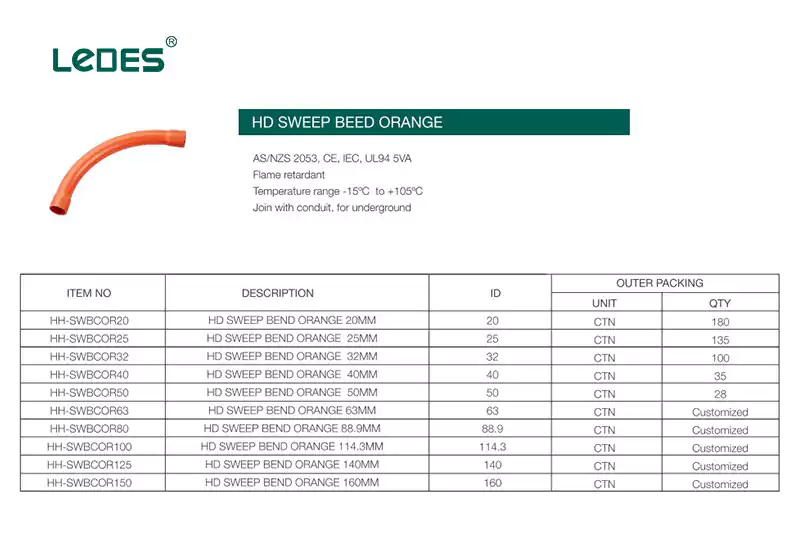
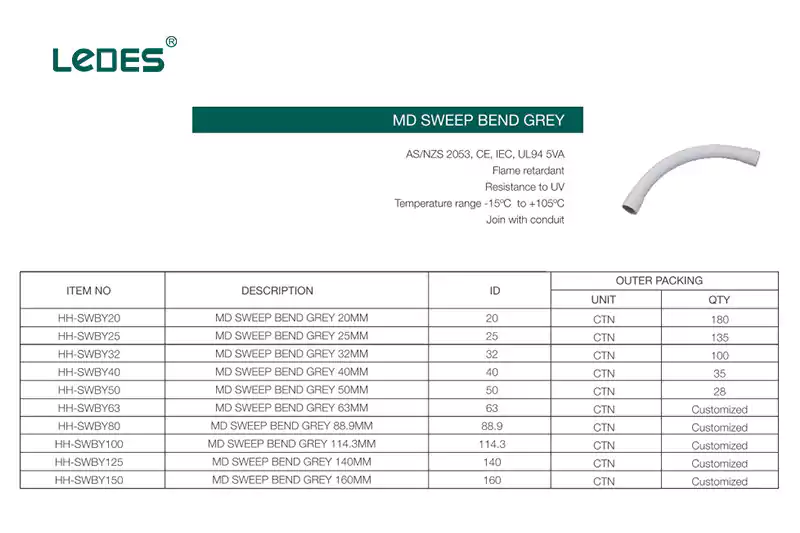
En Australia, los codos y las curvas pueden ser diferentes, tienen diferentes ángulos, como 90 grados, pero hay muchos tipos diferentes, que incluyen:
Curvas de barrido de servicio pesado: Una curva de barrido de alta resistencia es un accesorio robusto para conductos, diseñado para aplicaciones exigentes donde la durabilidad y la resistencia son primordiales. Estas curvas están diseñadas para soportar cargas pesadas, temperaturas extremas y condiciones ambientales adversas, a la vez que proporcionan cambios de dirección suaves para sistemas de conductos eléctricos.
Curva de barrido de servicio mediano: Una curva de barrido de resistencia media proporciona un equilibrio entre resistencia y flexibilidad en sistemas de conductos. Estas curvas ofrecen un radio moderado, lo que las hace adecuadas para una amplia gama de instalaciones eléctricas.
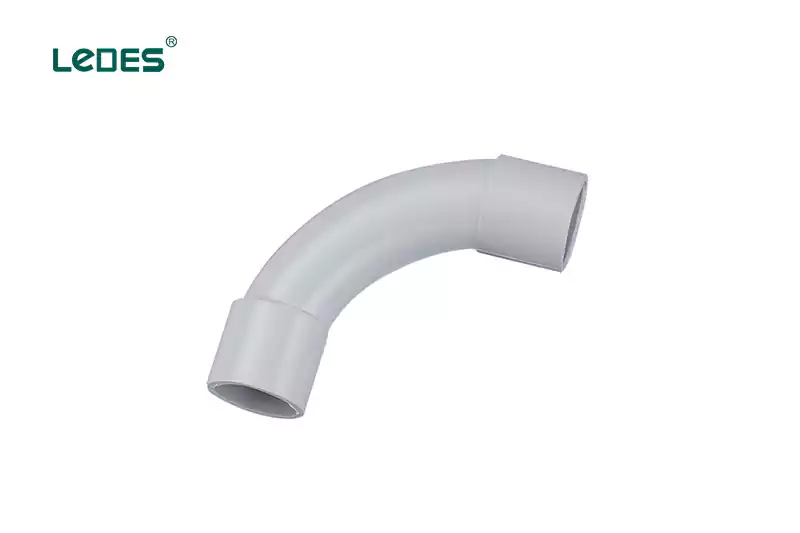

Curva estándar: Una curva estándar, también conocida como codo estándar, es un accesorio de uso general para conductos que se utiliza para cambiar la dirección de un sistema de conductos. Estas curvas suelen tener un ángulo fijo, comúnmente de 90 grados, y están ampliamente disponibles para diversos tamaños de conductos.
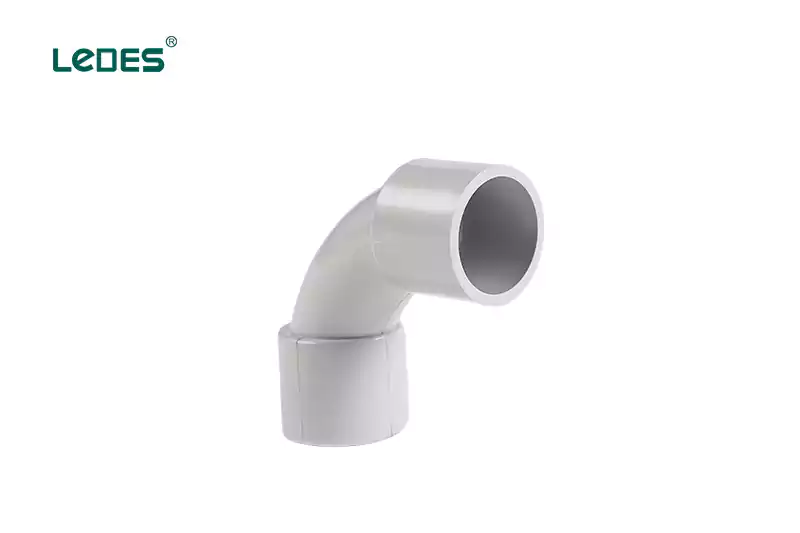

Codo sólido: Un codo sólido es un accesorio para conductos que proporciona un cambio de dirección rígido e inamovible para un sistema de conductos. Generalmente está hecho del mismo material que el propio conducto y se utiliza cuando se requiere un ángulo permanente y seguro.
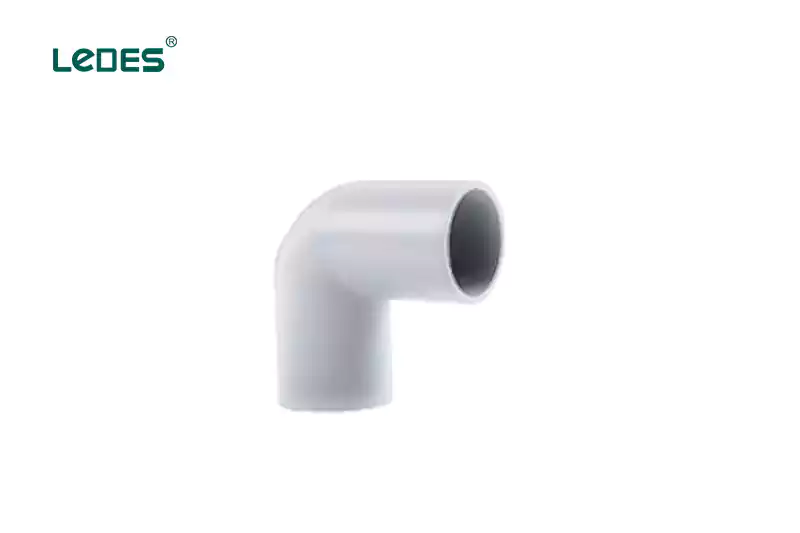

Codo de 90 grados: Una curva para cambio de dirección de 90 grados, sin extremo de enchufe.
Una curva estándar, también conocida como codo estándar, es un accesorio de conducto de uso común que proporciona un ángulo fijo de cambio de dirección para un sistema de conductos. Estas curvas suelen tener un ángulo predeterminado, normalmente de 90 grados, y están ampliamente disponibles en varios tamaños para adaptarse a diferentes diámetros de conductos.
Las características clave de las curvas estándar incluyen:
- Ángulo fijo: las curvas estándar tienen un ángulo fijo, como 90 grados, 45 grados u otros ángulos comunes. Proporcionan un giro brusco en el sistema de conductos, lo que permite cambios de dirección en un ángulo específico.
- Especificaciones predefinidas: Las curvas estándar se fabrican con especificaciones predefinidas, incluido el ángulo de la curva y el diámetro o tamaño del conducto al que está diseñada para adaptarse. Estas especificaciones están estandarizadas y se encuentran ampliamente disponibles en el mercado.
Un codo especial, también conocido como codo personalizado o curva personalizada, se refiere a un accesorio de conducto que está diseñado y fabricado específicamente para cumplir con requisitos únicos en términos de curvatura y especificaciones. A diferencia de las curvas estándar, los codos especiales ofrecen la flexibilidad de personalizar el ángulo de la curva y las dimensiones según las necesidades específicas del proyecto.
Las características clave de los codos especiales incluyen:
- Curvatura personalizable: los codos especiales brindan la posibilidad de personalizar la curvatura, lo que permite ángulos y giros precisos en el sistema de conductos. Esta personalización permite que el accesorio se adapte a los requisitos específicos de la instalación, adaptándose a obstáculos únicos, características arquitectónicas o limitaciones de espacio.
- Especificaciones personalizadas: Los codos especiales son accesorios hechos a pedido que se pueden personalizar según las especificaciones específicas del proyecto. Esto incluye el ángulo de la curva, el radio de la curvatura, el diámetro o tamaño del conducto y otras dimensiones según sea necesario.
- Proceso de fabricación: Los codos especiales generalmente se fabrican a través de procesos de fabricación especializados que implican doblar el conducto al ángulo y la curvatura deseados, lo que garantiza un ajuste preciso para la aplicación específica.
En resumen, la principal diferencia entre un codo estándar y un codo especial radica en la posibilidad de personalizar la curvatura y las especificaciones. Mientras que los codos estándar ofrecen ángulos fijos y especificaciones predefinidas, los codos especiales brindan la flexibilidad de adaptar el ángulo, el radio y las dimensiones del codo para cumplir con los requisitos específicos del proyecto.
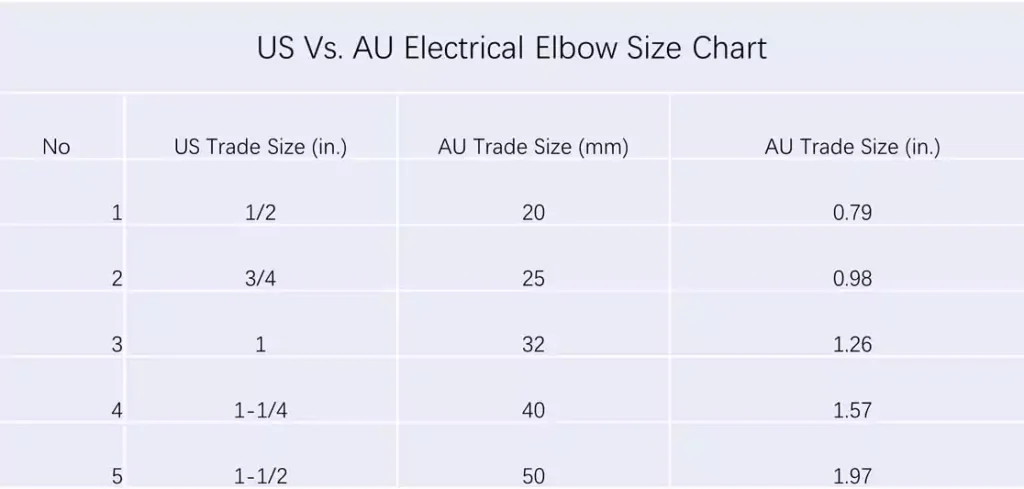
Los tamaños de los codos para conductos eléctricos pueden variar entre países, y las unidades de medida utilizadas también pueden diferir. A continuación, se incluye una explicación que destaca las diferencias entre Estados Unidos y Australia, junto con una descripción general de los tamaños más utilizados.
En Estados Unidos, los codos de los conductos eléctricos suelen designarse según los tamaños comerciales, que representan el diámetro interior (DI) aproximado del conducto. Los tamaños comerciales comunes para los codos incluyen 1/2″, 3/4″, 1″, 1-1/4″, 1-1/2″, 2″, 2-1/2″, 3″, 3-1/2″, 4″ y más grandes.
En Australia, los tamaños de los conductos eléctricos se miden normalmente con el sistema métrico, específicamente en milímetros (mm). Los tamaños métricos más utilizados para los codos incluyen 16 mm, 20 mm, 25 mm, 32 mm, 40 mm, 50 mm, 63 mm, 80 mm, 100 mm y mayores.
Los codos de los conductos eléctricos se pueden clasificar en dos categorías principales de materiales: plástico y metal. Dentro de cada categoría, hay materiales específicos que se utilizan comúnmente para los codos de los conductos.
- PVC (cloruro de polivinilo):El PVC es una opción popular para los codos de conductos de plástico debido a su precio asequible, su peso ligero y su facilidad de instalación. Es resistente a la corrosión y proporciona un buen aislamiento eléctrico. Los codos de conductos de PVC se utilizan comúnmente en aplicaciones residenciales y comerciales.
- Fibra de vidrio: Los codos de conductos de fibra de vidrio están hechos de plástico reforzado compuesto de fibras de vidrio incrustadas en una matriz de resina. Ofrecen una excelente resistencia a la corrosión, los productos químicos y las temperaturas extremas. Los codos de conductos de fibra de vidrio se utilizan comúnmente en entornos industriales y hostiles donde la durabilidad es crucial.
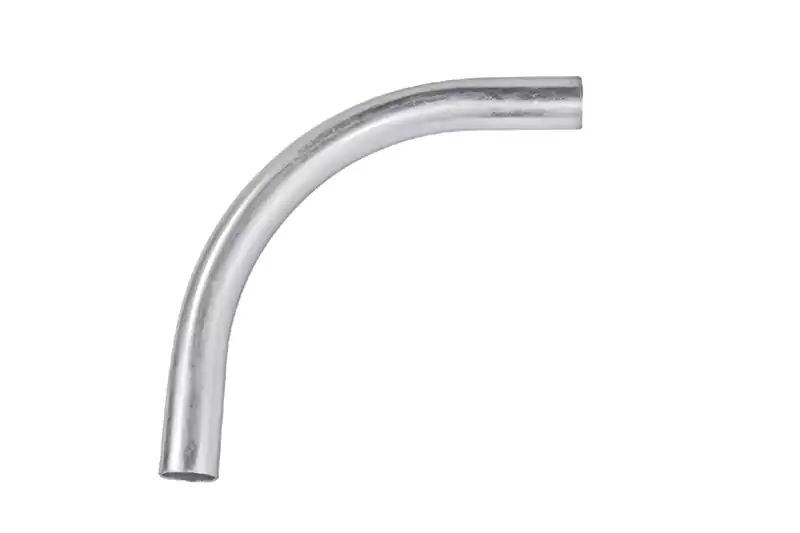

- Acero galvanizado: Los codos de conducto de acero galvanizado están hechos de acero recubierto con una capa de zinc para brindar resistencia a la corrosión. Son fuertes, duraderos y se utilizan ampliamente en aplicaciones comerciales e industriales. Los codos de conducto de acero galvanizado son conocidos por su alta resistencia mecánica y son adecuados para instalaciones al aire libre.
- Acero: Los codos de conducto de acero están hechos de acero simple sin ningún revestimiento protector adicional. Ofrecen robustez y resistencia, pero son susceptibles a la oxidación. Los codos de conducto de acero se utilizan comúnmente en entornos industriales donde la durabilidad es esencial, pero la resistencia a la corrosión puede no ser una preocupación principal.

- Aluminio: Los conductos de aluminio son livianos, resistentes a la corrosión y fáciles de instalar. Se utilizan comúnmente en aplicaciones residenciales y comerciales ligeras. Los conductos de aluminio suelen elegirse por su bajo peso y su resistencia al óxido y la corrosión.

- Zinc: Los codos de conducto de zinc están hechos de acero recubierto con una capa de zinc para protegerlos contra la corrosión. Ofrecen una resistencia moderada y resistencia a la corrosión. Los codos de conducto de zinc se utilizan comúnmente en instalaciones eléctricas interiores donde la durabilidad y la rentabilidad son importantes.
Al seleccionar el material para las curvas de los conductos, es fundamental tener en cuenta los requisitos del proyecto. Los materiales metálicos ofrecen mayor resistencia y una vida útil teórica más larga, pero son más pesados y más propensos a oxidarse. Por otro lado, los materiales plásticos no se oxidan, son más livianos y son rentables. Sin embargo, pueden tener menor resistencia y una vida útil teórica comparativamente más corta que las curvas de metal.
En última instancia, la elección del material de la curva del conducto depende de factores como las necesidades del proyecto, el presupuesto, las condiciones ambientales y el equilibrio deseado entre durabilidad, resistencia a la corrosión, peso y costo.
Los codos se utilizan principalmente para cambiar la dirección de los conductos eléctricos. A continuación, se incluye un resumen de sus usos:
- Cambio de dirección: Los codos para conductos se utilizan principalmente para cambiar la dirección de los conductos eléctricos. Proporcionan un giro suave y gradual para el conducto, lo que le permite sortear obstáculos, esquinas u otros elementos estructurales. Los codos vienen en varios ángulos, como 90 grados, 45 grados, 30 grados y 22,5 grados, lo que proporciona flexibilidad en el tendido del sistema de conductos.
- Protección del cable: Los codos ayudan a proteger los cables eléctricos dentro del conducto al minimizar la flexión excesiva. Cuando los cables se someten a curvas pronunciadas, se puede tensar el aislamiento y provocar daños o desgaste prematuro. Los codos para conductos ofrecen un cambio de dirección controlado y gradual, lo que reduce el riesgo de abrasión del aislamiento, rotura de cables o fallas eléctricas.
- Optimización del espacio: En espacios reducidos o áreas con espacio limitado para conductos, los codos son fundamentales para optimizar el uso del espacio. Al permitir que el conducto haga giros bruscos o pase por esquinas, los codos permiten un enrutamiento eficiente de los cables y ayudan a garantizar que el sistema de conductos se ajuste al espacio disponible. Esto es particularmente importante en aplicaciones donde las limitaciones de espacio o las características arquitectónicas plantean desafíos para la instalación.
- Acceso y Tracción: Ciertos tipos de codos sirven para propósitos específicos relacionados con el acceso y el tendido de cables. Los codos de esquina interior están diseñados para usarse en esquinas donde es necesario el acceso a la canalización. Cuentan con tapas o puntos de acceso removibles, lo que permite un mantenimiento más fácil o el tendido de cables adicionales. Los codos de tiro, también conocidos como codos de barrido, tienen un radio de curvatura más grande que facilita el tendido de cables a través del conducto. Minimizan el riesgo de daño a los cables durante la instalación o al agregar o reemplazar cables.
Al incorporar codos para conductos en las instalaciones eléctricas, los profesionales pueden lograr un enrutamiento eficiente de los cables, protegerlos, adaptarse a espacios difíciles y garantizar un acceso conveniente para realizar tareas de mantenimiento o modificaciones futuras. Estos accesorios versátiles desempeñan un papel fundamental en la creación de un sistema de conductos bien diseñado y funcional.

La conformidad de los codos de conducto de PVC con los códigos locales puede variar entre distintas regiones, como Estados Unidos (UL651) y Australia (AS/NZS 2053). A continuación, se muestran algunos ejemplos de las diferencias según UL651 y AS/NZS 2053:
- Requisitos de tipos
La norma australiana AS/NZS 2053 especifica requisitos de prueba explícitos para diferentes tipos de codos de conducto, que van desde los de servicio liviano hasta los de servicio extra pesado. También incluye requisitos numéricos específicos para la resistencia al impacto. Además, la norma AS/NZS 2053 exige el marcado en el codo del conducto, donde el tipo de servicio correspondiente, como servicio liviano (LD) o servicio pesado (HD), se imprime en la superficie del conducto. Esto permite una fácil identificación de la clasificación de resistencia del conducto. Por el contrario, la norma UL651 no tiene requisitos específicos para el marcado de los codos de conducto.
- Definiciones de pruebas de llama
La definición y los procedimientos de prueba para la resistencia a la llama también difieren entre UL651 y AS2053/NZS 2053:
La norma UL651 establece que un accesorio (incluidos los codos de los conductos) no debe continuar ardiendo durante más de 5 segundos después de la tercera aplicación de la llama de prueba. También especifica que no deben caer partículas ni gotas en llamas del accesorio durante o después de cualquier aplicación de la llama de prueba.
La norma AS/NZS 2053 describe en detalle el procedimiento de prueba de llama. Requiere que el quemador se apoye en un ángulo de 45 ±2° con respecto a la vertical. La llama se aplica a las muestras de conducto de modo que la distancia desde la parte superior del tubo del quemador hasta el mismo, medida a lo largo del eje de la llama, sea de 100 ± 10 mm, y el eje de la llama se cruce con la superficie de la muestra en un punto a 100 ± 5 mm del extremo superior de la abrazadera inferior, y de modo que el eje de la llama se cruce con el eje de la muestra.
La llama se aplica durante un período de 60 ±1 s y la muestra no debe moverse durante la prueba. La norma AS2053 también especifica que la prueba de llama debe realizarse en tres muestras.
Tenga en cuenta que la información proporcionada proviene de Standards Australia y UL (Underwriters Laboratories Inc.), y estas organizaciones tienen la autoridad final en la interpretación de las normas mencionadas.
En conclusión, las variaciones en los estándares de prueba entre las distintas regiones pueden generar diferencias en los indicadores de desempeño de los codos para conductos. Sin embargo, siempre que los productos cumplan con los requisitos de los códigos locales, su calidad y su idoneidad para el uso están garantizadas.
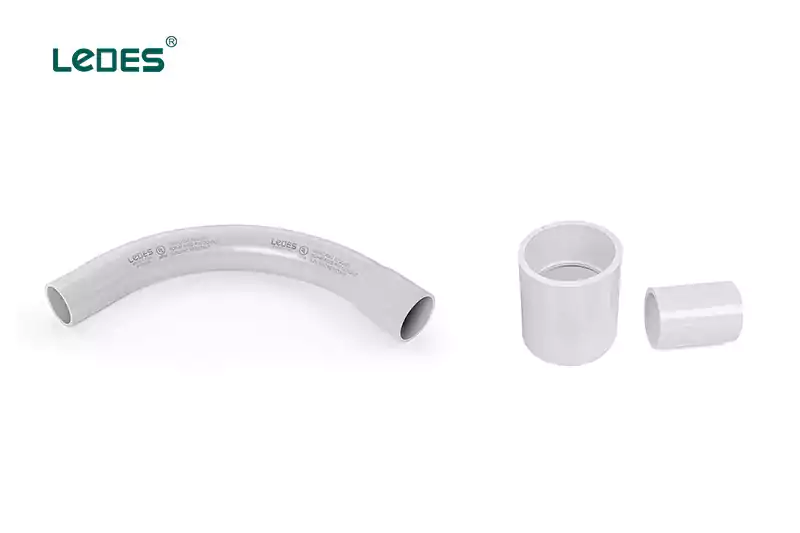

Apariencia:
En primer lugar, ambos se pueden distinguir fácilmente en función de su apariencia. Un codo de conducto normalmente tiene una forma curva o doblada, similar a una sección doblada de conducto. Por otro lado, un acoplador tiene un diseño recto, similar a una sección recta de conducto.
Objetivo:
La principal diferencia entre los codos y los acopladores para conductos radica en su diseño y finalidad. Los codos para conductos se utilizan principalmente para cambiar la dirección de un conducto. Vienen en curvas preformadas de 45 y 90 grados, adecuadas tanto para conductos metálicos como no metálicos. Los codos de esquina interior y de tracción son especialmente útiles en espacios reducidos o cuando es necesario acceder a la canalización.
Por otro lado, los acopladores se emplean comúnmente para unir un tramo de conducto a una toma de corriente o caja de interruptores montada en la superficie. Proporcionan un medio para conectar secciones separadas de conducto, lo que facilita la continuación del tramo de conducto o su conexión a una toma de corriente o caja de conexiones.
Debido a sus distintos diseños y aplicaciones previstas, es importante evitar confusiones entre codos y acopladores de conductos durante los procesos de adquisición y construcción.
- Reúna los materiales y herramientas necesarios:
Codos de conductos metálicos
Tubos de conducción de metal
Conectores o acoplamientos de conductos
Sierra para metales o cortador de tubos
Herramienta de desbarbado o cuchillo multiuso
Destornillador o llave (si es necesario para los conectores)
- Medir y cortar los tubos de conducción de metal:
Determine la longitud deseada de los tubos que conducen al codo.
Utilice una sierra para metales o un cortatubos para cortar los conductos metálicos a la longitud adecuada. Asegúrese de que los cortes sean rectos y limpios.
- Prepare los codos de los conductos metálicos:
Afloje los tornillos de fijación o las contratuercas de los codos para abrirlos.
- Conecte los tubos de conducto metálico a los codos:
Inserte un extremo del tubo conductor de metal en el extremo abierto del codo.
Si el codo de metal tiene tornillos de fijación o contratuercas, apriételos firmemente para mantener el tubo del conducto en su lugar.
Si utiliza un acoplamiento o conector, siga las instrucciones del fabricante para conectar el tubo conductor al codo.
- Conecte los tubos de conducto metálico restantes:
Repita el proceso descrito en el paso 4 para conectar tubos metálicos adicionales al otro extremo del codo.
Utilice acoplamientos o conectores para unir firmemente los conductos metálicos. Apriételos correctamente con un destornillador o una llave.
- Asegure el conjunto de conductos metálicos:
Asegúrese de que el conjunto de conductos metálicos esté correctamente alineado y sostenido.
Utilice correas o abrazaderas para asegurar el conducto a una pared u otra superficie adecuada.

- Reúna los materiales y herramientas necesarios:
Codos de conductos de plástico
Tubos de plástico para conductos
Conectores o acoplamientos de conductos
Sierra para metales o cortador de tubos
Herramienta de desbarbado o cuchillo multiuso
Cemento para conductos
- Medir y cortar los tubos de plástico:
Determine la longitud deseada de los tubos que conducen al codo.
Utilice una sierra para metales o un cortatubos para cortar los conductos de plástico a la longitud adecuada. Asegúrese de que los cortes sean rectos y limpios.
- Prepare los codos de conducto de plástico:
Limpie los extremos del conducto y el interior del codo con una herramienta desbarbadora o un cuchillo multiuso para eliminar rebabas o bordes ásperos.
- Conecte los tubos de plástico a los codos:
Aplique cemento para conductos en el interior del codo y en el exterior del tubo de conducto de plástico.
Inserte el tubo conductor en el codo y sujételo firmemente durante unos segundos para permitir que el cemento se asiente.
- Conecte los tubos de plástico restantes:
Repita el proceso descrito en el paso 4 para conectar tubos de plástico adicionales al otro extremo del codo.
Utilice acoplamientos o conectores para unir de forma segura los conductos de plástico. Siga las instrucciones del fabricante para la instalación.
- Asegure el conjunto del conducto de plástico:
Asegúrese de que el conjunto de conductos de plástico esté correctamente alineado y apoyado.
Utilice correas o abrazaderas para asegurar el conducto a una pared u otra superficie adecuada.
Recuerde seguir las instrucciones específicas proporcionadas por el fabricante de los codos y conectores de conductos que esté utilizando. Además, respete los códigos y las normas eléctricas locales al instalar conductos para cableado eléctrico. Si no está seguro sobre algún aspecto de la instalación, es recomendable consultar a un electricista o profesional calificado.
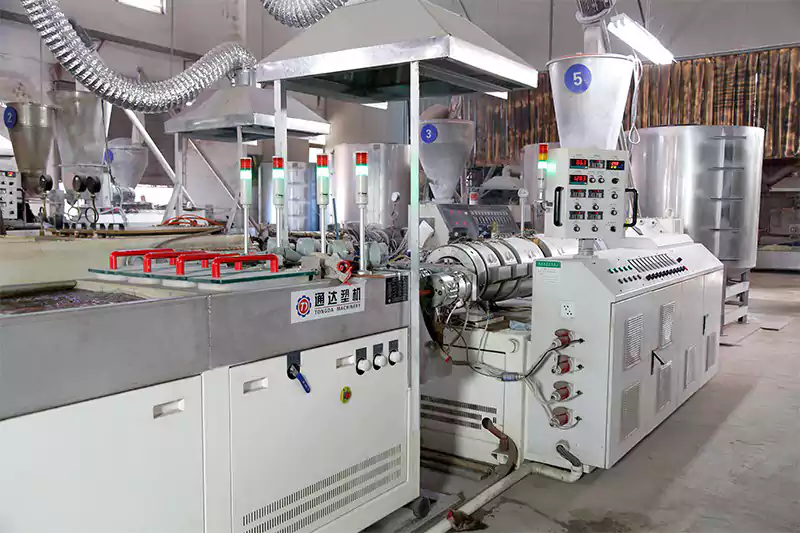

A continuación se muestra un esquema general del proceso de fabricación de codos de plástico PVC:
- Preparación de resina de PVC: El primer paso es preparar la resina de PVC mezclándola con aditivos y estabilizadores para lograr las propiedades deseadas, como resistencia, flexibilidad y resistencia a los rayos UV y a los productos químicos.
- Extrusión de tubos de PVC: La resina de PVC se introduce en una máquina extrusora, donde se calienta y se funde para formar un compuesto de PVC fundido. A continuación, el PVC fundido se empuja a través de una matriz, que le da la forma de un tubo continuo. El tubo extruido se enfría y se solidifica a medida que pasa por un baño de agua o una cámara de enfriamiento.
- Preparación del molde: Se preparan cavidades de molde para la forma del codo. Estos moldes suelen estar hechos de metal y constan de dos mitades que encajan entre sí. Las cavidades del molde se mecanizan con precisión para crear la forma y las dimensiones deseadas del codo.
- Moldeo por inyección: En este paso, los tubos de PVC enfriados y solidificados del proceso de extrusión se cortan en longitudes específicas y se introducen en una máquina de moldeo por inyección. La máquina de moldeo por inyección consta de un barril calentado y un mecanismo de tornillo. Los trozos de tubo de PVC se introducen en el barril, donde se funden y se transportan mediante el tornillo hasta la cavidad del molde.
- Moldeando la forma del codo: El PVC fundido se inyecta en la cavidad del molde a alta presión. El molde está diseñado para crear la forma del codo, incluido el ángulo y el radio deseados. El material de PVC llena las cavidades del molde y toma la forma del codo.
- Enfriamiento y solidificación: Después de inyectar el material de PVC en el molde, se deja enfriar y solidificar. El enfriamiento se puede acelerar mediante el uso de canales de enfriamiento o rociadores de agua. Este paso garantiza que el material de PVC conserve su forma y estabilidad.
- Apertura y expulsión del molde: Una vez que el material de PVC se ha solidificado, se abre el molde y se expulsa el codo de PVC recién formado de la cavidad del molde. La expulsión se puede facilitar mediante el uso de pasadores expulsores o chorros de aire.
- Recorte y acabado: Los codos de PVC expulsados pueden tener material sobrante o rebabas que se deben eliminar. Se realiza un recorte para eliminar las partes no deseadas y lograr una superficie lisa y terminada. Esto se puede hacer de forma manual o utilizando un equipo de recorte automático.
- Control de calidad e inspección: Los codos de PVC se someten a controles de calidad para garantizar que cumplen con las especificaciones y estándares requeridos. Esto puede incluir controles dimensionales, inspecciones visuales y pruebas de resistencia y durabilidad.
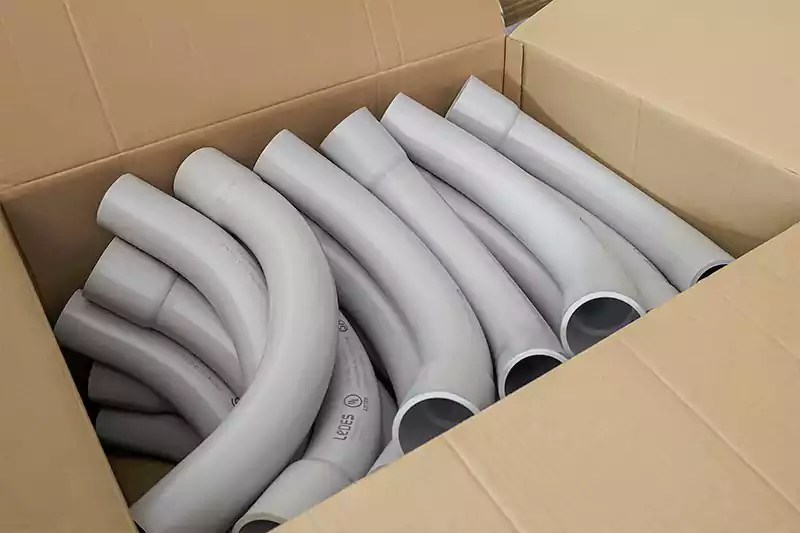

- Embalaje y distribución: Después de pasar los controles de calidad, los codos de PVC se empaquetan y se preparan para su distribución. Pueden estar agrupados, en cajas o colocados sobre palés, según los estándares de embalaje del fabricante. Los codos de PVC empaquetados se envían a los distribuidores o clientes.
Evalúe las necesidades básicas del producto en función de su proyecto o entorno de uso. Por ejemplo, determine si necesita los codos para empotrarlos en edificios residenciales estándar, para un uso prolongado en exteriores o si estarán expuestos a condiciones de humedad. Al considerar las ventajas y desventajas de los distintos productos de codos, podemos ayudarlo a tomar la decisión correcta. Si es un contratista o distribuidor de proyectos, comuníquese con nosotros para obtener más asesoramiento de compra.

Seleccione productos que se ajusten a su proyecto y a su presupuesto. Esto garantiza que cumpla con los requisitos del proyecto y, al mismo tiempo, minimice los costos de adquisición y obtenga productos de buena calidad. Además del costo de compra de los productos, considere los costos de transporte e instalación. Por ejemplo, como se mencionó anteriormente, los codos de metal son más pesados, lo que genera mayores gastos de transporte e instalación. Por lo tanto, es importante tener en cuenta estos costos al asignar su presupuesto total.
En función de los requisitos de instalación y construcción, determine la cantidad y los estándares de calidad necesarios. Esto le permitirá comprar la cantidad deseada de codos dentro de su presupuesto y cumpliendo con los requisitos de calidad.
Existen diferentes tipos de codos disponibles de varias marcas. Comprar productos de marcas reconocidas puede resultar un poco más caro, pero la calidad es significativamente mejor. Las marcas conocidas han pasado por certificaciones locales. Comprar marcas desconocidas puede resultar en posibles problemas de calidad y las pérdidas resultantes podrían superar con creces el valor del producto. Si los precios de las marcas locales son demasiado altos o necesita compras al por mayor, puede considerar comprar directamente a los fabricantes, como Ledes. Como fabricante, Ledes opera como una fábrica sin intermediarios, ofreciendo precios relativamente más bajos. Además, con más de 14 años de experiencia en exportación y al servicio de miles de clientes, Ledes garantiza la entrega oportuna de los productos una vez que realiza su pedido.
Si desea consultar sobre nuestros productos, Por favor haga clic aquí para enviarnos un correo electrónico.
En conclusión, los codos para conductos desempeñan un papel fundamental en las instalaciones eléctricas, ya que proporcionan flexibilidad y un tendido eficiente de cables y alambres. En este artículo se ha proporcionado una descripción general completa de los codos para conductos, que abarca sus tipos, materiales, tamaños y consideraciones de instalación.
Recuerde que seleccionar los codos de conducto adecuados es esencial para una instalación eléctrica segura y eficiente. Al elegir nuestros productos de alta calidad, puede garantizar un rendimiento confiable y tranquilidad para sus proyectos.
Si está interesado en codos para conductos, como fabricante, ofrecemos precios de mayorista de codos de PVC. Puede enviar un formulario de contacto o Envíenos un correo electrónico para solicitar un catálogo de productos y cotización sin cargo. Nos dedicamos a proporcionar codos para conductos de alta calidad y un excelente servicio al cliente. No dude en comunicarse con nosotros para obtener más información o realizar un pedido. ¡Esperamos poder servirle!



